
The Internet is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a network of networks that consists of private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the inter-linked hypertext documents and applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), electronic mail, telephony, and file sharing.

Wireless community networks (WCNs) or wireless community projects or simply community networks, are non-centralized, self-managed and collaborative networks organized in a grassroots fashion by communities, NGO's and cooperatives in order to provide a viable alternative to municipal wireless networks for consumers.
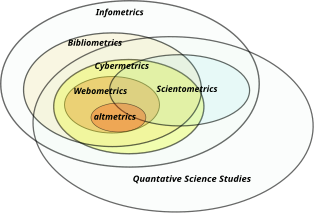
Information science is an academic field which is primarily concerned with analysis, collection, classification, manipulation, storage, retrieval, movement, dissemination, and protection of information. Practitioners within and outside the field study the application and the usage of knowledge in organizations in addition to the interaction between people, organizations, and any existing information systems with the aim of creating, replacing, improving, or understanding information systems.
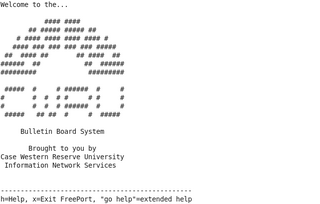
A free-net was originally a computer system or network that provided public access to digital resources and community information, including personal communications, through modem dialup via the public switched telephone network. The concept originated in the health sciences to provide online help for medical patients. With the development of the Internet free-net systems became the first to offer limited Internet access to the general public to support the non-profit community work. The Cleveland Free-Net (cleveland.freenet.edu), founded in 1986, was the pioneering community network of this kind in the world.

Wireless communication is the transfer of information between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most common wireless technologies use radio waves. With radio waves, intended distances can be short, such as a few meters for Bluetooth or as far as millions of kilometers for deep-space radio communications. It encompasses various types of fixed, mobile, and portable applications, including two-way radios, cellular telephones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), and wireless networking. Other examples of applications of radio wireless technology include GPS units, garage door openers, wireless computer mouse, keyboards and headsets, headphones, radio receivers, satellite television, broadcast television and cordless telephones. Somewhat less common methods of achieving wireless communications involve other electromagnetic phenomena, such as light and magnetic or electric fields, or the use of sound.

Internet access is the ability of individuals and organizations to connect to the Internet using computer terminals, computers, and other devices; and to access services such as email and the World Wide Web. Internet access is sold by Internet service providers (ISPs) delivering connectivity at a wide range of data transfer rates via various networking technologies. Many organizations, including a growing number of municipal entities, also provide cost-free wireless access and landlines.
Network society is the expression coined in 1991 related to the social, political, economic and cultural changes caused by the spread of networked, digital information and communications technologies. The intellectual origins of the idea can be traced back to the work of early social theorists such as Georg Simmel who analyzed the effect of modernization and industrial capitalism on complex patterns of affiliation, organization, production and experience.

Community informatics (CI) is an interdisciplinary field that is concerned with using information and communication technology (ICT) to empower members of communities and support their social, cultural, and economic development. Community informatics may contribute to enhancing democracy, supporting the development of social capital, and building well connected communities; moreover, it is probable that such similar actions may let people experience new positive social change. In community informatics, there are several considerations which are the social context, shared values, distinct processes that are taken by members in a community, and social and technical systems. It is formally located as an academic discipline within a variety of academic faculties including information science, information systems, computer science, planning, development studies, and library science among others and draws on insights on community development from a range of backgrounds and disciplines. It is an interdisciplinary approach interested in using ICTs for different forms of community action, as distinct from pure academic study about ICT effects.

A hotspot is a physical location where people can obtain Internet access, typically using Wi-Fi technology, via a wireless local-area network (WLAN) using a router connected to an Internet service provider.
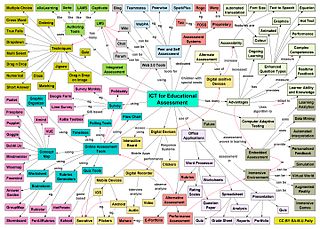
Information and communications technology (ICT) is an extensional term for information technology (IT) that stresses the role of unified communications and the integration of telecommunications and computers, as well as necessary enterprise software, middleware, storage and audiovisual, that enable users to access, store, transmit, understand and manipulate information.

A telecentre is a public place where people can access computers, the Internet, and other digital technologies that enable them to gather information, create, learn, and communicate with others while they develop essential digital skills. Telecentres exist in almost every country, although they sometimes go by a different names including public internet access center (PIAP), village knowledge center, infocenter, Telecottage, Electronic Village Hall, community technology center (CTC), community multimedia center (CMC), multipurpose community telecentre (MCT), Common/Citizen Service Centre (CSC) and school-based telecentre. While each telecentre is different, their common focus is on the use of digital technologies to support community, economic, educational, and social development—reducing isolation, bridging the digital divide, promoting health issues, creating economic opportunities, and reaching out to youth for example.
Nonprofit technology is the deliberative use of technology by nonprofit organizations to maximize potential in numerous areas, primarily in supporting the organization mission and meeting reporting requirements to funders and regulators.
Municipal broadband is broadband Internet access owned by public entities. Services are often provided either fully or partially by local governments to residents within certain areas or jurisdictions. Common connection technologies include unlicensed wireless, licensed wireless, and fiber optic cable. Many cities that previously deployed Wi-Fi based solutions, like Comcast and Charter Spectrum, are switching to municipal broadband. Municipal fiber-to-the-home networks are becoming more prominent because of increased demand for modern audio and video applications, which are increasing bandwidth requirements by 40% per year. Supporters of municipal broadband argue that when cities create their own internet and broadband, customers ultimately get faster internet speeds, lower prices, and better customer service than from internet service providers. The purpose of municipal broadband is to provide internet access to those who cannot afford internet from internet service providers and local governments are increasingly investing in said services for their communities.

A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies, based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies.

Île Sans Fil is a non-profit community wireless network that provides free public wireless Internet access to mobile users in public spaces throughout the island of Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The organization works with cafés, restaurants, bars, stores, community organizations, and individuals to provide free Internet access in public spaces. As of April 2010, the network had over 140,000 registered users and over 212 live hotspots. In 2016, the organization changed it operating name to Zone Access Public Montréal
The University of MichiganSchool of Information (UMSI) or iSchool in Ann Arbor is a graduate school offering baccalaureate, magisterial, and doctoral degrees in informatics and information science.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Internet.

The Chebucto Community Net (CCN) is a Canadian FreeNet operating in Nova Scotia's Halifax Regional Municipality (HRM). It is registered as a non-profit society under Nova Scotia's Registry of Joint Stocks using the name Chebucto Community Net Society. The name "Chebucto" comes from the local l'nu word for Halifax Harbour meaning "big water".

South African wireless community networks are wireless networks that allow members to talk, send messages, share files and play games independent of the commercial landline and mobile telephone networks. Most of them use WiFi technology and many are wireless mesh networks. A wireless community network may connect to the public switched telephone network and/or the Internet, but there are various restrictions on connectivity in South Africa. Wireless community networks are particularly useful in areas where commercial telecommunications services are unavailable or unaffordable.
Computer technology for developing areas is often through the donation of technology to developing areas. Many institutions, government, charitable, and for-profit organizations require technology development often involving hardware or software design, and the coordination of donors, distributors, and deployers. Technical development overlaps with the fields of technical training, maintenance and support.













