Related Research Articles

The Arc de Triomphe de l'Étoile, often called simply the Arc de Triomphe, is one of the most famous monuments in Paris, France, standing at the western end of the Champs-Élysées at the centre of Place Charles de Gaulle, formerly named Place de l'Étoile—the étoile or "star" of the juncture formed by its twelve radiating avenues. The location of the arc and the plaza is shared between three arrondissements, 16th, 17th (north), and 8th (east). The Arc de Triomphe honours those who fought and died for France in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, with the names of all French victories and generals inscribed on its inner and outer surfaces. Beneath its vault lies the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier from World War I.

The Paris Commune was a French revolutionary government that seized power in Paris on 18 March 1871 and controlled parts of the city until 28 May 1871. During the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, the French National Guard had defended Paris, and working-class radicalism grew among its soldiers. Following the establishment of the French Third Republic in September 1870 and the complete defeat of the French Army by the Germans by March 1871, soldiers of the National Guard seized control of the city on March 18. The Communards killed two French army generals and refused to accept the authority of the Third Republic; instead, the radicals set about establishing their own independent government.

Marie Joseph Louis Adolphe Thiers was a French statesman and historian. He was the second elected President of France and first President of the Third Republic.

In politics, a red flag is predominantly a symbol of left-wing ideologies, including socialism, communism, anarchism, and the labour movement. The originally empty or plain red flag has been associated with left-wing politics since the French Revolution (1789–1799). The red flag and red as a political colour are the oldest symbols of socialism.

The Paris Commune during the French Revolution was the government of Paris from 1789 until 1795. Established in the Hôtel de Ville just after the storming of the Bastille, it consisted of 144 delegates elected by the 60 divisions of the city. Before its formal establishment, there had been much popular discontent on the streets of Paris over who represented the true Commune, and who had the right to rule the Parisian people. The first mayor was Jean Sylvain Bailly, a relatively moderate Feuillant who supported constitutional monarchy. He was succeeded in November 1791 by Pétion de Villeneuve after Bailly's unpopular use of the National Guard to disperse a riotous assembly in the Champ de Mars.

The National Guard is a French military, gendarmerie, and police reserve force, active in its current form since 2016 but originally founded in 1789 during the French Revolution.

Louis Charles Delescluze was a French revolutionary leader, journalist, and military commander of the Paris Commune.

The Hôtel de Ville is the city hall of Paris, France, standing on the Place de l'Hôtel-de-Ville – Esplanade de la Libération in the 4th arrondissement. The south wing was originally constructed by Francis I beginning in 1535 until 1551. The north wing was built by Henry IV and Louis XIII between 1605 and 1628. It was burned by the Paris Commune, along with all the city archives that it contained, during the Semaine Sanglante, the Commune's final days, in May 1871. The outside was rebuilt following the original design, but larger, between 1874 and 1882, while the inside was considerably modified. It has been the headquarters of the municipality of Paris since 1357. It serves multiple functions, housing the local government council, since 1977 the Mayors of Paris and their cabinets, and also serves as a venue for large receptions. It was designated a monument historique by the French government in 1975.

Louise Michel was a teacher and prominent figure during the Paris Commune. Following her penal transportation to New Caledonia she embraced anarchism. When returning to France she emerged as an important French anarchist and went on speaking tours across Europe. The journalist Brian Doherty has called her the "French grande dame of anarchy." Her use of a black flag at a demonstration in Paris in March 1883 was also the earliest known of what would become known as the anarchy black flag.

Pétroleuses were, according to popular rumours at the time, female supporters of the Paris Commune, accused of burning down much of Paris during the last days of the Commune in May 1871. During May, when Paris was being recaptured by loyalist Versaillais troops, rumours circulated that lower-class women were committing arson against private property and public buildings, using bottles full of petroleum or paraffin which they threw into cellar windows, in a deliberate act of spite against the government. Many Parisian buildings, including the Hôtel de Ville, the Tuileries Palace, the Palais de Justice and many other government buildings were in fact set afire by the soldiers of the Commune during the last days of the Commune, prompting the press and Parisian public opinion to blame the pétroleuses.

Elisabeth Dmitrieff was a Russian revolutionary and feminist activist. The illegitimate daughter of a Russian aristocrat and a German nurse, she had a comfortable upbringing but was marginalized within the Russian aristocracy due to the circumstances of her birth, leading to her interest in Marxism and the radical ideas of Nikolay Chernyshevsky. She entered into a marriage of convenience with Mikhail Tomanovski, a colonel who had retired early due to illness, in order to access her inheritance, which she used to fund revolutionary causes such as the Russian-language journal Narodnoye delo. Her money and married status allowed her to leave Russia and study in Geneva, where she participated in founding the Geneva section of the International Workingmen's Association. Sent by the Geneva section as an envoy to London, she became close to Karl Marx and his daughter Jenny.

John Mustard Merriman was an American historian specializing in modern French history. He was a Charles Seymour Professor of History at Yale University.

Maximilien François Marie Isidore de Robespierre was a French lawyer and statesman, widely recognized as one of the most influential and controversial figures of the French Revolution. Robespierre fervently campaigned for the voting rights of all men and their unimpeded admission to the National Guard. Additionally, he advocated the right to petition, the right to bear arms in self-defence, and the abolition of the Atlantic slave trade. He was a radical Jacobin leader who came to prominence as a member of the Committee of Public Safety, an administrative body of the First French Republic. His legacy has been heavily influenced by his actual or perceived participation in repression of the Revolution's opponents, but is notable for his progressive views for the time.
A workers' council, also called labor council, is a type of council in a workplace or a locality made up of workers or of temporary and instantly revocable delegates elected by the workers in a locality's workplaces. In such a system of political and economic organization, the workers themselves are able to exercise decision-making power. Furthermore, the workers within each council decide on what their agenda is and what their needs are. The council communist Antonie Pannekoek describes shop-committees and sectional assemblies as the basis for workers' management of the industrial system. A variation is a soldiers' council, where soldiers direct a mutiny. Workers and soldiers have also operated councils in conjunction. Workers' councils may in turn elect delegates to central committees, such as the Congress of Soviets.

Robert Paul Tombs is a British historian of France. He is professor emeritus of French history at the University of Cambridge and a fellow of St John's College, Cambridge. Prior to this, he was a reader in the subject until 2007. Tombs is the recipient of the Ordre des Palmes académiques awarded by the French government.
In the history of labor, socialism, and revolutions, the historiography of the Paris Commune connects its 1871 events with the revolutions of 1848 and 1917. Historical interpretation of the Commune influenced subsequent revolutionary ideology and sociopolitical events. As of the late 20th century, there were two main historiographical schools of thought: the political interpretation, that the Commune was a patriotic eruption of fury in response to circumstantial hardship following the Siege of Paris; and the social interpretation, that the Commune was the result of macro socioeconomic forces boiling over, e.g., that it was a war of class struggle. Histories in the latter interpretation have used the Commune's events to make ideological points on behalf of their authors, either that the Commune was an illegitimate, criminal aggression, or that the Commune was the consummation of revolutionary momentum. Similarly, historians within both the political and social interpretations have disagreed as to whether the Commune was inevitable or accidental, a harbinger of the future or a sunset for revolutionary zeal.
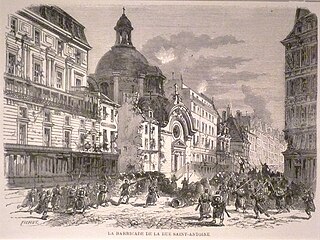
The semaine sanglante was a weeklong battle in Paris from 21 to 28 May 1871, during which the French Army recaptured the city from the Paris Commune. This was the final battle of the Paris Commune.

The Battle of Courbevoie was the first battle of the 1871 Paris Commune.

The Declaration to the French People is a summary of the 1871 Paris Commune's political program by its government, the Commune. It was written by three journalists: Charles Delescluze, Jules Valles, and Pierre Denis, a Jacobin, socialist, and Proudhonist, respectively. The Commune adopted the summary three weeks into their term. Only one elected official dissented. The declaration inveighs against the Versailles government and aligns the Commune with other provinces. The program is made in the name of Paris, not the working classes or revolution, and primarily demands a republican government and secondly, Commune autonomy extended to all of France, giving local bodies control over administration, economics, education, and security. It referenced a federation between communes.

On 1 March 1871 the Imperial German Army paraded through Paris to mark their victory in the Franco-Prussian War. The city had been under siege by Prussian forces since September 1870, with Prussia being unified into the German Empire on 18 January 1871. The Armistice of Versailles of 28 January ended hostilities, but the city remained in French hands. Preliminary peace terms were agreed in the 26 February Treaty of Versailles, which allowed 30,000 German troops to occupy Paris from 1 March until the treaty was ratified.
References
- ↑ Tombs, Robert (2014). The Paris Commune 1871. Taylor & Francis. p. 74. ISBN 978-1-317-88384-5.
- ↑ Tombs 2014, p. 73.
- ↑ Merriman, John (2014). Massacre: The Life and Death of the Paris Commune. Basic Books. p. 74. ISBN 978-0-465-05682-8.
- ↑ Merriman 2014, p. 75.