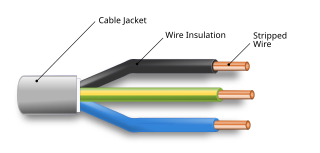
An electrical cable is an assembly of one or more wires running side by side or bundled, which is used to carry electric current.

An electrician is a tradesperson specializing in electrical wiring of buildings, transmission lines, stationary machines, and related equipment. Electricians may be employed in the installation of new electrical components or the maintenance and repair of existing electrical infrastructure. Electricians may also specialize in wiring ships, airplanes, and other mobile platforms, as well as data and cable lines.

A submersible pump is a device which has a hermetically sealed motor close-coupled to the pump body. The whole assembly is submerged in the fluid to be pumped. The main advantage of this type of pump is that it prevents pump cavitation, a problem associated with a high elevation difference between the pump and the fluid surface. Submersible pumps push fluid to the surface, rather than jet pumps, which create a vacuum and rely upon atmospheric pressure. Submersibles use pressurized fluid from the surface to drive a hydraulic motor downhole, rather than an electric motor, and are used in heavy oil applications with heated water as the motive fluid.

Electrical wiring is an electrical installation of cabling and associated devices such as switches, distribution boards, sockets, and light fittings in a structure.
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom is commonly understood to be an electrical installation for operation by end users within domestic, commercial, industrial, and other buildings, and also in special installations and locations, such as marinas or caravan parks. It does not normally cover the transmission or distribution of electricity to them.

A power cable is an electrical cable, an assembly of one or more electrical conductors, usually held together with an overall sheath. The assembly is used for transmission of electrical power. Power cables may be installed as permanent wiring within buildings, buried in the ground, run overhead, or exposed. Power cables that are bundled inside thermoplastic sheathing and that are intended to be run inside a building are known as NM-B.

Heat-shrink tubing is a shrinkable plastic tube used to insulate wires, providing abrasion resistance and environmental protection for stranded and solid wire conductors, connections, joints and terminals in electrical wiring. It can also be used to repair the insulation on wires or to bundle them together, to protect wires or small parts from minor abrasion, and to create cable entry seals, offering environmental sealing protection. Heat-shrink tubing is ordinarily made of polyolefin, which shrinks radially when heated, to between one-half and one-sixth of its diameter.
A thermoplastic-sheathed cable (TPS) consists of a toughened outer sheath of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) thermoplastic, covering one or more individual annealed copper conductors, themselves insulated with PVC. This type of wiring is commonly used for residential and light commercial construction in many countries. The flat version of the cable, with two insulated conductors and an uninsulated earth conductor, is referred to as twin and earth. In mainland Europe, a round equivalent is more common.

Knob-and-tube wiring is an early standardized method of electrical wiring in buildings, in common use in North America from about 1880 to the 1930s. It consisted of single-insulated copper conductors run within wall or ceiling cavities, passing through joist and stud drill-holes via protective porcelain insulating tubes, and supported along their length on nailed-down porcelain knob insulators. Where conductors entered a wiring device such as a lamp or switch, or were pulled into a wall, they were protected by flexible cloth insulating sleeving called loom. The first insulation was asphalt-saturated cotton cloth, then rubber became common. Wire splices in such installations were twisted together for good mechanical strength, then soldered and wrapped with rubber insulating tape and friction tape, or made inside metal junction boxes.

A cable harness, also known as a wire harness, wiring harness, cable assembly, wiring assembly or wiring loom, is an assembly of electrical cables or wires which transmit signals or electrical power. The cables are bound together by a durable material such as rubber, vinyl, electrical tape, conduit, a weave of extruded string, or a combination thereof.

The Western Union splice or Lineman splice is a method of joining electrical cable, developed in the nineteenth century during the introduction of the telegraph and named for the Western Union telegraph company. This method can be used where the cable may be subject to loading stress. The wrapping pattern design causes the join to tighten as the conductors pull against each other.
Sumitomo Electric Industries, Ltd. is a manufacturer of electric wire and optical fiber cables. Its headquarters are in Chūō-ku, Osaka, Japan. The company's shares are listed in the first section of the Tokyo, Nagoya Stock Exchanges, and the Fukuoka Stock Exchange. In the period ending March 2021, the company reported consolidated sales of US$26,5 billion.

A fiber-optic cable, also known as an optical-fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable is used. Different types of cable are used for optical communication in different applications, for example long-distance telecommunication or providing a high-speed data connection between different parts of a building.
In electrical power distribution, armoured cable usually means steel wire armoured cable (SWA) which is a hard-wearing power cable designed for the supply of mains electricity. It is one of a number of armoured electrical cables – which include 11 kV Cable and 33 kV Cable – and is found in underground systems, power networks and cable ducting.

A high-voltage cable is a cable used for electric power transmission at high voltage. A cable includes a conductor and insulation. Cables are considered to be fully insulated. This means that they have a fully rated insulation system that will consist of insulation, semi-con layers, and a metallic shield. This is in contrast to an overhead line, which may include insulation but not fully rated for operating voltage. High-voltage cables of differing types have a variety of applications in instruments, ignition systems, and alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) power transmission. In all applications, the insulation of the cable must not deteriorate due to the high-voltage stress, ozone produced by electric discharges in air, or tracking. The cable system must prevent contact of the high-voltage conductor with other objects or persons, and must contain and control leakage current. Cable joints and terminals must be designed to control the high-voltage stress to prevent the breakdown of the insulation.

A tube, or tubing, is a long hollow cylinder used for moving fluids or to protect electrical or optical cables and wires.

Copper tubing is most often used for heating systems and as a refrigerant line in HVAC systems. Copper tubing is slowly being replaced by PEX tubing in hot and cold water applications. There are two basic types of copper tubing, soft copper and rigid copper. Copper tubing is joined using flare connection, compression connection, pressed connection, or solder. Copper offers a high level of corrosion resistance but is becoming very costly.

Copper has been used in electrical wiring since the invention of the electromagnet and the telegraph in the 1820s. The invention of the telephone in 1876 created further demand for copper wire as an electrical conductor.

An electrical conduit is a tube used to protect and route electrical wiring in a building or structure. Electrical conduit may be made of metal, plastic, fiber, or fired clay. Most conduit is rigid, but flexible conduit is used for some purposes.

A towing sock or wire rope puller or wire pulling grip is a device that connects to the end of a cable, such as a power cable, in order to pull it through a tube or tunnel. It works by tightening around the cable when pulled, in the same manner as a Chinese finger trap. The towing sock is tubular and made of braided cable, open at one end and closed at the other where it connects to a tow line using an eye splice.















