In computing, a context switch is the process of storing the state of a process or thread, so that it can be restored and resume execution at a later point, and then restoring a different, previously saved, state. This allows multiple processes to share a single central processing unit (CPU), and is an essential feature of a multiprogramming or multitasking operating system. In a traditional CPU, each process - a program in execution - utilizes the various CPU registers to store data and hold the current state of the running process. However, in a multitasking operating system, the operating system switches between processes or threads to allow the execution of multiple processes simultaneously. For every switch, the operating system must save the state of the currently running process, followed by loading the next process state, which will run on the CPU. This sequence of operations that stores the state of the running process and loads the following running process is called a context switch.

Memory management is a form of resource management applied to computer memory. The essential requirement of memory management is to provide ways to dynamically allocate portions of memory to programs at their request, and free it for reuse when no longer needed. This is critical to any advanced computer system where more than a single process might be underway at any time.
In computer science, a semaphore is a variable or abstract data type used to control access to a common resource by multiple threads and avoid critical section problems in a concurrent system such as a multitasking operating system. Semaphores are a type of synchronization primitive. A trivial semaphore is a plain variable that is changed depending on programmer-defined conditions.
In object-oriented programming, the command pattern is a behavioral design pattern in which an object is used to encapsulate all information needed to perform an action or trigger an event at a later time. This information includes the method name, the object that owns the method and values for the method parameters.

In computing, at is a command in Unix-like operating systems, Microsoft Windows, and ReactOS used to schedule commands to be executed once, at a particular time in the future.
In computing, scheduling is the action of assigning resources to perform tasks. The resources may be processors, network links or expansion cards. The tasks may be threads, processes or data flows.

CUPS is a modular printing system for Unix-like computer operating systems which allows a computer to act as a print server. A computer running CUPS is a host that can accept print jobs from client computers, process them, and send them to the appropriate printer.

The cron command-line utility is a job scheduler on Unix-like operating systems. Users who set up and maintain software environments use cron to schedule jobs, also known as cron jobs, to run periodically at fixed times, dates, or intervals. It typically automates system maintenance or administration—though its general-purpose nature makes it useful for things like downloading files from the Internet and downloading email at regular intervals.
Signals are standardized messages sent to a running program to trigger specific behavior, such as quitting or error handling. They are a limited form of inter-process communication (IPC), typically used in Unix, Unix-like, and other POSIX-compliant operating systems.
The MCP is the operating system of the Burroughs B5000/B5500/B5700 and the B6500 and successors, including the Unisys Clearpath/MCP systems.
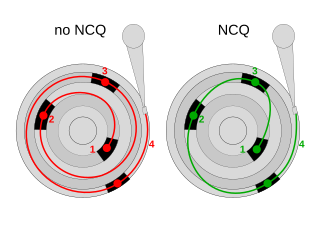
In computing, Native Command Queuing (NCQ) is an extension of the Serial ATA protocol allowing hard disk drives to internally optimize the order in which received read and write commands are executed. This can reduce the amount of unnecessary drive head movement, resulting in increased performance for workloads where multiple simultaneous read/write requests are outstanding, most often occurring in server-type applications.

In computing, a task is a unit of execution or a unit of work. The term is ambiguous; precise alternative terms include process, light-weight process, thread, step, request, or query. In the adjacent diagram, there are queues of incoming work to do and outgoing completed work, and a thread pool of threads to perform this work. Either the work units themselves or the threads that perform the work can be referred to as "tasks", and these can be referred to respectively as requests/responses/threads, incoming tasks/completed tasks/threads, or requests/responses/tasks.
In system software, a job queue, is a data structure maintained by job scheduler software containing jobs to run.
Tagged Command Queuing (TCQ) is a technology built into certain ATA and SCSI hard drives. It allows the operating system to send multiple read and write requests to a hard drive. ATA TCQ is not identical in function to the more efficient Native Command Queuing (NCQ) used by SATA drives. SCSI TCQ does not suffer from the same limitations as ATA TCQ.
CANDE is a command line shell and text editor on the MCP operating system which runs on the Unisys Clearpath series of mainframes. Originally implemented on Burroughs large systems, it has a range of features for interacting with the operating system execution environment, focused on executing, editing and compiling programs, and creating, copying, moving, renaming, and deleting files in general.

In computer storage, a disk buffer is the embedded memory in a hard disk drive (HDD) or solid-state drive (SSD) acting as a buffer between the rest of the computer and the physical hard disk platter or flash memory that is used for storage. Modern hard disk drives come with 8 to 256 MiB of such memory, and solid-state drives come with up to 4 GB of cache memory.

A process is a program in execution, and an integral part of any modern-day operating system (OS). The OS must allocate resources to processes, enable processes to share and exchange information, protect the resources of each process from other processes and enable synchronization among processes. To meet these requirements, The OS must maintain a data structure for each process, which describes the state and resource ownership of that process, and which enables the operating system to exert control over each process.
A trim command allows an operating system to inform a solid-state drive (SSD) which blocks of data are no longer considered to be "in use" and therefore can be erased internally.
OS 2200 is the operating system for the Unisys ClearPath Dorado family of mainframe systems. The operating system kernel of OS 2200 is a lineal descendant of Exec 8 for the UNIVAC 1108 and was previously known as OS 1100. Documentation and other information on current and past Unisys systems can be found on the Unisys public support website.
Enduro/X is an open-source middleware platform for distributed transaction processing. It is built on proven APIs such as X/Open group's XATMI and XA. The platform is designed for building real-time microservices based applications with a clusterization option. Enduro/X functions as an extended drop-in replacement for Oracle Tuxedo. The platform uses in-memory POSIX message queues which insures high inter-process communication throughput.






