
The Smithsonian Institution, or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge." Founded on August 10, 1846, it operates as a trust instrumentality and is not formally a part of any of the three branches of the federal government. The institution is named after its founding donor, British scientist James Smithson. It was originally organized as the United States National Museum, but that name ceased to exist administratively in 1967.
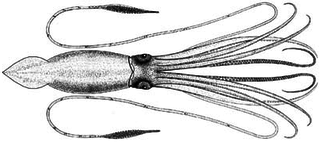
The giant squid is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid in the family Architeuthidae. It can grow to a tremendous size, offering an example of abyssal gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum size at around 12–13 m (39–43 ft) for females and 10 m (33 ft) for males, from the posterior fins to the tip of the two long tentacles. The mantle of the giant squid is about 2 m long, and the length of the squid excluding its tentacles rarely exceeds 5 m (16 ft). Claims of specimens measuring 20 m (66 ft) or more have not been scientifically documented.

The National Museum of the American Indian is a museum in the United States devoted to the culture of the indigenous peoples of the Americas. It is part of the Smithsonian Institution group of museums and research centers.

The National Museum of Natural History (NMNH) is a natural history museum administered by the Smithsonian Institution, located on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., United States. It has free admission and is open 364 days a year. In 2022, with 3.9 million visitors, it was the most-visited museum in the United States.

Frank Alexander Wetmore was an American ornithologist and avian paleontologist. He was the sixth Secretary of the Smithsonian Institution. He was also an elected member of both the American Philosophical Society and the United States National Academy of Sciences.

Charles Whitney Gilmore was an American paleontologist who gained renown in the early 20th century for his work on vertebrate fossils during his career at the United States National Museum. Gilmore named many dinosaurs in North America and Mongolia, including the Cretaceous sauropod Alamosaurus, Alectrosaurus, Archaeornithomimus, Bactrosaurus, Brachyceratops, Chirostenotes, Mongolosaurus, Parrosaurus, Pinacosaurus, Styracosaurus ovatus and Thescelosaurus.

Edmund Heller was an American zoologist. He was President of the Association of Zoos & Aquariums for two terms, from 1935-1936 and 1937-1938.

Cephalopods, which include squids and octopuses, vary enormously in size. The smallest are only about 1 centimetre (0.39 in) long and weigh less than 1 gram (0.035 oz) at maturity, while the giant squid can exceed 10 metres (33 ft) in length and the colossal squid weighs close to half a tonne (1,100 lb), making them the largest living invertebrates. Living species range in mass more than three-billion-fold, or across nine orders of magnitude, from the lightest hatchlings to the heaviest adults. Certain cephalopod species are also noted for having individual body parts of exceptional size.

The thorny whiplash squid, known as Asperoteuthis acanthoderma is a large species of squid belonging to the family Chiroteuthidae. It is characterised by the tiny, pointed tubercules present on its skin and a Y-shaped groove in the funnel locking apparatus.

Edith Anne "Edie" Widder Smith is an American oceanographer, marine biologist, author and the Co-founder, CEO and Senior Scientist at the Ocean Research & Conservation Association.
The Smithsonian Ocean Portal is an educational website created and maintained by the Smithsonian Institution's National Museum of Natural History in Washington, DC. The website features regularly updated, original content from the museum's research, collections, and Sant Ocean Hall as well as content provided by a number of collaborating organizations. According to the site's statement of purpose, the Ocean Portal was created to "help increase public knowledge about the ocean and marine science, raise public awareness of the ocean's importance to all life, and inspire millions of online visitors to become caring ocean stewards." Supported by private donations, the Ocean Portal is designed to appeal to a broad audience, but the primary audiences are young adults, ocean enthusiasts, educators, and children ages 9–13.

William Wyvill Fitzhugh IV is an American archaeologist and anthropologist who directs the Smithsonian’s Arctic Studies Center and is a Senior Scientist at the National Museum of Natural History. He has conducted archaeological research throughout the circumpolar region investigating cultural responses to climate and environmental change and European contact. He has published numerous books and more than 150 journal articles, and has produced large international exhibitions and popular films. Of particular note are the many exhibition catalogues he has had edited, which make syntheses of scholarly research on these subjects available to visitors to public exhibitions.

The Department of Entomology is a research department and collection unit of the Smithsonian Institution's National Museum of Natural History (NMNH), located in Washington, D.C. The department houses the U.S. National Insect Collection, one of the largest entomological collections in the world, with over 35 million specimens housed in 132,354 drawers, 33,000 jars or vials, and 23,000 slides in more than 5,200 cabinets. The department also includes research scientists and technical staff from the Smithsonian Institution, the United States Department of Agriculture Systematic Entomology Lab (SEL) and United States Department of Defense Walter Reed Biosystematics Unit (WRBU).
Jonathan A. Coddington is an American museum scientist and biologist. From 2009 to 2014 he was the Associate Director for Science at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History (NMNH), located in Washington, D.C., United States. As of 2015, he is the Director of the Global Genome Initiative and Senior Scientist and Curator of Arachnids and Myriapods at the NMNH.

Sophie Lutterlough (1910–2009) was an American entomologist. Lutterlough began working at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History (NMNH) as an elevator operator in the 1940s at a time when discriminatory hiring practices prevented African-Americans from working in a curatorial or scientific capacity at the Museum. In the late 1950s, after having gained extensive knowledge of the museum's exhibitions, she asked for and achieved a role in entomological work, eventually restoring hundreds of thousands of insects, classifying thousands. She co-identified 40 type specimens, specimens that stand as the representative example of the species. In 1979, a mite was named in her honor.

The Search for the Giant Squid is a non-fiction book by Richard Ellis on the biology, history and mythology of the giant squid of the genus Architeuthis. It was well received upon its release in 1998. Though soon rendered outdated by important developments in giant squid research, it is still considered an important reference on the subject.















