Related Research Articles

Poultry are domesticated birds kept by humans for the purpose of harvesting animal products such as meat, eggs or feathers. The practice of raising poultry is known as poultry farming. These birds are most typically members of the superorder Galloanserae (fowl), especially the order Galliformes. The term also includes waterfowls of the family Anatidae but does not include wild birds hunted for food known as game or quarry.

Breed broiler is any chicken that is bred and raised specifically for meat production. Most commercial broilers reach slaughter weight between four and six weeks of age, although slower growing breeds reach slaughter weight at approximately 14 weeks of age. Typical broilers have white feathers and yellowish skin. Broiler or sometimes broiler-fryer is also used sometimes to refer specifically to younger chickens under 2.0 kilograms, as compared with the larger roasters.

Tyson Foods, Inc. is an American multinational corporation based in Springdale, Arkansas that operates in the food industry. The company is the world's second-largest processor and marketer of chicken, beef, and pork after JBS S.A. It is the largest meat company in America. It annually exports the largest percentage of beef out of the United States. Together with its subsidiaries, it operates major food brands, including Jimmy Dean, Hillshire Farm, Ball Park, Wright Brand, Aidells, and State Fair. Tyson Foods ranked No. 79 in the 2020 Fortune 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue.

Charoen Pokphand Foods Public Company Limited, a company of the Charoen Pokphand Group, is an agro-industrial and food conglomerate headquartered in Thailand. It is one of the world's largest producers of feed and shrimp, and is also a global top three producer of poultry and pork.

Hock burns are lesions found on the hock joints of chickens and other birds raised on broiler farms. They are considered a form of contact dermatitis. These marks occur when the ammonia from the waste of other birds burns through the skin of the leg, leaving a brown ulcer mark. The condition has been found to be a source of pain for birds, can cause mobility issues, and may increase the risk of bacterial diseases. In severe cases, hock burns can cause visible scabs to form.

Chicken is the most common type of poultry in the world. Owing to the relative ease and low cost of raising chickens—in comparison to mammals such as cattle or hogs—chicken meat and chicken eggs have become prevalent in numerous cuisines.
Intensive animal farming, industrial livestock production, and macro-farms, also known as factory farming, is a type of intensive agriculture, specifically an approach to animal husbandry designed to maximize production while minimizing costs. To achieve this, agribusinesses keep livestock such as cattle, poultry, and fish at high stocking densities, at large scale, and using modern machinery, biotechnology, and global trade. The main products of this industry are meat, milk and eggs for human consumption.

Poultry farming is the form of animal husbandry which raises domesticated birds such as chickens, ducks, turkeys and geese to produce meat or eggs for food. Poultry – mostly chickens – are farmed in great numbers. More than 60 billion chickens are killed for consumption annually. Chickens raised for eggs are known as layers, while chickens raised for meat are called broilers.
Animal ethics is a branch of ethics which examines human-animal relationships, the moral consideration of animals and how nonhuman animals ought to be treated. The subject matter includes animal rights, animal welfare, animal law, speciesism, animal cognition, wildlife conservation, wild animal suffering, the moral status of nonhuman animals, the concept of nonhuman personhood, human exceptionalism, the history of animal use, and theories of justice. Several different theoretical approaches have been proposed to examine this field, in accordance with the different theories currently defended in moral and political philosophy. There is no theory which is completely accepted due to the differing understandings of what is meant by the term ethics; however, there are theories that are more widely accepted by society such as animal rights and utilitarianism.

Pig farming, pork farming, or hog farming is the raising and breeding of domestic pigs as livestock, and is a branch of animal husbandry. Pigs are farmed principally for food and skins.
Pale, soft, exudative meat, or PSE meat, describes a carcass quality condition known to occur in pork, beef, and poultry. It is characterized by an abnormal color, consistency, and water holding capacity, making the meat dry and unattractive to consumers. The condition is believed to be caused by abnormal muscle metabolism following slaughter, due to an altered rate of glycolysis and a low pH within the muscle fibers. A mutation point in the ryanodine receptor gene (RYR1) in pork, associated to stress levels prior to slaughter are known to increase the incidence of PSE meat. Although the term "soft" may look positive, it refers to raw meat. When cooked, there is higher cook loss and the final product is hard, not juicy.

Pain negatively affects the health and welfare of animals. "Pain" is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage." Only the animal experiencing the pain can know the pain's quality and intensity, and the degree of suffering. It is harder, if even possible, for an observer to know whether an emotional experience has occurred, especially if the sufferer cannot communicate. Therefore, this concept is often excluded in definitions of pain in animals, such as that provided by Zimmerman: "an aversive sensory experience caused by actual or potential injury that elicits protective motor and vegetative reactions, results in learned avoidance and may modify species-specific behaviour, including social behaviour." Nonhuman animals cannot report their feelings to language-using humans in the same manner as human communication, but observation of their behaviour provides a reasonable indication as to the extent of their pain. Just as with doctors and medics who sometimes share no common language with their patients, the indicators of pain can still be understood.
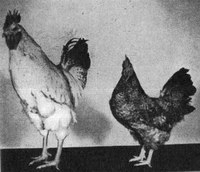
Dwarfism in chickens is an inherited condition found in chickens consisting of a significant delayed growth, resulting in adult individuals with a distinctive small size in comparison with normal specimens of the same breed or population.

The broiler industry is the process by which broiler chickens are reared and prepared for meat consumption. Worldwide, in 2005 production was 71,851,000 tonnes. From 1985 to 2005, the broiler industry grew by 158%.
The Chicken of Tomorrow Contest was an animal husbandry contest held between 1946 and 1948 and sponsored by the American grocery store chain A&P, in partnership with the US Department of Agriculture (USDA), to encourage the development of broiler chickens breeds with more meat. Most broiler chickens around the world descend from the contest such as the Cobb 500.
Woody breast is an abnormal muscle condition that impacts the texture and usability of chicken breast meat. The affected meat is described as tough, chewy, and gummy due to stiff or hardened muscle fibers that spread through the filet. The specific cause is not known but may be related to factors associated with rapid growth rates. Companies often use a three-point scale to grade the woodiness of a particular breast. Although distasteful to many, meat that exhibits woody breast is not known to be harmful to humans who consume it. When detected by suppliers, product shown to have the condition present may be discounted or processed as ground chicken. Woody breast has become so prevalent in the broiler industry that the U.S. Poultry & Egg Association has helped fund four research projects with over $250,000 in an effort to understand and address the condition. Estimates placed the total cost to the global industry as high as US$1 billion in 2020 for losses associated with managing the woody breast condition in broiler chickens.

Ngaio Jessica Beausoleil is a New Zealand academic, and is a full professor at Massey University, specialising in animal welfare and the cross-disciplinary field of conservation welfare.

Foam depopulation or foaming is a means of mass killing farm animals by spraying foam over a large area to obstruct breathing and ultimately cause suffocation. It is usually used to attempt to stop disease spread. Foaming has also been used to kill farm animals after backlogs in slaughtering occurred during the COVID-19 pandemic. Foam depopulation has been used on poultry and pigs and has seen initial research for use on cattle. It has faced criticism from some groups. Some veterinarians have called it inhumane, along with many animal rights and animal welfare organizations who cite the pain caused by suffocation or the harm experienced by the stray survivors.
The breeding and raising of broiler chickens has created health and animal welfare issues, such as cardiovascular and skeletal dysfunction.
White striping is a condition in poultry where white fat deposits replace muscle in stripes along muscle fibers. It is considered a type of myopathy, primarily of the Pectoralis major muscle. There does not appear to be direct harm to birds specifically from white striping. However, some scientists and animal welfare groups have called its presence indicative of the industry's use of fast-growing birds, who have higher rates of health issues and welfare concerns such as hock burns. Using fast-growing birds is linked to overall higher rates of white striping.
References
- ↑ Vidal, John (2018-12-27). "'It's God's plan': the man who dreams of bringing intensive chicken farming to Africa". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077 . Retrieved 2024-06-23.
- ↑ Cobb500 Broiler Performance & Nutrition Supplement (2022) (PDF) (Report). Cobb-Vantress. 2022.
- 1 2 Torrella, Kenny (2023-02-10). "How a shipping error more than a century ago launched the $30 billion chicken industry". Vox. Retrieved 2024-06-23.
- ↑ Ungoed-Thomas, Jon (2022-04-16). "'Frankenchicken' at the centre of fight for animal welfare". The Observer. ISSN 0029-7712 . Retrieved 2024-06-23.
- ↑ Gunther, Marc (August 9, 2018). "Former Tyson Foods CEO Brings Chicken Farming To Rwanda — But Can It Last?". NPR.
- ↑ Mock, Sarah (2020-08-17). "From farm to factory: the unstoppable rise of American chicken". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077 . Retrieved 2024-06-23.
- ↑ Wegner, Marcin; Kokoszyński, Dariusz; Żochowska-Kujawska, Joanna; Kotowicz, Marek (2023-09-21). "Effect of Genotype and Sex on Chemical Composition, Physicochemical Properties, Texture and Microstructure of Spent Broiler Breeder Meat". Agriculture. 13 (9): 1848. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13091848 . ISSN 2077-0472.
- ↑ Bugos, Glenn E. (1992). "Intellectual Property Protection in the American Chicken–Breeding Industry". Business History Review. 66 (1): 127–168. doi:10.2307/3117055. ISSN 0007-6805. JSTOR 3117055.
- ↑ Martinez, Stephen (April 1999). Vertical Coordination in the Pork and Broiler Industries: Implications for Pork and Chicken Products (Report). U.S. Department of Agriculture.
- ↑ "Cobb-Vantress set to buy unit of rival | Arkansas Democrat Gazette". www.arkansasonline.com. 2008-01-09. Retrieved 2024-11-23.
- ↑ Usborne, Simon (2021-11-24). "The £3 chicken: how much should we actually be paying for the nation's favourite meat?". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077 . Retrieved 2024-11-23.
- ↑ Basaki, M.; Tabandeh, M. R.; Aminlari, M.; Asasi, K.; Mohsenifard, E.; Abdi-Hachesoo, B. (2019-06-25). "Sequence and expression analysis of cardiac ryanodine receptor 2 in broilers that died from sudden death syndrome". Avian Pathology. 48 (5): 444–453. doi:10.1080/03079457.2019.1618439. ISSN 0307-9457. PMID 31081346.
- ↑ Kwon, Byung-Yeon; Park, Jina; Kim, Da-Hye; Lee, Kyung-Woo (2024-04-05). "Assessment of Welfare Problems in Broilers: Focus on Musculoskeletal Problems Associated with Their Rapid Growth". Animals. 14 (7): 1116. doi: 10.3390/ani14071116 . ISSN 2076-2615. PMC 11011155 . PMID 38612355.
- ↑ Dinev, I.; Denev, S.A.; Edens, F.W. (Sep 2012). "Comparative clinical and morphological studies on the incidence of tibial dyschondroplasia as a cause of lameness in three commercial lines of broiler chickens". Journal of Applied Poultry Research. 21 (3): 637–644. doi: 10.3382/japr.2010-00303 .
- ↑ Mayahi, Mansoor; Talazadeh, Forough; Abdolshah, Mahya (2016-11-15). "Effect of genetic strains (Ross 308, Cobb 500 and Hubbard F15) on immune response against Newcastle disease vaccine in broiler chickens". International Journal of Enteric Pathogens. 4 (4): 37–39. doi:10.15171/ijep.2016.18. ISSN 2345-3362.
- ↑ Villagómez-Cortés, José Alfredo; Guevara-Torres, Blanca Leydi; Landin-Grandvallet, Luis Antonio; Tirado-Madrid, Alberto (2021). "Comparison of locomotion problems and its economic impact on Cobb and Ross broiler strains". Veterinary Science Research. 3 (2): 40–46. doi: 10.30564/vsr.v3i2.4126 . ISSN 2661-3867.