Related Research Articles
Leishmaniasis is a disease caused by parasites of the Leishmania type. It is spread by the bite of certain types of sandflies. The disease can present in three main ways: cutaneous, mucocutaneous, or visceral. The cutaneous form presents with skin ulcers, while the mucocutaneous form presents with ulcers of the skin, mouth, and nose, and the visceral form starts with skin ulcers and then later presents with fever, low red blood cells, and enlarged spleen and liver.
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and immune-mediated disease that affects the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It is not an actual lichen, and is only named that because it looks like one. It is characterized by polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous papules and plaques with overlying, reticulated, fine white scale, commonly affecting dorsal hands, flexural wrists and forearms, trunk, anterior lower legs and oral mucosa. Although there is a broad clinical range of LP manifestations, the skin and oral cavity remain as the major sites of involvement. The cause is unknown, but it is thought to be the result of an autoimmune process with an unknown initial trigger. There is no cure, but many different medications and procedures have been used in efforts to control the symptoms.

Mycosis fungoides, also known as Alibert-Bazin syndrome or granuloma fungoides, is the most common form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. It generally affects the skin, but may progress internally over time. Symptoms include rash, tumors, skin lesions, and itchy skin.

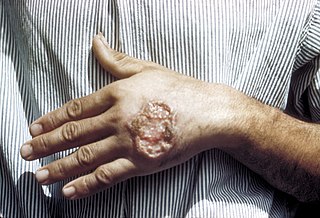
Tuberculosis verrucosa cutis is a rash of small, red papular nodules in the skin that may appear 2–4 weeks after inoculation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a previously infected and immunocompetent individual.

Cutaneous leishmaniasis is the most common form of leishmaniasis affecting humans. It is a skin infection caused by a single-celled parasite that is transmitted by the bite of a phlebotomine sandfly. There are about twenty species of Leishmania that may cause cutaneous leishmaniasis.

The iliohypogastric nerve is a nerve that originates from the lumbar plexus that supplies sensation to skin over the lateral gluteal and hypogastric regions and motor to the internal oblique and transverse abdominal muscles.

The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh is a cutaneous nerve that innervates the skin on the lateral part of the thigh.
Trachyonychia, is a condition characterized by rough accentuated linear ridges on the nails of the fingers and toes. When the condition occurs on all the twenty nails of the fingers and toes, it is known as twenty-nail dystrophy, most evident in childhood, favoring males.

Porokeratosis is a specific disorder of keratinization that is characterized histologically by the presence of a cornoid lamella, a thin column of closely stacked, parakeratotic cells extending through the stratum corneum with a thin or absent granular layer.

Cutaneous small-vessel vasculitis (CSVV), also known as hypersensitivity vasculitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic vasculitis, hypersensitivity angiitis, cutaneous leukocytoclastic angiitis, cutaneous necrotizing vasculitis and cutaneous necrotizing venulitis, is inflammation of small blood vessels, characterized by palpable purpura. It is the most common vasculitis seen in clinical practice.
Plummer's nail is a clinical sign in which there is onycholysis, or separation of the nail from the nail bed, particularly affecting the ring and little fingers. It occurs in patients with thyrotoxicosis. About 5% of hyperthyroid patients display abnormal nail changes. Plummer's nail is also associated with psoriasis, traumatic injury, and allergic contact dermatitis.
Paraneoplastic acrokeratosis, or Bazex syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by psoriasiform changes of hands, feet, ears, and nose, with involvement of the nails and periungual tissues being characteristic and indistinguishable from psoriatic nails. The condition is associated with carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract.

Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia refers to a groups of benign cutaneous disorders characterized by collections of lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells in the skin. Conditions included in this groups are:
Infantile acne is a cutaneous condition that usually presents between 3 to 6 months of age.

A Myxoid cyst is a cutaneous condition often characterized by nail plate depression and grooves.
Tripe palms, is a cutaneous condition characterized by ridged velvety lesions on the palms resembling the lining of a cow's stomach (tripe).

Kraurosis vulvae is a cutaneous condition characterized by atrophy and shrinkage of the skin of the vagina and vulva often accompanied by a chronic inflammatory reaction in the deeper tissues.
Laryngo-onycho-cutaneous syndrome is a rare epithelial disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion. It is characterized by abnormalities in the larynx, nails ("onycho-"), and skin ("cutaneous"). The disorder is only found in Punjabi Muslims and only a few cases have been reported.
Dysplastic nails are a cutaneous condition, and may be a subtle finding of ridging, flaking, or poor growth of the nails, or more diffuse with nearly complete loss of nails. This condition may be seen in a number of syndromes, including Dyskeratosis congenita and Nail–patella syndrome.
References
- ↑ Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.