
Ski jumping is a winter sport in which competitors aim to achieve the farthest jump after sliding down on their skis from a specially designed curved ramp. Along with jump length, competitor's aerial style and other factors also affect the final score. Ski jumping was first contested in Norway in the late 19th century, and later spread through Europe and North America in the early 20th century. Along with cross-country skiing, it constitutes the traditional group of Nordic skiing disciplines.

Holmenkollbakken is a large ski jumping hill located at Holmenkollen in Oslo, Norway. It has a hill size of HS134, a construction point of K-120, and a capacity for 70,000 spectators. Holmenkollen has hosted the Holmenkollen Ski Festival since 1892, which since 1980 have been part of the FIS Ski Jumping World Cup and 1983 the FIS Nordic Combined World Cup. It has also hosted the 1952 Winter Olympics and the FIS Nordic World Ski Championships in 1930, 1966, 1982 and 2011.

Ski flying is a winter sport discipline derived from ski jumping, in which much greater distances can be achieved. It is a form of competitive individual Nordic skiing where athletes descend at high speed along a specially designed takeoff ramp using skis only; jump from the end of it with as much power as they can generate; then glide – or 'fly' – as far as possible down a steeply sloped hill; and ultimately land within a target zone in a stable manner. Points are awarded for distance and stylistic merit by five judges. Events are governed by the International Ski Federation.
Ski jumping has been included in the program of every Winter Olympic Games. From 1924 through to 1956, the competition involved jumping from one hill whose length varied from each edition of the games to the next.

Daniela Iraschko-Stolz is an Austrian former ski jumper and footballer.

The Pine Mountain Ski Jump is a ski jump located in Iron Mountain, Michigan, Dickinson County. It is part of the Kiwanis Ski Club and hosts annual FIS Ski Jumping Continental Cup competitions. "Pine Mountain Slide is known throughout the world as one of the better jumping hills." Annually in February, it "hosts jumpers from around the world at the best tournament in the United States." Top-rated foreign jumpers compete. Currently Pine Mountain holds the U.S. records for the longest jump in World Cup competition at 140m, as well as the overall distance record at 144m (472.44feet). The facility also includes two smaller ski jumping hills that are built into the hill northwest of the large hill. Attendance is about 20,000 ski jumping fans year around.

Vikersundbakken or Vikersund Hill is a ski flying hill at Vikersund in Modum, Norway. It is one of the two largest purpose-built ski flying hills in the world. Nine world records have been set there, including the current record of 253.5 meters, set by Stefan Kraft. The complex consists of a large hill, a normal hill and several training hills.

The Hochfirst Ski Jump is a ski jumping hill located in Titisee-Neustadt in the state of Baden-Württemberg in Germany. The ski jump is named after the mountain Hochfirst in the Black Forest. It is the biggest natural ski jumping hill. This means that in contrast to many other ski jumping facilities, rather than an artificial tower, the natural gradient of the mountain slope was used for construction.

Mühlenkopfschanze is the largest ski jumping hill in the world located in Willingen (Hessen), Germany with a K-point of 130 metres (430 ft) and Hill size of 147 metres (482 ft).
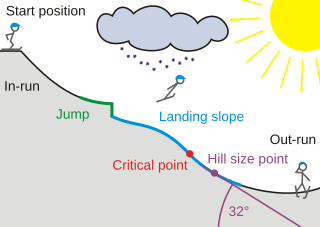
A ski jumping hill is a sports venue used for ski jumping. They vary in size from temporary handmade snow structures to permanent competition venues. At the top is an in-run where the jumper runs down to generate sufficient speed, before reaching the jump. The skier is then airborne until landing on the landing slope. The last part of the hill is the out-run, which may be either flat or even uphill, allowing the jumper to stop. The steepest point of the hill is the construction point, which is used to determine the score of a particular length. The size of a hill is measured in the hill size. Hills with a hill size exceeding HS185 are designated ski flying hills; there are five such hills in the world.

Kamil Wiktor Stoch is a Polish ski jumper. He is one of the most successful ski jumpers in the history of the sport, having won two World Cup titles, three Four Hills Tournaments, three individual gold medals at the Winter Olympics, individual and team gold at the Ski Jumping World Championships, and individual silver at the Ski Flying World Championships. His other tournament wins include Raw Air (twice), the Willingen Five, and Planica7.

Piotr Paweł Żyła is a Polish ski jumper. He is a member of the national team and competed at the 2014 Winter Olympics in Sochi. He is the 2021 and 2023 World Champion on the normal hill, a bronze medalist of 2017 World Championships in individual large hill event, 2017 World Champion and a two-time World Championship bronze medalist and in the team large hill event, also the two time Ski Flying World Championships bronze medalist in team.

Kulm is a ski flying hill located in Tauplitz/Bad Mitterndorf, Styria, Austria opened in 1950.

Trampolino Olimpico Italia is a ski jumping hill (K90), built in 1955 in Cortina d'Ampezzo, Italy. It was the site of the ski jumping, Nordic combined (K90/15.0) and team events for the 1956 Winter Olympics. The Nordic combined event used a shorter in-run to allow average jumps between 60 and 70 meters while the upper starting points on the in-run were calculated to allow jumps of 70 to 80 meters. The 1956 profile had a safety limit of 14.5 m beyond the critical point of 72 m.. Among many national and international competitions starting with the 1927 World Championships, was the inauguration of the FIS Ski Jumping World Cup in 1979. Since the venue lost its FIS-certification in 1990, the installation lies dormant. In its day, the Cortina Ski Jumping hill was regarded as one of the most innovative and still today as one of the most architecturally beautiful examples still in existence. The stadium holds a maximum of 40,000 spectators in the arena and an additional 10.000 in the stands on each side of the hill.
The men's normal hill individual ski jumping competition for the 2010 Winter Olympics in Vancouver, Canada was held on 12 and 13 February 2010 at Whistler Olympic Park in Whistler, British Columbia. It was the first medal event of the 2010 Games.

The hill size (HS) is the most important measurement for the size of a ski jumping hill. It is defined as the distance between the takeoff table and the end of the landing area, which is called hill size point. It is not measured as a straight line but on the surface of the hill. A typical slope inclination at hill size distance is 32° for normal hills, 31° for large hills, and 28° for ski flying hills.

The Tremplin du Praz is a ski jumping hill at Le Praz in Courchevel, France. The complex consists of four hills: a large hill with construction point of K125 (HS132), a normal hill at K90 (HS96), and two training hills at K60 and K25. The complex also has a cross-country skiing stadium used for Nordic combined. Jörg Ritzerfeld holds the large hill winter record of 134.0 metres and Nicolas Mayer the normal hill record of 100.5 metres.

Igman Olympic Jumps, also known as Malo Polje, is a defunct ski jumping hill on the mountain of Igman in Ilidža, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina. It consists of a large hill with a construction point (K-point) of 112 meters (367 ft) and a normal hill with a K-point of 90 meters (295 ft). Construction started in 1980 and the venue opened in 1982 to host ski jumping and Nordic combined at the 1984 Winter Olympics. The large hill event saw Finland's Matti Nykänen set the hill record of 116.0 meters (381 ft) in front of 90,000 spectators. No other International Ski Federation (FIS) sanctioned competitions have taken place at the hills. During the Siege of Sarajevo, the hills became a battleground and have since not been used. However, there are plans to rebuild the in-run, expand the large hill and build new spectator stands and visitor facilities.
The FIS Race (ski jumping) is the oldest series of ski jumping competitions arranged yearly by the International Ski Federation. It is considered the fourth level of international ski jumping, ranking below the World Cup, Continental Cup and FIS Cup. Most of the events are held on normal hills and large hills, with a construction point of 90 meters. All top level and other international events before the World Cup was founded were part of FIS (race) competitions.

















