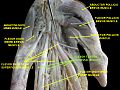
The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The term "carpus" and "carpal" is derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the carpal bones is to articulate with the radial and ulnar heads to form a highly mobile condyloid joint, to provide attachments for thenar and hypothenar muscles, and to form part of the rigid carpal tunnel which allows the median nerve and tendons of the anterior forearm muscles to be transmitted to the hand and fingers.

In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as wrist joints. This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum.
The flexor digitorum profundus is a muscle in the forearm of humans that flexes the fingers. It is considered an extrinsic hand muscle because it acts on the hand while its muscle belly is located in the forearm.
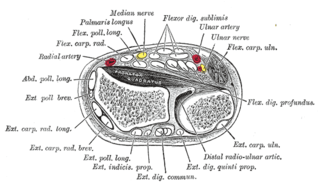
Flexor digitorum superficialis is an extrinsic flexor muscle of the fingers at the proximal interphalangeal joints.

In anatomy, flexor carpi radialis is a muscle of the human forearm that acts to flex and (radially) abduct the hand. The Latin carpus means wrist; hence flexor carpi is a flexor of the wrist.

In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.
In anatomy, a vinculum is a band of connective tissue, similar to a ligament, that connects a flexor tendon to a phalanx bone. They contain tiny vessels which supply blood to the tendon. In vertebrate anatomy, they are referred to as mesotendons.

The extensor digitorum muscle is a muscle of the posterior forearm present in humans and other animals. It extends the medial four digits of the hand. Extensor digitorum is innervated by the posterior interosseous nerve, which is a branch of the radial nerve.
In human anatomy, the extensor pollicis longus muscle (EPL) is a skeletal muscle located dorsally on the forearm. It is much larger than the extensor pollicis brevis, the origin of which it partly covers and acts to stretch the thumb together with this muscle.
The flexor pollicis longus is a muscle in the forearm and hand that flexes the thumb. It lies in the same plane as the flexor digitorum profundus. This muscle is unique to humans, being either rudimentary or absent in other primates. A meta-analysis indicated accessory flexor pollicis longus is present in around 48% of the population.

In human anatomy, the adductor pollicis muscle is a muscle in the hand that functions to adduct the thumb. It has two heads: transverse and oblique.
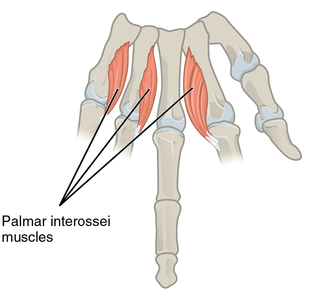
In human anatomy, the palmar or volar interossei are four muscles, one on the thumb that is occasionally missing, and three small, unipennate, central muscles in the hand that lie between the metacarpal bones and are attached to the index, ring, and little fingers. They are smaller than the dorsal interossei of the hand.

In human anatomy, the abductor digiti minimi is a skeletal muscle situated on the ulnar border of the palm of the hand. It forms the ulnar border of the palm and its spindle-like shape defines the hypothenar eminence of the palm together with the skin, connective tissue, and fat surrounding it. Its main function is to pull the little finger away from the other fingers.

The interphalangeal joints of the hand are the hinge joints between the phalanges of the fingers that provide flexion towards the palm of the hand.

In human anatomy, the extensor indicis [proprius] is a narrow, elongated skeletal muscle in the deep layer of the dorsal forearm, placed medial to, and parallel with, the extensor pollicis longus. Its tendon goes to the index finger, which it extends.

The medial epicondyle of the humerus is an epicondyle of the humerus bone of the upper arm in humans. It is larger and more prominent than the lateral epicondyle and is directed slightly more posteriorly in the anatomical position. In birds, where the arm is somewhat rotated compared to other tetrapods, it is called the ventral epicondyle of the humerus. In comparative anatomy, the more neutral term entepicondyle is used.
The posterior compartment of the forearm contains twelve muscles which primarily extend the wrist and digits. It is separated from the anterior compartment by the interosseous membrane between the radius and ulna.

In the human body, the carpal tunnel or carpal canal is a flattened body cavity on the flexor (palmar/volar) side of the wrist, bounded by the carpal bones and flexor retinaculum. It forms the passageway that transmits the median nerve and the tendons of the extrinsic flexor muscles of the hand from the forearm to the hand. There are described cases of the anatomical variant median artery occurrence.

Extensor tendon compartments of the wrist are anatomical tunnels on the back of the wrist that contain tendons of muscles that extend the wrist and the digits.

The extrinsic extensor muscles of the hand are located in the back of the forearm and have long tendons connecting them to bones in the hand, where they exert their action. Extrinsic denotes their location outside the hand. Extensor denotes their action which is to extend, or open flat, joints in the hand. They include the extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL), extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB), extensor digitorum (ED), extensor digiti minimi (EDM), extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU), abductor pollicis longus (APL), extensor pollicis brevis (EPB), extensor pollicis longus (EPL), and extensor indicis (EI).