
Scottish Gaelic,also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic,is a Goidelic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language,Scottish Gaelic,as well as both Irish and Manx,developed out of Old Irish. It became a distinct spoken language sometime in the 13th century in the Middle Irish period,although a common literary language was shared by the Gaels of both Ireland and Scotland until well into the 17th century. Most of modern Scotland was once Gaelic-speaking,as evidenced especially by Gaelic-language place names.

Argyll and Bute is one of 32 unitary council areas in Scotland and a lieutenancy area. The current lord-lieutenant for Argyll and Bute is Jane Margaret MacLeod. The administrative centre for the council area is in Lochgilphead at Kilmory Castle,a 19th-century Gothic Revival building and estate. The current council leader is Councillor Jim Lynch.

Clan Campbell is a Highland Scottish clan,historically one of the largest and most powerful of the Highland clans. The Clan Campbell lands are in Argyll and within their lands lies Ben Cruachan. The chief of the clan became Earl of Argyll and later Duke of Argyll.

Dunoon is the main town on the Cowal Peninsula in the south of Argyll and Bute,west of Scotland. It is located on the western shore of the upper Firth of Clyde,to the south of the Holy Loch and to the north of Innellan. As well as forming part of the council area of Argyll and Bute,Dunoon also has its own community council. Dunoon was a burgh until 1976.

Duke of Argyll is a title created in the peerage of Scotland in 1701 and in the peerage of the United Kingdom in 1892. The earls,marquesses,and dukes of Argyll were for several centuries among the most powerful noble families in Scotland. As such,they played a major role in Scottish history throughout the 16th,17th,and 18th centuries. The Duke of Argyll also holds the hereditary titles of chief of Clan Campbell and Master of the Household of Scotland.

Caledonian MacBrayne,in short form CalMac,is the trade name of CalMac Ferries Ltd,the major operator of passenger and vehicle ferries to the west coast of Scotland,serving ports on the mainland and 22 of the major islands. It is a subsidiary of holding company David MacBrayne,which is owned by the Scottish Government.
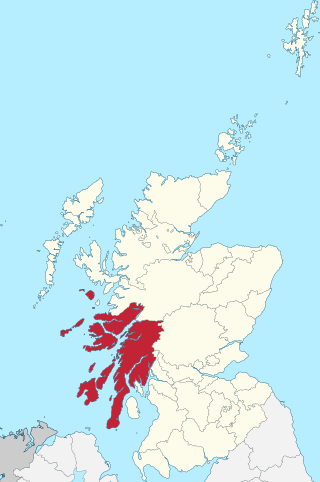
Argyll,sometimes called Argyllshire,is a historic county and registration county of western Scotland. The county ceased to be used for local government purposes in 1975 and most of the area now forms part of the larger Argyll and Bute council area.

Cowal is a rugged peninsula in Argyll and Bute,on the west coast of Scotland. It is connected to the mainland to the north,and is bounded by Loch Fyne to the west,by Loch Long and the Firth of Clyde to the east,and by the Kyles of Bute to the south.

Loch Long is a body of water in the council area of Argyll and Bute,Scotland. The Sea Loch extends from the Firth of Clyde at its southwestern end. It measures approximately 20 miles in length,with a width of between one and two miles. The loch also has an arm,Loch Goil,on its western side.
Archibald Campbell,4th Earl of Argyll or Archibald "the Red" Campbell,was a Scottish nobleman and politician.

Tarbert is a village in the west of Scotland,in the Argyll and Bute council area. It is built at the head of an inlet of Loch Fyne called East Loch Tarbert,on a narrow isthmus which connects Kintyre to the south with Knapdale to the north and separates East Loch Tarbert from the much longer West Loch Tarbert. Tarbert had a recorded population of 1,338 in the 2001 Census.

Clan Lamont is a Highland Scottish clan. The clan is said to descend from Ánrothán Ua Néill,an Irish prince of the O'Neill dynasty,and through him Niall Noigíallach,High King of Ireland. Clan Ewen of Otter,Clan MacNeil of Barra,Clan Lachlan,and Clan Sweeney are also descendants of Ánrothán. Traditional genealogy would therefore include Clan Lamont among the descendants of Conn Cétchathach.

Castle Sween,also known as Caisteal Suibhne,and Caistéal Suibhne,is located on the eastern shore of Loch Sween,in Knapdale,south of the forestry village of Achnamara on the west coast of Argyll,Scotland. Castle Sween is thought to be one of the earliest stone castles built in Scotland,having been built in the late 11th century. The castle's towers were later additions to wooden structures which have since vanished.

St John's Cathedral or the Cathedral Church of St John the Divine is a cathedral of the Scottish Episcopal Church,located in the town of Oban. It is one of the two cathedrals of the Diocese of Argyll and The Isles,and one of the sees of the Bishop of Argyll and The Isles.

The Diocese of Argyll and the Isles is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in Scotland,in the Province of Saint Andrews and Edinburgh.

Clan MacIver or Clan MacIvor,also known as Clan Iver,is a Scottish clan recognised by the Lord Lyon King of Arms. The clan,however,does not have a chief recognised by the Lord Lyon King of Arms. Because of this the clan can be considered an armigerous clan. The clan name of MacIver is of Gaelic origin,derived from an Old Norse personal name. Various forms of the surname MacIver,like MacGiver,are considered sept names of several historically large Scottish clans,such as clans Campbell and Mackenzie. There exists a Clan Iver society in Fife,Scotland.

Loch Eck is a freshwater loch located on the Cowal Peninsula,north of Dunoon,in Argyll and Bute,west of Scotland. It is seven miles long. It is oriented in a north-south direction. Its main inflow,at the northern end,is the River Cur,and its main outflow,at the southern end,is the River Eachaig,which meanders somewhat within the confines of the broad strath before flowing into the head of Holy Loch,about 5 km further south.

The Mod Cup,also known as the Aviemore Cup1995 - Royal National Mòd Programmes and fringe events >Royal National Mòd Programmes >[Mod / Mòd Naìseanta Rìoghail - An Comunn Gaidhealach - National Library of Scotland] is a trophy in the sport of shinty first competed for in 1969,traditionally played for by the two teams who are based closest to the host venue of the Royal National Mod. The current holders are Aberdour.(2022)

Evan MacColl was a Scottish-born bilingual poet in both Canadian Gaelic and Canadian English. He is commonly known in his native language as Bàrd Loch Fìne. Later he became known as "the Gaelic Bard of Canada".

Mackintosh MacKay was a Scottish minister and author who served as Moderator of the General Assembly of the Free Church of Scotland in 1849. He edited the Highland Society's prodigious Gaelic dictionary in 1828.


















