Related Research Articles

A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2017, there have existed supercomputers which can perform over 1017 FLOPS (a hundred quadrillion FLOPS, 100 petaFLOPS or 100 PFLOPS). For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigaFLOPS (1011) to tens of teraFLOPS (1013). Since November 2017, all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, Japan, and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers.
Grid computing is the use of widely distributed computer resources to reach a common goal. A computing grid can be thought of as a distributed system with non-interactive workloads that involve many files. Grid computing is distinguished from conventional high-performance computing systems such as cluster computing in that grid computers have each node set to perform a different task/application. Grid computers also tend to be more heterogeneous and geographically dispersed than cluster computers. Although a single grid can be dedicated to a particular application, commonly a grid is used for a variety of purposes. Grids are often constructed with general-purpose grid middleware software libraries. Grid sizes can be quite large.

A power outage is the loss of the electrical power network supply to an end user.

Net metering is an electricity billing mechanism that allows consumers who generate some or all of their own electricity to use that electricity anytime, instead of when it is generated. This is particularly important with renewable energy sources like wind and solar, which are non-dispatchable. Monthly net metering allows consumers to use solar power generated during the day at night, or wind from a windy day later in the month. Annual net metering rolls over a net kilowatt-hour (kWh) credit to the following month, allowing solar power that was generated in July to be used in December, or wind power from March in August.
Utility computing, or computer utility, is a service provisioning model in which a service provider makes computing resources and infrastructure management available to the customer as needed, and charges them for specific usage rather than a flat rate. Like other types of on-demand computing, the utility model seeks to maximize the efficient use of resources and/or minimize associated costs. Utility is the packaging of system resources, such as computation, storage and services, as a metered service. This model has the advantage of a low or no initial cost to acquire computer resources; instead, resources are essentially rented.
Micro combined heat and power, micro-CHP, µCHP or mCHP is an extension of the idea of cogeneration to the single/multi family home or small office building in the range of up to 50 kW. Usual technologies for the production of heat and power in one common process are e.g. internal combustion engines, micro gas turbines, stirling engines or fuel cells.

A negawatt market is a proposed idea of implementation of the demand response that uses an energy market where the commodity traded is a negawatt-hour, a unit of energy saved as a direct result of energy conservation measures.
SZTAKI Desktop Grid (SzDG) was a BOINC project located in Hungary run by the Computer and Automation Research Institute (SZTAKI) of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. It closed on June 21, 2018.
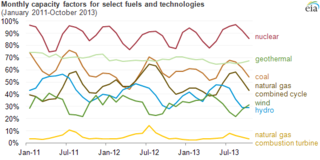
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is defined as that due to its continuous operation at full nameplate capacity over the relevant period. The capacity factor can be calculated for any electricity producing installation, such as a fuel consuming power plant or one using renewable energy, such as wind or the sun. The average capacity factor can also be defined for any class of such installations, and can be used to compare different types of electricity production.

In electrical engineering, a load profile is a graph of the variation in the electrical load versus time. A load profile will vary according to customer type, temperature and holiday seasons. Power producers use this information to plan how much electricity they will need to make available at any given time. Teletraffic engineering uses a similar load curve.
Sun Cloud was an on-demand Cloud computing service operated by Sun Microsystems prior to its acquisition by Oracle Corporation. The Sun Cloud Compute Utility provided access to a substantial computing resource over the Internet for US$1 per CPU-hour. It was launched as Sun Grid in March 2006. It was based on and supported open source technologies such as Solaris 10, Sun Grid Engine, and the Java platform.

A wind power forecast corresponds to an estimate of the expected production of one or more wind turbines in the near future, up to a year. Forecast are usually expressed in terms of the available power of the wind farm, occasionally in units of energy, indicating the power production potential over a time interval.

An engine–generator is the combination of an electrical generator and an engine mounted together to form a single piece of equipment. This combination is also called an engine–generator set or a gen-set. In many contexts, the engine is taken for granted and the combined unit is simply called a generator. An engine–generator may be a fixed installation, part of a vehicle, or made small enough to be portable.

A smart grid is an electrical grid which includes a variety of operation and energy measures including:
A power purchase agreement (PPA), or electricity power agreement, is a long-term contract between an electricity generator and a customer, usually a utility, government or company. PPAs may last anywhere between 5 and 20 years, during which time the power purchaser buys energy at a pre-negotiated price. Such agreements play a key role in the financing of independently owned electricity generators, especially producers of renewable energy like solar farms or wind farms.
Steele is a supercomputer that was installed at Purdue University on May 5, 2008. The high-performance computing cluster is operated by Information Technology at Purdue (ITaP), the university's central information technology organization. ITaP also operates clusters named Coates built in 2009, Rossmann built in 2010, and Hansen and Carter built in 2011. Steele was the largest campus supercomputer in the Big Ten outside a national center when built. It ranked 104th on the November 2008 TOP500 Supercomputer Sites list.
Dynamic Infrastructure is an information technology concept related to the design of data centers, whereby the underlying hardware and software can respond dynamically and more efficiently to changing levels of demand. In other words, data center assets such as storage and processing power can be provisioned to meet surges in user's needs. The concept has also been referred to as Infrastructure 2.0 and Next Generation Data Center.
Décrypthon is a project which uses grid computing resources to contribute to medical research. The word is a portmanteau of the French word "décrypter" and "telethon".

Japan operates a number of centers for supercomputing which hold world records in speed, with the K computer becoming the world's fastest in June 2011. and Fugaku took the lead in June 2020, and furthered it, as of November 2020, to 3 times faster than number two computer.
References
- Who wants to buy a computon?, The Economist, 12 March 2005 Grid computing: Electricity is sold by the kilowatt-hour. Now a researcher has proposed that computing power should be sold by the computon
- Hoffman, Thomas (May 26, 2003). "HP takes new pricing path for utility-based computing - It plans to measure on-demand IT services with a 'computon' metric". Computerworld . Archived from the original on 24 June 2003.