Related Research Articles

Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the "ascus", a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of Ascomycota are asexual and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens such as Cladonia belong to the Ascomycota.

A conidium, sometimes termed an asexual chlamydospore or chlamydoconidium, is an asexual, non-motile spore of a fungus. The word conidium comes from the Ancient Greek word for dust, κόνις (kónis). They are also called mitospores due to the way they are generated through the cellular process of mitosis. They are produced exogenously. The two new haploid cells are genetically identical to the haploid parent, and can develop into new organisms if conditions are favorable, and serve in biological dispersal.

Grape black rot is a fungal disease caused by an ascomycetous fungus, Guignardia bidwellii, that attacks grape vines during hot and humid weather. “Grape black rot originated in eastern North America, but now occurs in portions of Europe, South America, and Asia. It can cause complete crop loss in warm, humid climates, but is virtually unknown in regions with arid summers.” The name comes from the black fringe that borders growing brown patches on the leaves. The disease also attacks other parts of the plant, “all green parts of the vine: the shoots, leaf and fruit stems, tendrils, and fruit. The most damaging effect is to the fruit”.
Zythiostroma is a genus of canker fungus in the family Nectriaceae. The two or three species in the genus, which are anamorphs of the genus Nectria, have been found in Europe and Java.

Botryosphaeria dothidea is a plant pathogen that causes the formation of cankers on a wide variety of tree and shrub species. It has been reported on several hundred plant hosts and on all continents except Antarctica. B. dothidea was redefined in 2004, and some reports of its host range from prior to that time likely include species that have since been placed in another genus. Even so, B. dothidea has since been identified on a number of woody plants—including grape, mango, olive, eucalyptus, maple, and oak, among others—and is still expected to have a broad geographical distribution. While it is best known as a pathogen, the species has also been identified as an endophyte, existing in association with plant tissues on which disease symptoms were not observed. It can colonize some fruits, in addition to woody tissues.
Leptosphaeria coniothyrium is a plant pathogen. It can be found around the world.

Lasiodiplodia theobromae is a plant pathogen with a very wide host range. It causes rotting and dieback in most species it infects. It is a common post harvest fungus disease of citrus known as stem-end rot. It is a cause of bot canker of grapevine. It also infects Biancaea sappan, a species of flowering tree also known as Sappanwood.
Sphaceloma arachidis is a plant pathogen infecting peanuts.

Elsinoë ampelina is a plant pathogen, which is the causal agent of anthracnose on grape.
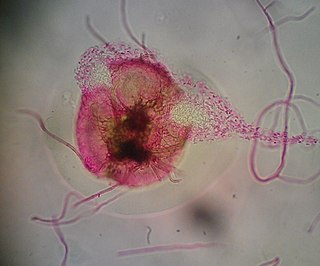
A pycnidium is an asexual fruiting body produced by mitosporic fungi, for instance in the order Sphaeropsidales or order Pleosporales. It is often spherical or inversely pearshaped (obpyriform) and its internal cavity is lined with conidiophores. When ripe, an opening generally appears at the top, through which the pycnidiospores escape.
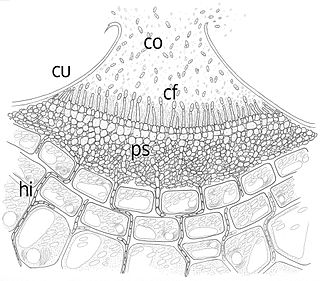
An acervulus is a small asexual fruiting body that erupts through the epidermis of host plants parasitised by mitosporic fungi of the form order Melanconiales. It has the form of a small cushion at the bottom of which short crowded conidiophores are formed. The spores escape through an opening at the top.

Buellia is a genus of mostly lichen-forming fungi in the family Caliciaceae. The fungi are usually part of a crustose lichen. In this case, the lichen species is given the same name as the fungus. But members may also grow as parasites on lichens (lichenicolous). The algae in the lichen is always a member of the genus Trebouxia.
Conidiomata are blister-like fruiting structures produced by a specific type of fungus called a coelomycete. They are formed as a means of dispersing asexual spores call conidia, which they accomplish by creating the blister-like formations which then rupture to release the contained spores.

The fungi imperfecti or imperfect fungi are fungi which do not fit into the commonly established taxonomic classifications of fungi that are based on biological species concepts or morphological characteristics of sexual structures because their sexual form of reproduction has never been observed. They are known as imperfect fungi because only their asexual and vegetative phases are known. They have asexual form of reproduction, meaning that these fungi produce their spores asexually, in the process called sporogenesis.

Raspberry spur blight is caused by the fungus Didymella applanata. This plant pathogen is more problematic on red raspberries (Rubus idaeus) than on black or purple raspberries. The fungus infects the leaves first and then spreads to the cane. It causes necrotic spots on the cane near the base of the petiole attachment. Raspberry spur blight can cause a significant reduction in yield, fruit blight, premature leaf drop, and weak bud and cane growth. The magnitude of damage is not clearly understood in the United States, however, studies from Scotland suggest damage to the cane itself is limited. The disease has minor economic impacts by reducing leaves in the summer or killing buds. Major economic damage occurs if the disease manages to kill the entire cane. In the United States, this disease is found in Oregon and Washington.
Sphaeropsidales is an order of Coelomycetes fungi.

Tzeanania is a monotypic genus of fungi established in 2018. It is the only genus in the family Tzeananiaceae and contains the single species Tzeanania taiwanensis. The species is a parasite which grows on fruiting bodies of the fungus Ophiocordyceps macroacicularis, which is itself a parasite of moth larvae. So far it is only known from one collection which was made in Taiwan.
Sarcostroma is a genus of fungi in the family Sporocadaceae. Most species of this genus are saprobes, endophytes or pathogens on leaves.
Haloplaca is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the subfamily Teloschistaceae of the family Teloschistaceae. It contains three species of crustose lichens. The genus was circumscribed by Ulf Arup and colleagues in 2013, with Haloplaca britannica assigned as the type species. The genus name alludes to the preference of its species for salt-rich environments. All three species occur in the United Kingdom, but H. suaedae also occurs in Greece, Morocco and Turkey. Haloplaca species occur near the sea, either on rocks or on plant debris.
Microsphaeropsis olivacea is a fungal species belonging to the family Didymosphaeriaceae. It is recognized for its diverse ecological roles, ranging from saprobic activities on dead organic matter to pathogenic interactions with various hosts, including plants and occasionally humans.
References
- ↑ Wijayawardene, Nalin N.; Mckenzie, Eric H.C.; Chukeatirote, Ekachai; Wang, Yong; Hyde, Kevin D. (2012). "Coelomycetes". Cryptogamie, Mycologie. 33 (3): 215–244. doi:10.7872/crym.v33.iss3.2012.215.