The topic of this article may not meet Wikipedia's general notability guideline .(January 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Colored coins are a class of methods for associating real world assets with addresses on the bitcoin network. Examples could be a deed for a house, stocks, bonds or futures. [1] The technology could also be used to track and register intellectual property assets. [2] [3]

In financial accounting, an asset is any resource owned by the business. Anything tangible or intangible that can be owned or controlled to produce value and that is held by a company to produce positive economic value is an asset. Simply stated, assets represent value of ownership that can be converted into cash. The balance sheet of a firm records the monetary value of the assets owned by that firm. It covers money and other valuables belonging to an individual or to a business.
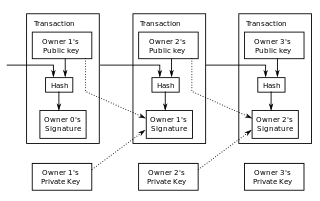
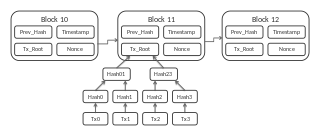
The bitcoin network is a peer-to-peer payment network that operates on a cryptographic protocol. Users send and receive bitcoins, the units of currency, by broadcasting digitally signed messages to the network using bitcoin cryptocurrency wallet software. Transactions are recorded into a distributed, replicated public database known as the blockchain, with consensus achieved by a proof-of-work system called mining. Satoshi Nakamoto, the designer of bitcoin claimed that design and coding of bitcoin began in 2007. The project was released in 2009 as open source software.
A deed is any legal instrument in writing which passes, affirms or confirms an interest, right, or property and that is signed, attested, delivered, and in some jurisdictions, sealed. It is commonly associated with transferring (conveyancing) title to property. The deed has a greater presumption of validity and is less rebuttable than an instrument signed by the party to the deed. A deed can be unilateral or bilateral. Deeds include conveyances, commissions, licenses, patents, diplomas, and conditionally powers of attorney if executed as deeds. The deed is the modern descendant of the medieval charter, and delivery is thought to symbolically replace the ancient ceremony of livery of seisin.
Contents
Through 2014/15 it was suggested that various coloured coin protocols could be of interest to banks and major financial institutions. [4] This prediction came true in June 2015 when NASDAQ announced they were developing a system in partnership with blockchain startup Chain using the Open Assets protocol developed and utilised by CoinPrism and built on by Get Hashing. [5] In late 2015 NASDAQ announced that the first ever trade had occurred using its new platform, Linq. [6]

A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates credit. Lending activities can be performed either directly or indirectly through capital markets. Due to their importance in the financial stability of a country, banks are highly regulated in most countries. Most nations have institutionalized a system known as fractional reserve banking under which banks hold liquid assets equal to only a portion of their current liabilities. In addition to other regulations intended to ensure liquidity, banks are generally subject to minimum capital requirements based on an international set of capital standards, known as the Basel Accords.

Financial institutions, otherwise known as banking institutions, are corporations that provide services as intermediaries of financial markets. Broadly speaking, there are three major types of financial institutions:
- Depository institutions – deposit-taking institutions that accept and manage deposits and make loans, including banks, building societies, credit unions, trust companies, and mortgage loan companies;
- Contractual institutions – insurance companies and pension funds
- Investment institutions – investment banks, underwriters, brokerage firms.
There are several competing implementations of the coloured coins idea, using differing methods, including those developed by CoinSpark, Colu and several built on the EPBOC protocol.