Related Research Articles

The aorta is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at the aortic bifurcation into two smaller arteries. The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation.

An artery is a blood vessel in humans and most other animals that takes oxygenated blood away from the heart in the systemic circulation to one or more parts of the body. Exceptions that carry deoxygenated blood are the pulmonary arteries in the pulmonary circulation that carry blood to the lungs for oxygenation, and the umbilical arteries in the fetal circulation that carry deoxygenated blood to the placenta. It consists of a multi-layered artery wall wrapped into a tube-shaped channel.

The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. Heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest, called the mediastinum.
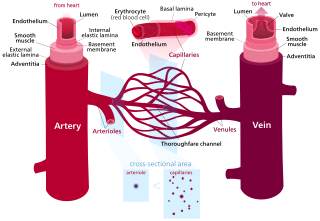
Blood vessels are the structures of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Blood vessels are typically needed to sustain life, because all of the body's tissues rely on their functionality.
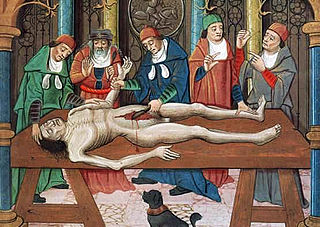
The history of anatomy extends from the earliest examinations of sacrificial victims to the sophisticated analyses of the body performed by modern anatomists and scientists. Written descriptions of human organs and parts can be traced back thousands of years to ancient Egyptian papyri, where attention to the body was necessitated by their highly elaborate burial practices.

William Harvey was an English physician who made influential contributions to anatomy and physiology. He was the first known physician to describe completely, and in detail, pulmonary and systemic circulation as well as the specific process of blood being pumped to the brain and the rest of the body by the heart.

Veins are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation, arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, in the deep veins.
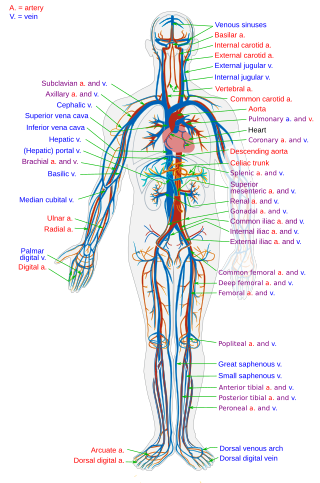
The circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels. The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms cardiovascular system and vascular system interchangeably with circulatory system.

A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the main pulmonary artery or pulmonary trunk from the heart, and the smallest ones are the arterioles, which lead to the capillaries that surround the pulmonary alveoli.

Exercitatio Anatomica de Motu Cordis et Sanguinis in Animalibus, commonly called De Motu Cordis, is the best-known work of the physician William Harvey, which was first published in 1628 and established the circulation of blood throughout the body. It is a landmark in the history of physiology, with Harvey combining observations, experiments, measurements, and hypotheses in an extraordinary fashion to arrive at his doctrine. His work is a model of its kind and had an immediate and far-reaching influence on Harvey's contemporaries; Thomas Hobbes said that Harvey was the only modern author whose doctrines were taught in his lifetime.

The pulmonary circulation is a division of the circulatory system in all vertebrates. The circuit begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lungs. In the lungs the blood is oxygenated and returned to the left atrium to complete the circuit.

The atrium is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves.

ʿAlāʾ al-Dīn Abū al-Ḥasan ʿAlī ibn Abī Ḥazm al-Qarashī, known as Ibn al-Nafīs, was an Arab polymath whose areas of work included medicine, surgery, physiology, anatomy, biology, Islamic studies, jurisprudence, and philosophy. He is known for being the first to describe the pulmonary circulation of the blood. The work of Ibn al-Nafis regarding the right sided (pulmonary) circulation pre-dates the later work (1628) of William Harvey's De motu cordis. Both theories attempt to explain circulation. The 2nd century Greek physician Galen's theory about the physiology of the circulatory system remained unchallenged until the works of Ibn al-Nafis, for which he has been described as "the father of circulatory physiology".
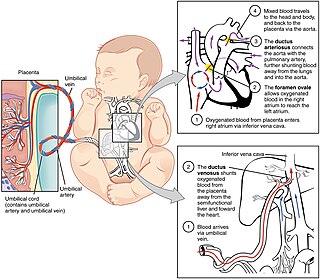
In humans, the circulatory system is different before and after birth. The fetal circulation is composed of the placenta, umbilical blood vessels encapsulated by the umbilical cord, heart and systemic blood vessels. A major difference between the fetal circulation and postnatal circulation is that the lungs are not used during the fetal stage resulting in the presence of shunts to move oxygenated blood and nutrients from the placenta to the fetal tissue. At birth, the start of breathing and the severance of the umbilical cord prompt various changes that quickly transform fetal circulation into postnatal circulation.

The smallest cardiac veins are small, valveless veins in the walls of all four heart chambers that drain venous blood from the myocardium directly into any of the heart chambers.
Theologus Autodidactus is an Arabic novel written by Ibn al-Nafis, originally titled The Treatise of Kāmil on the Prophet's Biography, and also known as Risālat Fādil ibn Nātiq. It was written sometime between 1268 and 1277 and is considered one of the earliest examples of a novel in Arabic literature. The novel contains elements of science fiction and is an early example of a coming-of-age tale and a desert island story. It was partly a response to the philosophical novel Hayy ibn Yaqdhan by Andalusi writer Ibn Tufail.

Paul Ghalioungui or Ghalioungi (1908–1987), MD (Cairo), MRCP (Lond), Professor of Medicine and former Chairman of Internal Medicine department, Ain Shams University Faculty of Medicine. An Egyptian endocrinologist, historian of Egyptian medicine, Egyptologist and an authority on Pharaonic medicine, he wrote a vivid history of Egyptian medicine in English, French, Arabic, German, and Spanish.
Swimming induced pulmonary edema (SIPE), also known as immersion pulmonary edema, is a life threatening condition that occurs when fluids from the blood leak abnormally from the small vessels of the lung (pulmonary capillaries) into the airspaces (alveoli).
Andrea Alpago was an Italian physician and arabist. In publications of his work in Latin, his name is frequently given as Andreas Alpagus Bellunensis, where "Bellunensis" refers to his birthplace of Belluno in northeastern Italy.
References
- 1 2 3 West, John (1985). "Ibn al-Nafis, the pulmonary circulation, and the Islamic Golden Age". Journal of Applied Physiology . 105 (6): 1877–1880. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.91171.2008. PMC 2612469 . PMID 18845773.
- ↑ West, John B. (2008). "Ibn al-Nafis, the pulmonary circulation, and the Islamic Golden Age". Journal of Applied Physiology. 105 (6): 1877–1880. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.91171.2008. ISSN 8750-7587. PMC 2612469 . PMID 18845773.
- ↑ Aloud, Abdurahim (2017-01-16). "Ibn al-Nafis and the discovery of the pulmonary circulation". The Southwest Respiratory and Critical Care Chronicles. 5 (17): 71–73. doi:10.12746/swrccc2017.0517.229. ISSN 2325-9205.
- ↑ Bondke Persson, A.; Persson, P. B. (2014). "Form and function in the vascular system". Acta Physiologica . 211 (3): 468–470. doi:10.1111/apha.12309. PMID 24800879. S2CID 26211642.
- ↑ Bosmia, Anand; Watanabe, Koichi; Shoja, Mohammadali M.; Loukas, Marios; Tubbs, R. Shane (2013). "Michael Servetus (1511–1553): Physician and heretic who described the pulmonary circulation". International Journal of Cardiology . 167 (2): 318–321. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.06.046. PMID 22748500.
"It is possible that Al-Nafis' book was known in 16th century Europe, for Andrea Alapago returned from thirty years in Arabia to Padua in 1520 with a Latin translation of the commentary
- ↑ Michelakis, E. D. (19 June 2014). "Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Yesterday, Today, Tomorrow". Circulation Research . 115 (1): 109–114. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.301132 . PMID 24951761.