Awards and honours
Elected Fellow of the Acoustical Society of America in 2002 [3]
Thomas Simm Littler prize from the British Society of Audiology in 2009 [3]
Awarded the 3-year veski innovation fellowship in 2013 [5]
Elected Fellow of the Australian Academy of Health and Medical Sciences 2021 [8]
Related Research Articles

Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children,hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spoken language,and in adults it can create difficulties with social interaction and at work. Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent. Hearing loss related to age usually affects both ears and is due to cochlear hair cell loss. In some people,particularly older people,hearing loss can result in loneliness.

A cochlear implant (CI) is a surgically implanted neuroprosthesis that provides a person who has moderate-to-profound sensorineural hearing loss with sound perception. With the help of therapy,cochlear implants may allow for improved speech understanding in both quiet and noisy environments. A CI bypasses acoustic hearing by direct electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve. Through everyday listening and auditory training,cochlear implants allow both children and adults to learn to interpret those signals as speech and sound.
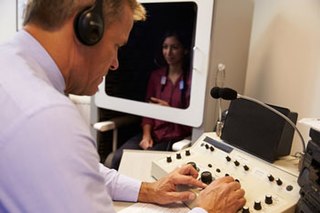
Audiology is a branch of science that studies hearing,balance,and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies,audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds. If hearing loss is identified,audiologists determine which portions of hearing are affected,to what degree,and where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found. If an audiologist determines that a hearing loss or vestibular abnormality is present,they will provide recommendations for interventions or rehabilitation.
Graeme Milbourne Clark is an Australian Professor of Otolaryngology at the University of Melbourne. Worked in ENT surgery,electronics and speech science contributed towards the development of the multiple-channel cochlear implant. His invention was later marketed by Cochlear Limited.

The All India Institute of Speech and Hearing,commonly known as AIISH (AYE-SH),is located in Manasagangotri,Mysore,India. It is an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. The institute was established in 1966 with a focus on training professionals for speech and hearing sciences.

Central Institute for the Deaf (CID) is a school for the deaf that teaches students using listening and spoken language,also known as the auditory-oral approach. The school is located in St. Louis,Missouri. CID is affiliated with Washington University in St. Louis.
Marion Downs was an American audiologist and professor emerita at the University of Colorado Health Sciences Center in Denver. She pioneered universal newborn hearing screening in the early 1960s and spent over 30 years advocating for its adoption in hospitals,as well as for the provision of hearing aids to infants displaying hearing loss. Her efforts were aimed at raising awareness within the medical community about the developmental challenges associated with childhood deafness. Thanks to her initiatives,95 percent of newborns born in America today undergo screening for hearing loss. As a result of her efforts,95 percent of all newborns in America today are screened for hearing loss. She devoted her professional life to the promotion of early identification of hearing loss in newborns,infants,and young children and to helping deaf and hard of hearing individuals lead fulfilling lives.
Neurotology or neuro-otology is a subspecialty of otolaryngology—head and neck surgery,also known as ENT medicine. Neuro-otology is closely related to otology,clinical neurology and neurosurgery.
Ingo R. Titze is a voice scientist and executive director of the National Center for Voice and Speech and Adjunct Professor in the Department of Otolaryngology/Head and Neck Surgery at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City. He also teaches at the Summer Vocology Institute,also housed at the University of Utah. He is a Distinguished Professor at the Department of Communication Sciences and Disorders at the University of Iowa and has written several books relating to the human voice.

The Bionics Institute is an Australian medical research institute focusing on medical device development. It is located in Melbourne,Australia.
Monita Chatterjee is an auditory scientist and the Director of the Auditory Prostheses &Perception Laboratory at Boys Town National Research Hospital. She investigates the basic mechanisms underlying auditory processing by cochlear implant listeners.
Sharon G. Kujawa is a clinical audiologist,Director of Audiology Research at the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary,Associate Professor of Otology and Laryngology at Harvard Medical School,and Adjunct Faculty of Harvard-MIT Health Sciences and Technology.and specialist in otolaryngology,Her specialty is the effects of noise exposure and aging on auditory function.

Debara Lyn Tucci is an American otolaryngologist,studying ear,nose,and throat conditions. She co-founded the Duke Hearing Center and currently serves as a professor of Surgery and Director of the Cochlear Implant Program at Duke University. In September 2019 she became Director of the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders,one of the National Institutes of Health's 27 Institutes and Centers.
Elaine Saunders is an associate professor at the Swinburne University of Technology and executive director of Blamey Saunders,as well as an inventor,entrepreneur. She was elected a Fellow of the Australian Academy of Science Technology and Engineering in 2019. She is one of only nine women out of 160 to win the Clunies Ross award for entrepreneurship,and has won many other awards,as well as given numerous keynote addresses on the value of entrepreneurship and innovation in STEMM.

Laura K. Mackay is an Australian immunologist and Professor of Immunology at the University of Melbourne. Mackay is the Theme Leader in Immunology and Laboratory Head at the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity. In 2022,she was the youngest Fellow elected to the Australian Academy of Health and Medical Sciences.

Richard Charles Dowell is an Australian audiologist,academic and researcher. He holds the Graeme Clark Chair in Audiology and Speech Science at University of Melbourne. He is a former director of Audiological Services at Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital.

Jean Littlejohn was an Australian surgeon,early practitioner of the developing field of otorhinolaryngology,and pioneer of deafness research. She joined the Royal Victorian Eye and Ear Hospital in Melbourne,Australia and maintained a long association with the hospital until her retirement in 1974.
Susan Ellen Shore is an American audiologist who is the Merle Lawrence Collegiate Professor of Otolaryngology at the University of Michigan. She was elected Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science in 2021.
Judy R. Dubno is an American scientist and researcher in the field of audiology. She is a distinguished university professor and director of research in the department of otolaryngology at the Medical University of South Carolina in Charleston. She is recognized for her scientific contributions to the understanding of presbycusis,a condition of hearing loss that occurs gradually for many aging adults. She has been involved in the development and implementation of several new methods for assessing hearing loss,including the Hearing in Noise Test (HINT) and Speech Intelligibility Index (SII). She has won numerous awards for her work,including the Jerger Career Award for Research in Audiology in 2011. She served as President of the Acoustical Society of America from 2014 to 2015.

Charlotte Martinez Tantoco Chiong is a Filipino otolaryngologist with a subspecialty in neurotology,focusing on hearing health,cochlear implants,and neurotological skull base surgery based in Malolos and Manila,Philippines. She is best known for her research on children's implantable hearing devices,which built the foundation for the Republic Act No. 9709 of the Philippines that organized a universal screening program for hearing loss in newborns.
References
- ↑ "Colette McKay – veski announcement profile" (PDF). veski.org.au. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ↑ "Prof Colette McKay". findanexpert.unimelb.edu.au. Retrieved 2023-10-07.
- 1 2 3 4 "Professor Colette McKay, Translational Hearing Research and Principal Scientist - Bionics Institute". www.bionicsinstitute.org. Retrieved 2023-10-10.
- ↑ "History of Audiology". The University of Manchester. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- 1 2 "Colette McKay · veski". www.veski.org.au. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ↑ "EarGenie hearing test for babies - Bionics Institute". www.bionicsinstitute.org. 2022-04-27. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- ↑ "Breakthrough invention assists treatment of deaf and hearing impaired newborns". www.9news.com.au. 2023-05-08. Retrieved 2023-10-11.
- 1 2 "Professor Colette McKay - AAHMS". aahms.org. 2022-05-16. Retrieved 2023-10-10.