Related Research Articles
Taliesin was an early Brittonic poet of Sub-Roman Britain whose work has possibly survived in a Middle Welsh manuscript, the Book of Taliesin. Taliesin was a renowned bard who is believed to have sung at the courts of at least three kings.

Coel, also called Coel Hen and King Cole, is a figure prominent in Welsh literature and legend since the Middle Ages. Early Welsh tradition knew of a Coel Hen, a c. 4th-century leader in Roman or Sub-Roman Britain and the progenitor of several kingly lines in Yr Hen Ogledd, a region of the Brittonic-speaking area of what is now northern England and southern Scotland.

Cunedda ap Edern, also called Cunedda Wledig, was an important early Welsh leader, and the progenitor of the Royal dynasty of Gwynedd, one of the very oldest of western Europe.
The Thirteen Treasures of the Island of Britain are a series of items in late-medieval Welsh tradition. Lists of the items appear in texts dating to the 15th and 16th centuries. The number of treasures is always given as thirteen, but some later versions list different items, replacing or combining entries to maintain the number.

Peredur is the name of a number of men from the boundaries of history and legend in sub-Roman Britain. The Peredur who is most familiar to a modern audience is the character who made his entrance as a knight in the Arthurian world of Middle Welsh prose literature.
Rhun ap Maelgwn Gwynedd, also known as Rhun Hir ap Maelgwn Gwynedd, sometimes spelt as 'Rhûn', was King of Gwynedd. He came to the throne on the death of his father, King Maelgwn Gwynedd. There are no historical records of his reign in this early age. A story preserved in both the Venedotian Code and an elegy by Taliesin says that he waged a war against Rhydderch Hael of Alt Clut and the kings of Gododdin or Manaw Gododdin. The small scattered settlement of Caerhun in the Conwy valley is said to be named for him, though without strong authority. Rhun also appears in several medieval literary stories, as well as in the Welsh Triads. His wife was Perwyr ferch Rhûn "Ryfeddfawr" and their son was Beli ap Rhun "Hîr".

Y Gododdin is a medieval Welsh poem consisting of a series of elegies to the men of the Brittonic kingdom of Gododdin and its allies who, according to the conventional interpretation, died fighting the Angles of Deira and Bernicia at a place named Catraeth in about AD 600. It is traditionally ascribed to the bard Aneirin and survives only in one manuscript, the "Book of Aneirin".
Pabo Post Prydain was a king from the Hen Ogledd or Old North of sub-Roman Britain. According to tradition Pabo "the Pillar of Britain" was driven out of the North in 460 and settled in Anglesey. He is said to have been buried in the area. From the 14th century at least, when a stone cross was erected in the ruler's memory in the abbey's churchyard, Pabo has been identified as its founder, having retired, as many Welsh kings are said to have done, to a heremitic retreat.
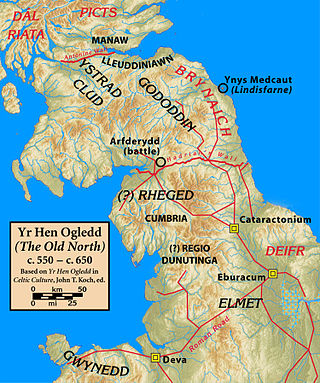
Yr Hen Ogledd, or in English the Old North, is the historical region that was inhabited by the Brittonic people of sub-Roman Britain in the Early Middle Ages, now Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands, alongside the Celtic Kingdom of Elmet. Its population spoke a variety of the Brittonic language known as Cumbric which is closely related to, if not a dialect of Old Welsh. The people of Wales and the Hen Ogledd considered themselves to be one people, and both were referred to as Cymry ('fellow-countrymen') from the Brittonic word combrogi. The Hen Ogledd was distinct from the parts of North Britain inhabited by the Picts, Anglo-Saxons, and Scoti.

Rhydderch Hael, Riderch I of Alt Clut, or Rhydderch of Strathclyde, was a ruler of Alt Clut, a Brittonic kingdom in the Hen Ogledd or "Old North" of Britain. He was one of the most famous kings in the Hen Ogledd, and appears frequently in later medieval works in Welsh and Latin.
Cinuit may have been an early ruler of the Brittonic kingdom of Alt Clut, later known as Strathclyde, in Britain's Hen Ogledd or "Old North". The Harleian genealogies indicate that he was the son of Ceretic Guletic, who may be identified with the warlord Ceredig rebuked by Saint Patrick in one of his letters. According to the same pedigrees, he was the father of Dumnagual Hen, an important but obscure ancestor figure in Welsh tradition. The later genealogy Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd replaces Cinuit as Dumnagual's father with a certain Idnyuet, said to be the son of Maxen Wledic. However, the Bonedd does include a "Cynwyd Cynwydion" in the ancestry of Clydno Eiddyn, and a Triad attached to the text mentions the "three hundred swords of the Cynwydion" as one of three formidable north British war bands, along with those of Coel Hen and Cynfarch.
Dyfnwal Hen or Dumnagual Hen was a ruler of the Brittonic kingdom of Alt Clut, later known as Strathclyde, probably sometime in the early 6th century. His biography is vague, but he was regarded as an important ancestor figure for several kingly lines in the Hen Ogledd or "Old North" of Britain. As an ancestor figure, he compares to Coel Hen, another obscure figure credited with founding a number of northern dynasties.
Clinoch is thought to have been a ruler of Alt Clut, the Brittonic kingdom later known as Strathclyde, some time in the 6th century. The Harleian genealogies name Clinoch as the son of Dumnagual Hen, his probable predecessor as King of Alt Clut, and the father of Tutagual, his probable successor. The Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd, a later genealogy of rulers in the Hen Ogledd or "Old North" of Britain, names the descendant between Dumnagual and Tutagual, Kedic.
Gwallog ap Lleenog was a hero of the Hen Ogledd. He has long been considered a probable sixth-century king of the sub-Roman state of Elmet in the Leeds area of modern Yorkshire, though some more recent scholarship would identify him more tentatively simply as a 'king of an unidentified region in the north'.
Mynyddog Mwynfawr was, according to Welsh tradition founded on the early Welsh language poem Y Gododdin, a Brittonic ruler of the kingdom of Gododdin in the Hen Ogledd.
Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd is a brief Middle Welsh tract which claims to give the pedigrees of twenty 6th century rulers of the Hen Ogledd, the Brittonic-speaking parts of southern Scotland and northern England. It is attested in a number of manuscripts, the earliest being NLW, Peniarth MS 45, which has been dated to the late 13th century. The text may have been composed in the 12th century. The historicity of much of the information is spurious or in doubt. Although certain parts are in agreement with the earlier Harleian genealogies, the text represents a substantial revision seeking to integrate the branches of many rulers and heroes who are prominent in other traditions, such as the Rheged prince Llywarch Hen.

Aeron was a kingdom of the Brythonic-speaking Hen Ogledd, presumed to have been located in the region of the River Ayr in what is now southwestern Scotland. It existed during the post-Roman era, perhaps earlier, and disappeared before or during the 7th-century conquest of the region by the ascendant Kingdom of Northumbria.
Talhaearn Tad Awen, was, according to medieval Welsh sources, a celebrated British poet of the sub-Roman period. He ranks as one of the earliest, if not the earliest, named poets to have composed and performed in Welsh. The better known poets Aneirin and Taliesin, who may have been slightly younger contemporaries, also belong to this early generation, the first of those known to modern scholars as the Cynfeirdd. Whereas medieval Welsh manuscripts preserve verse composed by or otherwise ascribed to the latter two figures, no such work survives for Talhaearn and in fact, his former fame seems to have largely vanished by the later Middle Ages.

Cynon ap Clydno or in some translations Kynon or Cynan was an Arthurian hero from Welsh mythology. His quest to the Castle of Maidens and his subsequent trial against the Black Knight, serve as a prelude to the adventure of Owain and The Lady of the Fountain. Cynon is closely associated with Sir Calogrenant, who takes his role in other versions of the tale.

Eidyn was the region around modern Edinburgh in Britain's sub-Roman and early medieval periods, approximately the 5th–7th centuries. It centred on the stronghold of Din Eidyn, thought to have been at Castle Rock, now the site of Edinburgh Castle, and apparently included much of the area below the Firth of Forth. It was the most important district of the Brittonic kingdom of Gododdin, and a significant power in the Hen Ogledd, or Old North, the Brittonic-speaking area of what is now southern Scotland and northern England.
References
- Bromwich, Rachel (2006). Trioedd Ynys Prydein: The Triads of the Island of Britain. University Of Wales Press. ISBN 0-7083-1386-8.