ISO/IEC 7816 is an international standard related to electronic identification cards with contacts, especially smart cards, managed jointly by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC).
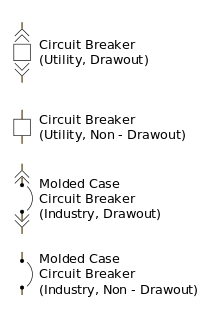
A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by excess current from an overload or short circuit. Its basic function is to interrupt current flow after a fault is detected. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset to resume normal operation.

An electrolytic capacitor is a polarized capacitor whose anode or positive plate is made of a metal that forms an insulating oxide layer through anodization. This oxide layer acts as the dielectric of the capacitor. A solid, liquid, or gel electrolyte covers the surface of this oxide layer, serving as the cathode or negative plate of the capacitor. Due to their very thin dielectric oxide layer and enlarged anode surface, electrolytic capacitors have a much higher capacitance-voltage (CV) product per unit volume than ceramic capacitors or film capacitors, and so can have large capacitance values. There are three families of electrolytic capacitor: aluminum electrolytic capacitors, tantalum electrolytic capacitors, and niobium electrolytic capacitors.
A surge protector is an appliance or device designed to protect electrical devices from voltage spikes.

In mathematics, in the field of differential equations, a boundary value problem is a differential equation together with a set of additional constraints, called the boundary conditions. A solution to a boundary value problem is a solution to the differential equation which also satisfies the boundary conditions.

In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, thereby stopping or interrupting the current. It is a sacrificial device; once a fuse has operated it is an open circuit, it must be replaced or rewired, depending on type.

A current transformer (CT) is a type of transformer that is used to reduce or multiply an alternating current (AC). It produces a current in its secondary which is proportional to the current in its primary.

In an electric power system, switchgear is composed of electrical disconnect switches, fuses or circuit breakers used to control, protect and isolate electrical equipment. Switchgear is used both to de-energize equipment to allow work to be done and to clear faults downstream. This type of equipment is directly linked to the reliability of the electricity supply.
Extra-low voltage (ELV) is an electricity supply voltage in a range which carries a low risk of dangerous electrical shock. There are various standards that define extra-low voltage. The International Electrotechnical Commission member organizations and the UK IET define an ELV device or circuit as one in which the electrical potential between conductor or electrical conductor and earth (ground) does not exceed 50 V a.c. or 120 V d.c..

Capacitors are manufactured in many forms, styles, lengths, girths, and from many materials. They all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by an insulating layer. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices.
Power-system protection is a branch of electrical power engineering that deals with the protection of electrical power systems from faults through the disconnection of faulted parts from the rest of the electrical network. The objective of a protection scheme is to keep the power system stable by isolating only the components that are under fault, whilst leaving as much of the network as possible still in operation. Thus, protection schemes must apply a very pragmatic and pessimistic approach to clearing system faults. The devices that are used to protect the power systems from faults are called protection devices.

A ceramic capacitor is a fixed-value capacitor where the ceramic material acts as the dielectric. It is constructed of two or more alternating layers of ceramic and a metal layer acting as the electrodes. The composition of the ceramic material defines the electrical behavior and therefore applications. Ceramic capacitors are divided into two application classes:
Electrical safety testing is essential to ensure safe operating standards for any product that uses electricity. Various governments and agencies have developed stringent requirements for electrical products that are sold world-wide. In most markets it is mandatory for a product to conform to safety standards promulgated by safety and standard agencies such as UL, CE, VDE, CSA, BSI, CCC and so on. To conform to such standards, the product must pass safety tests such as the high voltage test, Insulation Resistance Test, Ground (Earth) Bond and Ground Continuity Test and Leakage Current Test. These tests are described in IEC 60335, IEC 61010 and many other national and international standards.

In utility and industrial electric power transmission and distribution systems, a digital protective relay is a computer-based system with software-based protection algorithms for the detection of electrical faults. Such relays are also termed as microprocessor type protective relays. They are functional replacements for electro-mechanical protective relays and may include many protection functions in one unit, as well as providing metering, communication, and self-test functions.

A tantalum electrolytic capacitor is an electrolytic capacitor, a passive component of electronic circuits. It consists of a pellet of porous tantalum metal as an anode, covered by an insulating oxide layer that forms the dielectric, surrounded by liquid or solid electrolyte as a cathode. Because of its very thin and relatively high permittivity dielectric layer, the tantalum capacitor distinguishes itself from other conventional and electrolytic capacitors in having high capacitance per volume and lower weight.

A polymer capacitor, or more accurately a polymer electrolytic capacitor, is an electrolytic capacitor (e-cap) with a solid electrolyte of a conductive polymer. There are four different types:

In electrical engineering, a protective relay is a relay device designed to trip a circuit breaker when a fault is detected. The first protective relays were electromagnetic devices, relying on coils operating on moving parts to provide detection of abnormal operating conditions such as over-current, over-voltage, reverse power flow, over-frequency, and under-frequency.

In electrical engineering utilization categories are defined by IEC standards and indicate the type of electrical load and duty cycle of the loads to ease selection of contactors and relays.

Film capacitors, plastic film capacitors, film dielectric capacitors, or polymer film capacitors, generically called "film caps" as well as power film capacitors, are electrical capacitors with an insulating plastic film as the dielectric, sometimes combined with paper as carrier of the electrodes.

Aluminium electrolytic capacitors are polarized electrolytic capacitors whose anode electrode (+) is made of a pure aluminum foil with an etched surface. The aluminum forms a very thin insulating layer of aluminium oxide by anodization that acts as the dielectric of the capacitor. A non-solid electrolyte covers the rough surface of the oxide layer, serving in principle as the second electrode (cathode) (-) of the capacitor. A second aluminum foil called “cathode foil” contacts the electrolyte and serves as the electrical connection to the negative terminal of the capacitor.















