The salivary glands in mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary glands can be classified as serous, mucous or seromucous (mixed).
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, e.g. secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion, is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the cell plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structure at the cell plasma membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell.
In biochemistry, an effector molecule is usually a small molecule that selectively binds to a protein and regulates its biological activity. In this manner, effector molecules act as ligands that can increase or decrease enzyme activity, gene expression, or cell signaling. Effector molecules can also directly regulate the activity of some mRNA molecules (riboswitches).
Gastric acid, gastric juice, or stomach acid, is a digestive fluid formed in the stomach and is composed of hydrochloric acid (HCl), potassium chloride (KCl), and sodium chloride (NaCl). The acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins, by activating digestive enzymes, and making ingested proteins unravel so that digestive enzymes break down the long chains of amino acids. Gastric acid is produced by cells in the lining of the stomach, which are coupled in feedback systems to increase acid production when needed. Other cells in the stomach produce bicarbonate, a base, to buffer the fluid, ensuring that it does not become too acidic. These cells also produce mucus, which forms a viscous physical barrier to prevent gastric acid from damaging the stomach. The pancreas further produces large amounts of bicarbonate and secretes bicarbonate through the pancreatic duct to the duodenum to completely neutralize any gastric acid that passes further down into the digestive tract.

Larvaceans are solitary, free-swimming tunicates found throughout the world's oceans. Like most tunicates, appendicularians are filter feeders. Unlike most other tunicates, they live in the pelagic zone, specifically in the upper sunlit portion of the ocean or sometimes deeper. They are transparent planktonic animals, generally less than 1 cm (0.39 in) in body length.
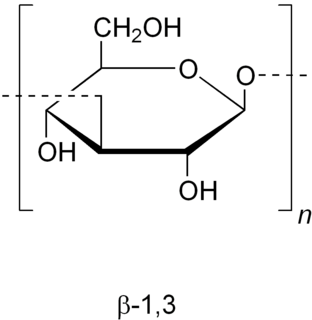
Digestive enzymes are a group of enzymes that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks, in order to facilitate their absorption by the body. Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tracts of animals and in the traps of carnivorous plants, where they aid in the digestion of food, as well as inside cells, especially in their lysosomes, where they function to maintain cellular survival. Digestive enzymes of diverse specificities are found in the saliva secreted by the salivary glands, in the secretions of cells lining
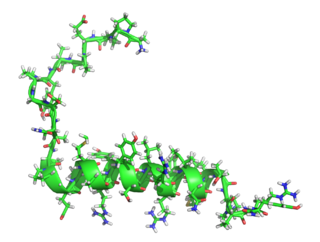
Pancreatic polypeptide (PP) is a polypeptide secreted by PP cells in the endocrine pancreas predominantly in the head of the pancreas. It consists of 36 amino acids and has molecular weight about 4200 Da.
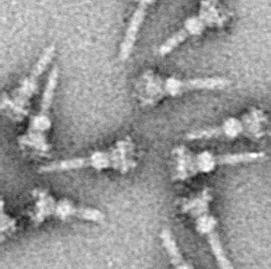
Type three secretion system is a protein appendage found in several Gram-negative bacteria.
Conglutinin is a collectin protein.
Surfactant protein A is an innate immune system collectin. It is water-soluble and has collagen-like domains similar to SP-D. It is part of the innate immune system and is used to opsonize bacterial cells in the alveoli marking them for phagocytosis by alveolar macrophages. SP-A may also play a role in negative feedback limiting the secretion of pulmonary surfactant. SP-A is not required for pulmonary surfactant to function but does confer immune effects to the organism.
Collectin liver 1 is a collectin. Its structure is similar to mannan-binding lectin (MBL).
The neuropeptide B/W receptors are members of the G-protein coupled receptor superfamily of integral membrane proteins which bind the neuropeptides B and W. These receptors are predominantly expressed in the CNS and have a number of functions including regulation of the secretion of cortisol.

Kruppel-like factor 7 (ubiquitous), also known as KLF7, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the KLF7 gene.
Collectin of 46 kDa (CL-46) is a collectin protein. It has two cysteine residues on the N-terminal segment, a hydrophilic loop near the carbohydrate recognition domain's binding site, and a N-glycosylation site in the collagen region. It is expressed in bovine liver and thymus glands and binds to pathogens, prompting elimination by macrophages.

In molecular biology, Pulmonary surfactant protein D (SP-D) is a protein domain predominantly found in lung surfactant. This protein plays a special role; its primary task is to act as a defence protein against any pathogens that may invade the lung. It also plays a role in lubricating the lung and preventing it from collapse. It has an interesting structure as it forms a triple-helical parallel coiled coil, helps the protein to fold into a trimer.
Ficolins (Fi+Col+Lin) are a group of oligomeric lectins with subunits consisting of both collagen (Col)-like long thin stretches and fibrinogen (Fi)-like globular domains with lectin (Lin) activity usually specific for N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc). Like collectins (Col+lectin) such as mannan-binding lectin, ficolins are secreted, lectin-type pattern recognition receptors, and similarly activate the lectin pathway of complement activation.
Gcn4 is a transcription factor and a “master regulator” for gene expression which regulates close to one tenth of the yeast genome. In a study by Razaghi et al, amino acid starvation activated the transcription factor Gcn4p, resulting in transcriptional induction of almost all genes involved in amino acid biosynthesis, including HIS4. Thus involvement of Gcn4 in regulation of both histidinol dehydrogenase HIS4 and interferon gamma hIFNγ was hypothesised as a scenario explaining the increased level of hIFNγ under amino acid starvation.