
The economy of the Czech Republic is a developed export-oriented social market economy based in services, manufacturing, and innovation that maintains a high-income welfare state and the European social model. The Czech Republic participates in the European Single Market as a member of the European Union, and is therefore a part of the economy of the European Union. It uses its own currency, the Czech koruna, instead of the euro. It is a member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). The Czech Republic ranks 16th in inequality-adjusted human development and 24th in World Bank Human Capital Index, ahead of countries such as the United States, the United Kingdom or France. It was described by The Guardian as "one of Europe's most flourishing economies".

The economy of Estonia is an advanced economy and the country is a member of the European Union and of the eurozone. Estonia's economy is heavily influenced by developments in the Finnish and Swedish economies.

The economy of North Macedonia has become more liberalized, with an improved business environment, since its independence from Yugoslavia in 1991, which deprived the country of its key protected markets and the large transfer payments from Belgrade. Prior to independence, North Macedonia was Yugoslavia's poorest republic. An absence of infrastructure, United Nations sanctions on its largest market, and a Greek economic embargo hindered economic growth until 1996.

The economy of Romania is a complex high-income economy with a skilled labour force, ranked 12th in the European Union by total nominal GDP and 7th largest when adjusted by purchasing power parity. The World Bank notes that Romania’s efforts are focused on accelerating structural reforms and strengthening institutions in order to further converge with the European Union. The country's economic growth has been one of the highest in the EU since 2010, with the first half of 2022 seeing an unexpected 5.8% increase.

The economy of Slovenia is a developed economy, and the country enjoys a high level of prosperity and stability as well as above-average GDP per capita by purchasing power parity at 83% of the EU28 average in 2015. The nominal GDP in 2023 is 68.108 billion USD, nominal GDP per capita (GDP/pc) in 2023 is USD 32,214. The highest GDP/pc is in central Slovenia, where the capital city Ljubljana is located. It is part of the Western Slovenia statistical region, which has a higher GDP/pc than eastern Slovenia.

Customs is an authority or agency in a country responsible for collecting tariffs and for controlling the flow of goods, including animals, transports, personal effects, and hazardous items, into and out of a country. Traditionally, customs has been considered as the fiscal subject that charges customs duties and other taxes on import and export. In recent decades, the views on the functions of customs have considerably expanded and now covers three basic issues: taxation, security, and trade facilitation.

Eurostat is a Directorate-General of the European Commission located in the Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Eurostat's main responsibilities are to provide statistical information to the institutions of the European Union (EU) and to promote the harmonisation of statistical methods across its member states and candidates for accession as well as EFTA countries. The organisations in the different countries that cooperate with Eurostat are summarised under the concept of the European Statistical System.
The Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System, also known as the Harmonized System (HS) of tariff nomenclature is an internationally standardized system of names and numbers to classify traded products. It came into effect in 1988 and has since been developed and maintained by the World Customs Organization (WCO), an independent intergovernmental organization based in Brussels, Belgium.

The economy of the European Union is the joint economy of the member states of the European Union (EU). It is the third largest economy in the world in nominal terms, after the United States and China, and the third one in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms, after China and the United States. The European Union's GDP estimated to be around $16.6 trillion (nominal) in 2022 representing around one sixth of the global economy. Germany has by far the biggest national GDP of all EU countries, followed by France and Italy.
Foreign affiliate trade statistics (FATS), also known as transnational corporation (TNC) data details the economic operations of foreign direct investment-based enterprises.
Intrastat is the system for collecting information and producing statistics on the trade in goods between countries of the European Union (EU). It began operation on 1 January 1993, when it replaced customs declarations as the source of trade statistics within the EU. The requirements of Intrastat are similar in all member states of the EU, although there are important exceptions.
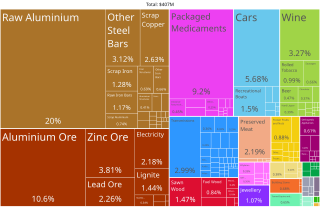
The economy of Montenegro is currently in a process of transition, as it navigates the impacts of the Yugoslav Wars, the decline of industry following the dissolution of the Yugoslavia, and economic sanctions imposed by the United Nations. Montenegro joined the World Trade Organization on 29 April 2012. Montenegro joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organization on 5 June 2017. The accession of Montenegro to the European Union is planned for 2025.
Standard International Trade Classification (SITC) is a classification of goods used to classify the exports and imports of a country to enable comparing different countries and years. The classification system is maintained by the United Nations. The SITC classification, is currently at revision four, which was promulgated in 2006.

An import is the receiving country in an export from the sending country. Importation and exportation are the defining financial transactions of international trade.

Council Regulation (EEC) No 2658/87 of 23 July 1987, creates the goods nomenclature called the Combined Nomenclature, or in abbreviated form 'CN', established to meet, at one and the same time, the requirements both of the Common Customs Tariff and of the external trade statistics of the European Union. It is closely related to the Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States.
Economy-wide material flow accounts (EW-MFA) is a framework to compile statistics linking flows of materials from natural resources to a national economy. EW-MFA are descriptive statistics, in physical units such as tonnes per year.

Since the end of apartheid, foreign trade in South Africa has increased, following the lifting of several sanctions and boycotts which were imposed as a means of ending apartheid.
The World Integrated Trade Solution (WITS) is a trade software provided by the World Bank for users to query several international trade databases.
The international trade of fine art is most precisely defined as the trade across nations of unique, non-reproducible works by an artist. The art trade contradicts typical international trade models since it is a culturally significant good. It is not treated by consumers the same way any other commodity would because of the aesthetic value that is unique to each piece. Despite existing as a finite physical piece, unique art is still considered intellectual property. This sparks the debate as to whether art exports should be restricted for nationalistic and cultural reasons, or liberalized for the sake of a healthier international market.
The Joint Harmonised EU Programme of Business and Consumer Surveys consists of economic tendency surveys which are conducted in all EU Member States and candidate countries. Based on the results of the surveys, a set of harmonized economic indicators is calculated for all participating countries, typically used for analysis and short-term forecasting of economic developments, as well as economic research. Furthermore, the indicators lend themselves to detecting turning points in the business cycle and are a complement to official statistical data on economic developments, which are released with a significantly longer time-lag .











