
The Roman legion, the largest military unit of the Roman army, comprised 4,200 infantry and 300 equites (cavalry) in the period of the Roman Republic and 5,600 infantry and 200 auxilia in the period of the Roman Empire.
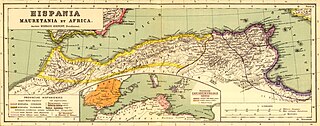
Mauretania is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It stretched from central present-day Algeria westwards to the Atlantic, covering northern present-day Morocco, and southward to the Atlas Mountains. Its native inhabitants, of Berber ancestry, were known to the Romans as the Mauri and the Masaesyli.

The Jovians and Herculians were the senior palatine imperial guard units under the rule of Roman Emperor Diocletian. They continued in existence thereafter as senior units in the field armies of the Western and Eastern Roman Empires.

Dux Britanniarum was a military post in Roman Britain, probably created by Emperor Diocletian or Constantine I during the late third or early fourth century. The Dux (literally, " leader" was a senior officer in the late Roman army of the West in Britain. It is listed in the Notitia Dignitatum as being one of the three commands in Britain, along with the Comes Britanniarum and Count of the Saxon Shore.

The Comes Britanniarum was a military post in Roman Britain with command over the mobile field army from the mid-4th century onwards. It is listed in the List of Offices as being one of the three commands in Britain, along with the Dux Britanniarum and the Comes litoris Saxonici. His troops were the main field army (comitatenses) in Britain and not the frontier guards (limitanei) commanded by the other two.
The limitanei, meaning respectively "the soldiers in frontier districts" or "the soldiers on the riverbank", were an important part of the late Roman and early Byzantine army after the reorganizations of the late 3rd and early 4th centuries. The limitanei, unlike the Comitatenses, palatīni, and Scholae, garrisoned fortifications along the borders of the Roman Empire and were not normally expected to fight far from their fortifications.
The comitatenses and later the palatini were the units of the field armies of the late Roman Empire. They were the soldiers that replaced the legionaries, who had formed the backbone of the Roman military since the late republic.
Auxilia palatina were infantry units of the Late Roman army, first raised by Constantine I as part of the new field army he created in about 325 AD.

The Taifals or Tayfals were a people group of Germanic or Sarmatian origin, first documented north of the lower Danube in the mid third century AD. They experienced an unsettled and fragmented history, for the most part in association with various Gothic peoples, and alternately fighting against or for the Romans. In the late fourth century some Taifali were settled within the Roman Empire, notably in western Gaul in the modern province of Poitou. They subsequently supplied mounted units to the Roman army and continued to be a significant source of cavalry for early Merovingian armies. By the sixth century their region of western Gaul had acquired a distinct identity as Thifalia.

The Diocese of Egypt was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of Egypt and Cyrenaica. Its capital was at Alexandria, and its governor had the unique title of praefectus augustalis instead of the ordinary vicarius. The diocese was initially part of the Diocese of the East, but in ca. 380, it became a separate entity, which lasted until its territories were overrun by the Muslim conquest of Egypt in the 640s.

In modern scholarship, the "late" period of the Roman army begins with the accession of the Emperor Diocletian in AD 284, and ends in 480 with the death of Julius Nepos, being roughly coterminous with the Dominate. During the period 395–476, the army of the Roman Empire's western half progressively disintegrated, while its counterpart in the East, known as the East Roman army remained largely intact in size and structure until the reign of Justinian I.

The Eastern Roman army refers to the army of the eastern section of the Roman Empire, from the empire's definitive split in 395 AD to the army's reorganization by themes after the permanent loss of Syria, Palestine and Egypt to the Arabs in the 7th century during the Byzantine-Arab Wars. The East Roman army was the continuation of the Late Roman army of the 4th century, until it gradually transformed into what is now called the Byzantine army from the 7th century onwards.
The palatini were elite units of the Late Roman army mostly attached to the comitatus praesentales, or imperial escort armies. In the elaborate hierarchy of troop-grades, the palatini ranked below the scholares, but above the comitatenses and the limitanei.

Equites cataphractarii, or simply cataphractarii, were the most heavily armoured type of Roman cavalry in the Imperial Roman army and Late Roman army. The term derives from a Greek word, κατάφρακτος kataphraktos, meaning "covered over" or "completely covered".

The Cornuti ("horned") was an auxilia palatina unit of the Late Roman army, active in the 4th and 5th century. It was probably related to the Cornuti seniores and the Cornuti iuniores.

The equites stablesiani were a class of cavalry in the Late Roman army. They were one of several categories of cavalry unit or vexillatio created between the 260s and 290s as part of a reorganization and expansion of Roman cavalry forces initiated during the reign of Gallienus. These new cavalry vexillationes typically shared the basic regimental designation equites, and included equites Dalmatae, equites Mauri and equites scutarii.
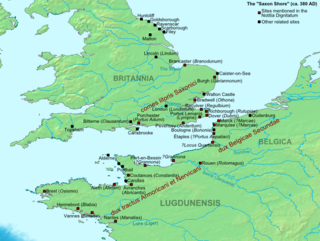
The Dux Belgicae secundae was a senior officer in the army of the Late Roman Empire who was the commander of the limitanei and of a naval squadron on the so-called Saxon Shore in Gaul.

Osroene, also spelled Osrohene and Osrhoene, was a Roman province which existed for nearly 400 years. It was formed after the absorption of the Kingdom of Osroene in 214 CE and served as a frontier province against the Sassanid Empire until the Muslim conquests of the 7th century.

The comes tractus Argentoratensis was in late antiquity commander of units of the mobile field army of the Western Roman Empire, operating along the Rhine frontier in the Diocese of Gaul.














