Color code or color coding may refer to:

A color code is a system for displaying information by using different colors.
Component may refer to:

An electronic color code is used to indicate the values or ratings of electronic components, usually for resistors, but also for capacitors, inductors, diodes and others. A separate code, the 25-pair color code, is used to identify wires in some telecommunications cables. Different codes are used for wire leads on devices such as transformers or in building wiring.
An, AN, aN, or an may refer to:
Color or colour is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, yellow, blue, green, etc.
Symbolism or symbolist may refer to:
Tan or TAN may refer to:
Ra is the Sun-god of Ancient Egypt.

In color theory, a color scheme is the choice of colors used in various artistic and design contexts. For example, the "Achromatic" use of a white background with black text is an example of a basic and commonly default color scheme in web design.
Chromatic, a word ultimately derived from the Greek noun χρῶμα (khrṓma), which means "complexion" or "color", and then from the Greek adjective χρωματικός, may refer to:
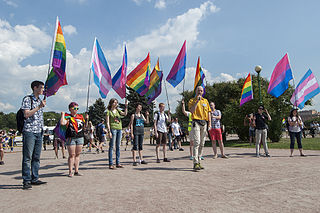
A pride flag is any flag that represents a segment or part of the LGBT community. Pride in this case refers to the notion of gay pride. The terms LGBT flag and queer flag are often used interchangeably.
GD, Gd, or gd may refer to:
In cartography, map coloring is the act of choosing colors as a form of map symbol to be used on a map. In mathematics, map coloring is the act of assigning colors to features of a map such that no two adjacent features have the same color using the minimum number of colors.

The Atari Video Music is the earliest commercial electronic music visualizer released. It was manufactured by Atari, Inc., and released in 1977 for $169.95. The system creates an animated visual display that responds to musical input from a Hi-Fi stereo system for the visual entertainment of consumers.
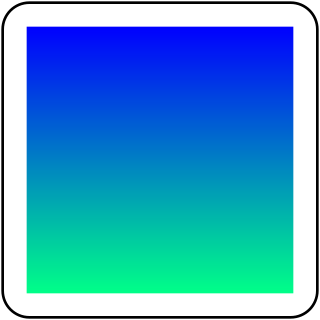
In computer graphics, a color gradient specifies a range of position-dependent colors, usually used to fill a region. For example, many window managers allow the screen background to be specified as a gradient. The colors produced by a gradient vary continuously with position, producing smooth color transitions.

Synesthesia or synaesthesia is a perceptual phenomenon in which stimulation of one sensory or cognitive pathway leads to involuntary experiences in a second sensory or cognitive pathway. People who report a lifelong history of such experiences are known as synesthetes. Awareness of synesthetic perceptions varies from person to person. In one common form of synesthesia, known as grapheme–color synesthesia or color–graphemic synesthesia, letters or numbers are perceived as inherently colored. In spatial-sequence, or number form synesthesia, numbers, months of the year, or days of the week elicit precise locations in space, or may appear as a three-dimensional map. Synesthetic associations can occur in any combination and any number of senses or cognitive pathways.
Color symbolism in art and anthropology refers to the use of color as a symbol in various cultures. There is great diversity in the use of colors and their associations between cultures and even within the same culture in different time periods. The same color may have very different associations within the same culture at any time. Diversity in color symbolism occurs because color meanings and symbolism occur on an individual, cultural and universal basis. Color symbolism is also context-dependent and influenced by changes over time. Symbolic representations of religious concepts or articles may include a specific color with which the concept or object is associated. There is evidence to suggest that colors have been used for this purpose as early as 90,000 BC.

Color psychology is the study of hues as a determinant of human behavior. Carl Jung has been credited as one of the pioneers in this field for his explorations into the properties and meanings of colors in our lives. Jung is quoted for saying, "colours are the mother tongue of the subconscious" Color influences perceptions that are not obvious, such as the taste of food. Colors have qualities that can cause certain emotions in people. Colors can also enhance the effectiveness of placebos. For example, red or orange pills are generally used as stimulants. How color influences individuals may differ depending on age, gender, and culture. For instance, heterosexual men tend to report that red outfits enhance female attractiveness, while heterosexual females deny any outfit color impacting that of men. Although color associations can vary contextually between cultures, color preference is to be relatively uniform across gender and race.

Data visualization achieves its significance today due to information technology: big data processed in computers with capable visualization software, combined with statistical techniques and color coding on electronic displays. This article is about color coding in data visualization.

The colors pink and blue are associated with girls and boys respectively, in the United States, the United Kingdom and some other European countries.