Related Research Articles

A frontier is the political and geographical area near or beyond a boundary. A frontier can also be referred to as a "front". The term came from French in the 15th century, with the meaning "borderland"—the region of a country that fronts on another country. Unlike a border—a rigid and clear-cut form of state boundary—in the most general sense a frontier can be fuzzy or diffuse. For example, the frontier between the Eastern United States and the Old West in the 1800s was an area where European American settlements gradually thinned out and gave way to Native American settlements or uninhabited land. The frontier was not always a single continuous area, as California and various large cities were populated before the land that connected those to the East.
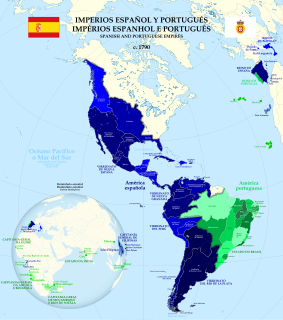
The Spanish colonization of the Americas began under the Crown of Castile and spearheaded by the Spanish conquistadors. The Americas were invaded and incorporated into the Spanish Empire, with the exception of Brazil, British America, and some small regions in South America and the Caribbean. The crown created civil and religious structures to administer this vast territory. The main motivations for colonial expansion were profit through resource extraction and the spread of Catholicism through indigenous conversions.

The Huilliche[wi.ˈʝi.tʃe], Huiliche or Huilliche-Mapuche are the southern partiality of the Mapuche macroethnic group of Chile. The Huilliche are the principal indigenous population of Chile from Toltén River to Chiloé Archipelago. According to Ricardo E. Latcham the term Huilliche started to be used in Spanish after the second founding of Valdivia in 1645, adopting the usage of the Mapuches of Araucanía for the southern Mapuche tribes. Huilliche means 'southerners'

The Mapuche are a group of indigenous inhabitants of present-day south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of present-day Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who shared a common social, religious, and economic structure, as well as a common linguistic heritage as Mapudungun speakers. Their influence once extended from Aconcagua Valley to Chiloé Archipelago and later spread eastward to Puelmapu, a land compromising part of the Argentine pampa and Patagonia. Today the collective group makes up over 80% of the indigenous peoples in Chile, and about 9% of the total Chilean population. The Mapuche are particularly concentrated in the Araucanía region. Many have migrated from rural areas to the cities of Santiago and Buenos Aires for economic opportunities.

The Captaincy General of Chile or Govenorate of Chile, was a territory of the Spanish Empire from 1541 to 1818 that was, for most of its existence, part of the Viceroyalty of Peru. It comprised most of modern-day Chile and southern parts of Argentina. Its capital was Santiago de Chile. In 1818 it declared itself independent, becoming the Republic of Chile. It had a number of Spanish governors over its long history and several kings.

García Hurtado de Mendoza y Manrique, 5th Marquis of Cañete was a Spanish Governor of Chile, and later Viceroy of Peru. He is often known simply as "Marquis of Cañete". Belonging to an influential family of Spanish noblemen Hurtado de Mendoza successfully fought in the Arauco War during his stay as Governor of Chile. The city of Mendoza is named after him. In his later position as Viceroy of Peru he sponsored Álvaro de Mendaña's transpacific expedition of 1595, who named the Marquesas Islands after him.

Chileans are people identified with the country of Chile, whose connection may be residential, legal, historical, or cultural. For most Chileans, several or all of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their Chilean identity. Chile is a multilingual and multicultural society, home to people of many different ethnicities and religions. Therefore, many Chileans do not equate their nationality with ethnicity, but with citizenship and allegiance to Chile. The overwhelming majority of Chileans are the product of varying degrees of admixture between European ethnic groups with peoples indigenous to Chile's modern territory.
Cuncos or Juncos is a poorly known subgroup of Huilliche people native to coastal areas of southern Chile and the nearby inland. Mostly a historic term, Cuncos are chiefly known for their long-running conflict with the Spanish.
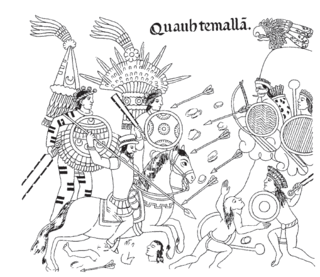
Indian auxiliaries or indios auxiliares is the term used in old Spanish chronicles and historical texts for the indigenous peoples who were integrated into the armies of the Spanish conquistadors with the purpose of supporting their advance and combat operations during the Conquest of America. They acted as guides, translators, or porters and in this role were also called yanakuna, particularly within the old Inca Empire and Chile. The term was also used for formations composed of indigenous warriors or Indios amigos, which they used for reconnaissance, combat, and as reserve in battle. The auxiliary Indians remained in use after the conquest, during some revolts, in border zones and permanent military areas, as in Chile in the Arauco War.

The Papal mediation in the Beagle conflict followed the failure of negotiations between Chile and Argentina, when, on 22 December 1978, the Argentinian Junta started Operation Soberanía, to invade Cape Horn and islands awarded to Chile by the Beagle Channel Arbitration. Soon after the event, Pope John Paul II offered to mediate and sent his personal envoy, Cardinal Antonio Samoré, to Buenos Aires. Argentina, in acceptance of the authority of the Pope over the overwhelmingly Catholic Argentine population, called off the military operation and accepted the mediation. On 9 January 1979, Chile and Argentina signed the Act of Montevideo formally requesting mediation by the Vatican and renouncing the use of force.

Coordinadora Arauco-Malleco (CAM) is an indigenous organization advocated to the creation of an autonomous Mapuche state in Araucanía, which is, they say, the revindication and recovery of former Mapuche lands. They are mostly renowned for their violent methods, often recurring to arson and armed attacks against "Fuerzas Especiales" of Carabineros de Chile. It was founded in 1998, in Tranaquepe, Chile, and is responsible for land occupation in the zones of Tirúa, Contulmo, Cañete and Temucuicui. Protesters from radicalized Mapuche communities have used these tactics against multinational forestry corporations and private individuals backed by CAM paramilitary power as a form of exerting political pressure.

The Mapuche conflict is the name given to the conflict originated from the claims of indigenist Mapuche communities and organizations to the States of Chile and Argentina. The activist in favor of the 'Mapuche cause' claim greater autonomy, recognition of rights, and the 'recovery' of land since the Chilean transition to democracy.
In Chilean historiography, Colonial Chile is the period from 1600 to 1810, beginning with the Destruction of the Seven Cities and ending with the onset of the Chilean War of Independence. During this time the Chilean heartland was ruled by Captaincy General of Chile. The period was characterized by a lengthy conflict between Spaniards and native Mapuches known as the Arauco War. Colonial society was divided in distinct groups including Peninsulars, Criollos, Mestizos, Indians and Black people.
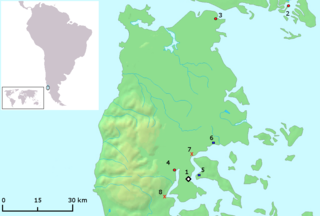
The Huilliche uprising of 1712 was an indigenous uprising against the Spanish encomenderos of the Chiloé Archipelago, which was then a part of the Captaincy General of Chile. The rebellion took place in the central part of the archipelago.
From 1850 to 1875, some 6,000 German immigrants settled in the region around Valdivia, Osorno and Llanquihue in Southern Chile as part of a state-led colonization scheme. Some of these immigrants had left Europe in the aftermath of the German revolutions of 1848–49. They brought skills and assets as artisans, farmers and merchants to Chile, contributing to the nascent country's economic and industrial development.
The Mapuche people of southern Chile and Argentina have a long history dating back as an archaeological culture to 600–500 BC. The Mapuche society had great transformations after Spanish contact in the mid–16th century. These changes included the adoption of Old World crops and animals and the onset of a rich Spanish–Mapuche trade in La Frontera and Valdivia. Despite these contacts Mapuche were never completely subjugated by the Spanish Empire. Between the 18th and 19th century Mapuche culture and people spread eastwards into the Pampas and the Patagonian plains. This vast new territory allowed Mapuche groups to control a substantial part of the salt and cattle trade in the Southern Cone.
The Parliament of Las Canoas was a diplomatic meeting between Mapuche-Huilliches and Spanish authorities in 1793 held at the confluence of Rahue River and Damas River near what is today the city of Osorno. The parliament was summoned by the Royal Governor of Chile Ambrosio O'Higgins after the Spanish had suppressed an uprising by the Mapuche-Huilliches of Ranco and Río Bueno in 1792. The parliament is historically relevant since the treaty signed at the end of the meeting allowed the Spanish to reestablish the city of Osorno and secure the transit rights between Valdivia and the Spanish mainland settlements near Chiloé Archipelago. The indigenous signatories recognized the king of Spain as their sovereign but they kept considerable autonomy in the lands they did not ceded. The treaty is unique in that it was the first time Mapuches formally ceded territory to the Spanish.
The Huilliche uprising of 1792 was an indigenous uprising against the Spanish penetration into Futahuillimapu, territory in southern Chile that had been de facto free of Spanish rule since 1602. The first part of the conflict was a series of Huilliche attacks on Spanish settlers and the mission in the frontier next to Bueno River. Following this a militia in charge of Tomás de Figueroa departed from Valdivia ravaging Huilliche territory in a quest to punish those involved in the attacks.

Futahuillimapu or Fütawillimapu is a traditional territory of the Huilliche people. Futahuillimapu spans the land between Bueno River and Reloncaví Sound. Futahuillimapu means "great land of the south."
In colonial and early republican Chile capitán de amigos were Spanish or Mestizo officials who surveilled friendly indigenous tribes. Capitanes de amigos were oversighted by higher ranking officials known as comisario de naciones. It was not uncommon for a capitán de amigos to live among the indegnous peoples he was in charge of, sometimes marrying indigenous women and even adopting prohibited customs such as polygamy. Knowing both Spanish and indigenous cultures some capines de amigos took advantage of this to profit in frontier trade. In times of indigenous revolts information provided by capitanes de amigos was crucial for Spanish or Chilean authorities.
References
- 1 2 3 "Tipos fronterizos". Memoria Chilena (in Spanish). Biblioteca Nacional de Chile . Retrieved January 12, 2021.
- 1 2 Rumian Cisterna, Salvador (2020-09-17). Gallito Catrilef: Colonialismo y defensa de la tierra en San Juan de la Costa a mediados del siglo XX (M.Sc. thesis) (in Spanish). University of Los Lagos.