Related Research Articles

Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a telecommunications standard defined by the American National Standards Institute and ITU-T for digital transmission of multiple types of traffic. ATM was developed to meet the needs of the Broadband Integrated Services Digital Network as defined in the late 1980s, and designed to integrate telecommunication networks. It can handle both traditional high-throughput data traffic and real-time, low-latency content such as telephony (voice) and video. ATM provides functionality that uses features of circuit switching and packet switching networks by using asynchronous time-division multiplexing. ATM was seen in the 1990s as a competitor to Ethernet and networks carrying IP traffic as, unlike Ethernet, it was faster and designed with quality-of-service in mind, but it fell out of favor once Ethernet reached speeds of 1 gigabits per second.
The erlang is a dimensionless unit that is used in telephony as a measure of offered load or carried load on service-providing elements such as telephone circuits or telephone switching equipment. A single cord circuit has the capacity to be used for 60 minutes in one hour. Full utilization of that capacity, 60 minutes of traffic, constitutes 1 erlang.

General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), also called 2.5G, is a mobile data standard on the 2G cellular communication network's global system for mobile communications (GSM). Networks and mobile devices with GPRS started to roll out around the year 2001. At the time of introduction it offered for the first time seamless mobile data transmission using packet data for an "always-on" connection, providing improved Internet access for web, email, WAP services, and Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS).

Frame Relay is a standardized wide area network (WAN) technology that specifies the physical and data link layers of digital telecommunications channels using a packet switching methodology. Originally designed for transport across Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) infrastructure, it may be used today in the context of many other network interfaces.
In telecommunications engineering, and in particular teletraffic engineering, the quality of voice service is specified by two measures: the grade of service (GoS) and the quality of service (QoS).
A virtual circuit (VC) is a means of transporting data over a data network, based on packet switching and in which a connection is first established across the network between two endpoints. The network, rather than having a fixed data rate reservation per connection as in circuit switching, takes advantage of the statistical multiplexing on its transmission links, an intrinsic feature of packet switching.
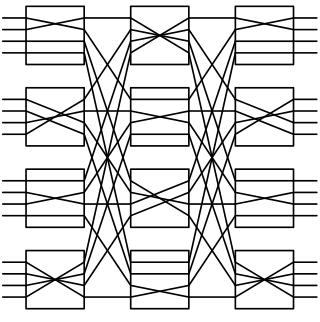
A nonblocking minimal spanning switch is a device that can connect N inputs to N outputs in any combination. The most familiar use of switches of this type is in a telephone exchange. The term "non-blocking" means that if it is not defective, it can always make the connection. The term "minimal" means that it has the fewest possible components, and therefore the minimal expense.

The base station subsystem (BSS) is the section of a traditional cellular telephone network which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the network switching subsystem. The BSS carries out transcoding of speech channels, allocation of radio channels to mobile phones, paging, transmission and reception over the air interface and many other tasks related to the radio network.

A business telephone system is a telephone system typically used in business environments, encompassing the range of technology from the key telephone system (KTS) to the private branch exchange (PBX).
Teletraffic engineering, telecommunications traffic engineering, or just traffic engineering when in context, is the application of transportation traffic engineering theory to telecommunications. Teletraffic engineers use their knowledge of statistics including queuing theory, the nature of traffic, their practical models, their measurements and simulations to make predictions and to plan telecommunication networks such as a telephone network or the Internet. These tools and knowledge help provide reliable service at lower cost.
Quality of service (QoS) mechanism controls the performance, reliability and usability of a telecommunications service. Mobile cellular service providers may offer mobile QoS to customers just as the fixed line PSTN services providers and Internet service providers may offer QoS. QoS mechanisms are always provided for circuit switched services, and are essential for non-elastic services, for example streaming multimedia. It is also essential in networks dominated by such services, which is the case in today's mobile communication networks.
Measurement of traffic within a network allows network managers and analysts to both make day-to-day decisions about operations and to plan for long-term developments. Traffic Measurements are used in many fundamental activities such as:
Dispatch is a procedure for assigning employees (workers) or vehicles to customers. Industries that dispatch include taxicabs, couriers, emergency services, as well as home and commercial services such as maid services, plumbing, HVAC, pest control and electricians.
The Elektronisches Wählsystem Digital (EWSD), translated to Electronic Digital Switching System in English, is a widely installed German telephone exchange system, originally introduced in 1975 by Siemens AG, but discontinued in 2017.
In telecommunications, busy-hour call attempts (BHCA) is a teletraffic engineering measurement used to evaluate and plan capacity for telephone networks. BHCA is the number of telephone calls attempted at the sliding 60-minute period during which occurs the maximum total traffic load in a given 24-hour period (BHCA), and the higher the BHCA, the higher the stress on the network processors. BHCA is not to be confused with busy hour call completion (BHCC) which measures the throughput capacity of the network. If a bottleneck in the network exists with a capacity lower than the estimated BHCA, then congestion will occur resulting in many failed calls and customer dissatisfaction.
MPT 1327 is an industry standard for trunked radio communications networks.
TXE, was a family of telephone exchanges developed by the British General Post Office (GPO), designed to replace the ageing Strowger switches.
Tax protesters in the United States advance a number of constitutional arguments asserting that the imposition, assessment and collection of the federal income tax violates the United States Constitution. These kinds of arguments, though related to, are distinguished from statutory and administrative arguments, which presuppose the constitutionality of the income tax, as well as from general conspiracy arguments, which are based upon the proposition that the three branches of the federal government are involved together in a deliberate, on-going campaign of deception for the purpose of defrauding individuals or entities of their wealth or profits. Although constitutional challenges to U.S. tax laws are frequently directed towards the validity and effect of the Sixteenth Amendment, assertions that the income tax violates various other provisions of the Constitution have been made as well.

A telephone exchange, also known as a telephone switch or central office, is a crucial component in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or large enterprise telecommunications systems. It facilitates the interconnection of telephone subscriber lines or digital system virtual circuits, enabling telephone calls between subscribers.
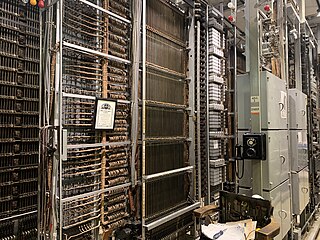
The Panel Machine Switching System is a type of automatic telephone exchange for urban service that was used in the Bell System in the United States for seven decades. The first semi-mechanical types of this design were installed in 1915 in Newark, New Jersey, and the last were retired in the same city in 1983.
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).