Related Research Articles
Biostatistics is a branch of statistics that applies statistical methods to a wide range of topics in biology. It encompasses the design of biological experiments, the collection and analysis of data from those experiments and the interpretation of the results.

In statistics, cluster sampling is a sampling plan used when mutually homogeneous yet internally heterogeneous groupings are evident in a statistical population. It is often used in marketing research.

Research is "creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization, and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion of past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole.

Statistics is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments.
In statistics, survey sampling describes the process of selecting a sample of elements from a target population to conduct a survey. The term "survey" may refer to many different types or techniques of observation. In survey sampling it most often involves a questionnaire used to measure the characteristics and/or attitudes of people. Different ways of contacting members of a sample once they have been selected is the subject of survey data collection. The purpose of sampling is to reduce the cost and/or the amount of work that it would take to survey the entire target population. A survey that measures the entire target population is called a census. A sample refers to a group or section of a population from which information is to be obtained.
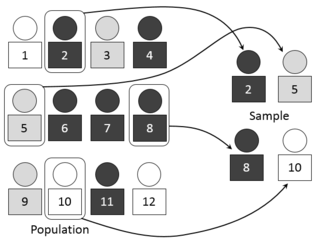
In statistics, quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is the selection of a subset or a statistical sample of individuals from within a statistical population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. The subset is meant to reflect the whole population and statisticians attempt to collect samples that are representative of the population. Sampling has lower costs and faster data collection compared to recording data from the entire population, and thus, it can provide insights in cases where it is infeasible to measure an entire population.
Statistical bias, in the mathematical field of statistics, is a systematic tendency in which the methods used to gather data and generate statistics present an inaccurate, skewed or biased depiction of reality. Statistical bias exists in numerous stages of the data collection and analysis process, including: the source of the data, the methods used to collect the data, the estimator chosen, and the methods used to analyze the data. Data analysts can take various measures at each stage of the process to reduce the impact of statistical bias in their work. Understanding the source of statistical bias can help to assess whether the observed results are close to actuality. Issues of statistical bias has been argued to be closely linked to issues of statistical validity.

A focus group is a group interview involving a small number of demographically similar participants. Their reactions to specific researcher/evaluator-posed questions are studied. Focus groups are used in market research to understand better people's reactions to products or services or participants' perceptions of shared experiences. The discussions can be guided or open. In market research, focus groups can explore a group's response to a new product or service. As a program evaluation tool, they can elicit lessons learned and recommendations for performance improvement. The idea is for the researcher to understand participants' reactions. If group members are representative of a larger population, those reactions may be expected to reflect the views of that larger population. Thus, focus groups constitute a research or evaluation method that researchers organize to collect qualitative data through interactive and directed discussions.
Sampling is the use of a subset of the population to represent the whole population or to inform about (social) processes that are meaningful beyond the particular cases, individuals or sites studied. Probability sampling, or random sampling, is a sampling technique in which the probability of getting any particular sample may be calculated. In cases where external validity is not of critical importance to the study's goals or purpose, researchers might prefer to use nonprobability sampling. Nonprobability sampling does not meet this criterion. Nonprobability sampling techniques are not intended to be used to infer from the sample to the general population in statistical terms. Instead, for example, grounded theory can be produced through iterative nonprobability sampling until theoretical saturation is reached.
Survey methodology is "the study of survey methods". As a field of applied statistics concentrating on human-research surveys, survey methodology studies the sampling of individual units from a population and associated techniques of survey data collection, such as questionnaire construction and methods for improving the number and accuracy of responses to surveys. Survey methodology targets instruments or procedures that ask one or more questions that may or may not be answered.
Qualitative marketing research involves a natural or observational examination of the philosophies that govern consumer behavior. The direction and framework of the research is often revised as new information is gained, allowing the researcher to evaluate issues and subjects in an in-depth manner. The quality of the research produced is heavily dependent on the skills of the researcher and is influenced by researcher bias.

Qualitative research is a type of research that aims to gather and analyse non-numerical (descriptive) data in order to gain an understanding of individuals' social reality, including understanding their attitudes, beliefs, and motivation. This type of research typically involves in-depth interviews, focus groups, or observations in order to collect data that is rich in detail and context. Qualitative research is often used to explore complex phenomena or to gain insight into people's experiences and perspectives on a particular topic. It is particularly useful when researchers want to understand the meaning that people attach to their experiences or when they want to uncover the underlying reasons for people's behavior. Qualitative methods include ethnography, grounded theory, discourse analysis, and interpretative phenomenological analysis. Qualitative research methods have been used in sociology, anthropology, political science, psychology, communication studies, social work, folklore, educational research, information science and software engineering research.

Quantitative research is a research strategy that focuses on quantifying the collection and analysis of data. It is formed from a deductive approach where emphasis is placed on the testing of theory, shaped by empiricist and positivist philosophies.

In its most common sense, methodology is the study of research methods. However, the term can also refer to the methods themselves or to the philosophical discussion of associated background assumptions. A method is a structured procedure for bringing about a certain goal, like acquiring knowledge or verifying knowledge claims. This normally involves various steps, like choosing a sample, collecting data from this sample, and interpreting the data. The study of methods concerns a detailed description and analysis of these processes. It includes evaluative aspects by comparing different methods. This way, it is assessed what advantages and disadvantages they have and for what research goals they may be used. These descriptions and evaluations depend on philosophical background assumptions. Examples are how to conceptualize the studied phenomena and what constitutes evidence for or against them. When understood in the widest sense, methodology also includes the discussion of these more abstract issues.
In sociology and statistics research, snowball sampling is a nonprobability sampling technique where existing study subjects recruit future subjects from among their acquaintances. Thus the sample group is said to grow like a rolling snowball. As the sample builds up, enough data are gathered to be useful for research. This sampling technique is often used in hidden populations, such as drug users or sex workers, which are difficult for researchers to access. As sample members are not selected from a sampling frame, snowball samples are subject to numerous biases. For example, people who have many friends are more likely to be recruited into the sample. When virtual social networks are used, then this technique is called virtual snowball sampling.
Sample size determination or estimation is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences about a population from a sample. In practice, the sample size used in a study is usually determined based on the cost, time, or convenience of collecting the data, and the need for it to offer sufficient statistical power. In complex studies, different sample sizes may be allocated, such as in stratified surveys or experimental designs with multiple treatment groups. In a census, data is sought for an entire population, hence the intended sample size is equal to the population. In experimental design, where a study may be divided into different treatment groups, there may be different sample sizes for each group.

Research design refers to the overall strategy utilized to answer research questions. A research design typically outlines the theories and models underlying a project; the research question(s) of a project; a strategy for gathering data and information; and a strategy for producing answers from the data. A strong research design yields valid answers to research questions while weak designs yield unreliable, imprecise or irrelevant answers.
Bootstrapping is any test or metric that uses random sampling with replacement, and falls under the broader class of resampling methods. Bootstrapping assigns measures of accuracy to sample estimates. This technique allows estimation of the sampling distribution of almost any statistic using random sampling methods.
With the application of probability sampling in the 1930s, surveys became a standard tool for empirical research in social sciences, marketing, and official statistics. The methods involved in survey data collection are any of a number of ways in which data can be collected for a statistical survey. These are methods that are used to collect information from a sample of individuals in a systematic way. First there was the change from traditional paper-and-pencil interviewing (PAPI) to computer-assisted interviewing (CAI). Now, face-to-face surveys (CAPI), telephone surveys (CATI), and mail surveys are increasingly replaced by web surveys. In addition, remote interviewers could possibly keep the respondent engaged while reducing cost as compared to in-person interviewers.
Thematic analysis is one of the most common forms of analysis within qualitative research. It emphasizes identifying, analysing and interpreting patterns of meaning within qualitative data. Thematic analysis is often understood as a method or technique in contrast to most other qualitative analytic approaches – such as grounded theory, discourse analysis, narrative analysis and interpretative phenomenological analysis – which can be described as methodologies or theoretically informed frameworks for research. Thematic analysis is best thought of as an umbrella term for a variety of different approaches, rather than a singular method. Different versions of thematic analysis are underpinned by different philosophical and conceptual assumptions and are divergent in terms of procedure. Leading thematic analysis proponents, psychologists Virginia Braun and Victoria Clarke distinguish between three main types of thematic analysis: coding reliability approaches, code book approaches and reflexive approaches. They describe their own widely used approach first outlined in 2006 in the journal Qualitative Research in Psychology as reflexive thematic analysis. Their 2006 paper has over 120,000 Google Scholar citations and according to Google Scholar is the most cited academic paper published in 2006. The popularity of this paper exemplifies the growing interest in thematic analysis as a distinct method.
References
- 1 2 Government of Canada, Statistics Canada (2021-09-02). "3.2.3 Non-probability sampling". www150.statcan.gc.ca. Retrieved 2024-03-29.
- ↑ Henry, Gary T. (1990). Practical sampling ([10. Nachdr.] ed.). Newbury Park: Sage Publications. ISBN 978-0803929586.
- ↑ Wright, Julius Sim, Chris (2002). Research in health care : concepts, designs and methods (Reprinted. ed.). Cheltenham: N. Thornes. ISBN 978-0748737185.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Given, Lisa M., ed. (2008). The Sage encyclopedia of qualitative research methods. Los Angeles, Calif.: Sage Publications. ISBN 978-1-4129-4163-1.
- ↑ Given, Lisa (2008). "Convenience Sample". The SAGE Encyclopedia of Qualitative Research Methods. SAGE Publications. doi:10.4135/9781412963909.n68. ISBN 9781412941631.
- ↑ Christensen, Burke Johnson, Larry (2012). Educational research : quantitative, qualitative, and mixed approaches (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks, Calif.: SAGE Publications. ISBN 978-1-4129-7828-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Palinkas, Lawrence A.; Horwitz, Sarah M.; Green, Carla A.; Wisdom, Jennifer P.; Duan, Naihua; Hoagwood, Kimberly (6 November 2013). "Purposeful Sampling for Qualitative Data Collection and Analysis in Mixed Method Implementation Research". Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research. 42 (5): 533–544. doi:10.1007/s10488-013-0528-y. PMC 4012002 . PMID 24193818.
- ↑ Teddlie, Charles; Yu, Fen (January 2007). "Mixed Methods Sampling". Journal of Mixed Methods Research. 1 (1): 77–100. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.609.692 . doi:10.1177/2345678906292430. S2CID 220286890.
- ↑ Bornstein, Marc H.; Jager, Justin; Putnick, Diane L. (28 April 2017). "Sampling in Developmental Science: Situations, Shortcomings, Solutions, and Standards". Developmental Review. 33 (4): 357–370. doi:10.1016/j.dr.2013.08.003. ISSN 0273-2297. PMC 4286359 . PMID 25580049.
- ↑ Bornstein, Marc H.; Jager, Justin; Putnick, Diane L. (28 April 2017). "Sampling in Developmental Science: Situations, Shortcomings, Solutions, and Standards". Developmental Review. 33 (4): 357–370. doi:10.1016/j.dr.2013.08.003. ISSN 0273-2297. PMC 4286359 . PMID 25580049.
- ↑ "Statistics - Sampling, Surveys, Methods | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 2024-03-29.