Coppa Nevigata is an archaeological site in the province of Foggia, southern Italy, southwest of Manfredonia, on the Apulian coast of the Gargano peninsula.
The earliest human presence on the site, which was situated on the edge of a coastal lagoon, with easy access to the sea and numerous natural resources, dates back to the Neolithic, between the 7th and 5th millennia BC. At a later date, a settlement of the final Neolithic period continued into the Bronze Age; occupation at the site is attested for the Protoapennine, Apennine, and Subapennine phases of the Italian Bronze Age.
During the Bronze Age, a significant settlement arose that had contacts with the civilizations of the Aegean; these contacts are most visible during the Subapennine phase, when fragments of Mycenaean ceramics are found at the site. From the beginning of the Protoapennine phase, there is evidence for the extraction of purple dye from murex shells and for pressing of olives to extract olive oil. The purple dye production, starting around 1800 BC, is the earliest yet attested in Italy. This dye production increased through the 14th century BC, but sharply dropped off by the 12th century in the Subapennine phase. Some areas near the fortifications and on the shore of the lagoon were dedicated both to the processing and storage of cereals and to the extraction of purple dye; these activities were later moved within the settlement. The site was defended by dry stone fortification walls.
The site is currently under periodic excavation by a team from Sapienza University of Rome, under the direction of Alberto Cazzella.

Tyrian purple, also known as, royal purple, imperial purple, or imperial dye, is a reddish-purple natural dye. The name Tyrian refers to Tyre, Lebanon. It is secreted by several species of predatory sea snails in the family Muricidae, rock snails originally known by the name 'Murex'. In ancient times, extracting this dye involved tens of thousands of snails and substantial labor, and as a result, the dye was highly valued. The colored compound is 6,6′-dibromoindigo.
The Apennine culture is a technology complex in central and southern Italy from the Italian Middle Bronze Age. In the mid-20th century the Apennine was divided into Proto-, Early, Middle and Late sub- phases, but now archaeologists prefer to consider as "Apennine" only the ornamental pottery style of the later phase of Middle Bronze Age (BM3). This phase is preceded by the Grotta Nuova facies and by the Protoapennine B facies and succeeded by the Subapennine facies of 13th-century. Apennine pottery is a burnished ware incised with spirals, meanders and geometrical zones, filled with dots or transverse dashes. It has been found on Ischia island in association with LHII and LHIII pottery and on Lipari in association with LHIIIA pottery, which associations date it to the Late Bronze Age as it is defined in Greece and the Aegean.
The Garfagnana is a historical and geographical region of central Italy, today part of the province of Lucca, in Tuscany. It is the upper valley or basin of the river Serchio, and thus lies between the main ridge of the Northern Apennines to the north-east and the Alpi Apuane to the west. The principal towns are Castelnuovo di Garfagnana and Barga.

Ranuccio Bianchi Bandinelli was an Italian archaeologist and art historian.
Clementina Panella is an Italian archaeologist, a professor at the University of Rome La Sapienza, where she teaches Methodology of Archaeology. She has guided and co-written a number of articles on the commercial pottery of ancient Italy.

Cottanello is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Rieti in the Italian region of Latium, located about 60 kilometres (37 mi) north of Rome and about 15 kilometres (9 mi) west of Rieti.
Canicattini Bagni is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Syracuse, Sicily (Italy), located about 190 kilometres (120 mi) southeast of Palermo and about 20 kilometres (12 mi) southwest of Syracuse. As of 31 December 2004, it had a population of 7,415 and an area of 15.1 square kilometres (5.8 sq mi).

The prehistory of Italy began in the Paleolithic period, when species of Homo colonized the Italian territory for the first time, and ended in the Iron Age, when the first written records appeared in Italy.

The rock drawings in Valcamonica are located in the Province of Brescia, Italy, and constitute the largest collections of prehistoric petroglyphs in the world. The collection was recognized by UNESCO in 1979 and was Italy's first recognized World Heritage Site. UNESCO has formally recognized more than 140,000 figures and symbols, but new discoveries have increased the number of catalogued incisions to between 200,000 and 300,000. The petroglyphs are spread on all surfaces of the valley, but concentrated in the areas of Darfo Boario Terme, Capo di Ponte, Nadro, Cimbergo and Paspardo.

Akrai was a Greek colony of Magna Graecia founded in Sicily by the Syracusans in 663 BC. It was located near the modern Palazzolo Acreide.

The Nuragic civilization, also known as the Nuragic culture, was a civilization or culture on the Mediterranean island of Sardinia, Italy, which lasted from the 18th century BC up to the Roman colonization in 238 BC. Others date the culture as lasting at least until the 2nd century AD and in some areas, namely the Barbagia, to the 6th century AD or possibly even to the 11th century AD.

The Giants of Mont'e Prama are ancient stone sculptures created by the Nuragic civilization of Sardinia, Italy. Fragmented into numerous pieces, they were discovered in March 1974 on farmland near Mont'e Prama, in the comune of Cabras, province of Oristano, in central-western Sardinia. The statues are carved in local sandstone and their height varies between 2 and 2.5 meters.

Roca is an archaeological site located on the Adriatic coast of Apulia in Southern Italy, a few kilometres from the modern town of Melendugno and close to the city of Lecce. The site, which has been explored since the end of the 1980s by a team of the University of Salento, has produced some of the best-preserved monumental architecture of the Bronze Age in Southern Italy, along with the largest set of Mycenaean pottery ever recovered west of mainland Greece.
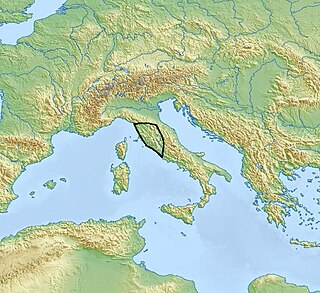
The Rinaldone culture was an Eneolithic culture that spread between the 4th and the 3rd millennium BC in northern and central Lazio, in southern Tuscany and, to a lesser extent, also in Marche and Umbria. It takes its name from the town of Rinaldone, near Montefiascone in the province of Viterbo, northern Lazio.
The Laterza culture or Laterza-Cellino San Marco culture is an Eneolithic culture in Southern Italy. It takes its name from the tombs discovered in the locality of Laterza, near Taranto, and Cellino San Marco, near Brindisi, in Apulia. It developed in Apulia and Basilicata, and to a lesser extent of Central Italy in the 3rd millennium BC, around 2950-2350 BC. As with many of the cultures of the late prehistoric period, it is known essentially from the style of pottery recovered from archaeological digs. The culture was defined in 1967 by Francesco Biancofiore, following research in a necropolis of the same name situated to the north-west of the city of Taranto, in southern Apulia.

The Pre-Nuragic period refers to the prehistory of Sardinia from the Paleolithic until the middle Bronze Age, when the Nuragic civilization flourished on the island.

The Roman furnaces in Alcamo are part of the archaeological complex of Alcamo Marina and were discovered in 2000.

The nuraghe Genna Maria is an archaeological site in the comune of Villanovaforru, province of South Sardinia.

Maria Floriani Squarciapino (1917-2003) was an Italian classical archaeologist and professor at La Sapienza University in Rome, known for her work on the Roman port city of Ostia.














