
The American Convention on Human Rights, also known as the Pact of San José, is an international human rights instrument. It was adopted by many countries in the Western Hemisphere in San José, Costa Rica, on 22 November 1969. It came into force after the eleventh instrument of ratification was deposited on 18 July 1978.
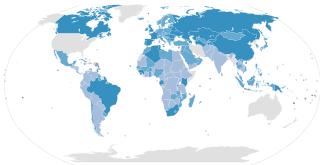
The ILO Convention Concerning Minimum Age for Admission to Employment C138, is a convention adopted in 1973 by the International Labour Organization. It requires ratifying states to pursue a national policy designed to ensure the effective abolition of child labour and to raise progressively the minimum age for admission to employment or work. It is one of eight ILO fundamental conventions. Convention C138 replaces several similar ILO conventions in specific fields of labour.
The Valletta Treaty is a multilateral treaty of the Council of Europe. The 1992 treaty aims to protect the European archaeological heritage "as a source of European collective memory and as an instrument for historical and scientific study". All remains and objects and any other traces of humankind from past times are considered to be elements of the archaeological heritage. The archaeological heritage shall include structures, constructions, groups of buildings, developed sites, moveable objects, monuments of other kinds as well as their context, whether situated on land or under water."
Hours of Work (Industry) Convention, 1919 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Unemployment Convention, 1919 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Placing of Seamen Convention, 1920 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Hours of Work Convention, 1930 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
The Convention concerning Hours of Work on Board Ship and Manning or Hours of Work and Manning (Sea) Convention, 1936 is an International Labour Organization Convention which never entered into force. It was established in 1936, and closed for ratification on 24 February 2002, when the 1996 Convention concerning Seafarers' Hours of Work and the Manning of Ships entered into force.
The Convention concerning Wages, Hours of Work on Board Ship and Manning is a convention of the International Labour Organization originally drafted in 1946 and revised conventions in 1949 and 1958, none of which entered into force.
Safety Provisions (Building) Convention, 1937 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Labour Clauses Convention, 1949 is an International Labour Organization (ILO) Convention adopted in Geneva on 29 June 1949. Its preamble states:
Having decided upon the adoption of certain proposals concerning labour clauses in public contracts ....
The Protection of Wages Convention, 1949 is an International Labour Organization (ILO) Convention.
Holidays with Pay (Agriculture) Convention, 1952 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Labour Statistics Convention, 1985 is an International Labour Organization Convention.
Seafarers' Hours of Work and the Manning of Ships Convention, 1996 is an International Labour Organization Convention.

The Maritime Labour Convention (MLC) is an International Labour Organization convention, number 186, established in 2006 as the fourth pillar of international maritime law and embodies "all up-to-date standards of existing international maritime labour Conventions and Recommendations, as well as the fundamental principles to be found in other international labour Conventions". The other "pillars are the SOLAS, STCW and MARPOL. The treaties applies to all ships entering the harbours of parties to the treaty, as well as to all ships flying the flag of state party.
The Conventions concerning Employment of Women during the Night are conventions drafted by the International Labour Organization (ILO) which prohibit women from performing industrial work during the night. The first convention was adopted in 1919 and revised versions were adopted in 1934 and 1948. A protocol to the convention was adopted in 1990 allowing for easing of the restriction under conditions. As of April 2011 the conventions had 27, 15, 46 (undenounced) ratifications respectively. The protocol was ratified 5 and denounced by 2.
The International Convention Concerning the Use of Broadcasting in the Cause of Peace is a 1936 League of Nations treaty whereby states agreed to prohibit the use of broadcasting for propaganda or the spreading of false news. It was the first international treaty to bind states to "restrict expression which constituted a threat to international peace and security".

European Convention for the Protection of Animals during International Transport refers to two animal welfare treaties regarding livestock transportation of the Council of Europe:
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.



