
A DNA microarray is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface. Scientists use DNA microarrays to measure the expression levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously or to genotype multiple regions of a genome. Each DNA spot contains picomoles of a specific DNA sequence, known as probes. These can be a short section of a gene or other DNA element that are used to hybridize a cDNA or cRNA sample under high-stringency conditions. Probe-target hybridization is usually detected and quantified by detection of fluorophore-, silver-, or chemiluminescence-labeled targets to determine relative abundance of nucleic acid sequences in the target. The original nucleic acid arrays were macro arrays approximately 9 cm × 12 cm and the first computerized image based analysis was published in 1981. It was invented by Patrick O. Brown. An example of its application is in SNPs arrays for polymorphisms in cardiovascular diseases, cancer, pathogens and GWAS analysis. It is also used for the identification of structural variations and the measurement of gene expression.
Comparative genomic hybridization(CGH) is a molecular cytogenetic method for analysing copy number variations (CNVs) relative to ploidy level in the DNA of a test sample compared to a reference sample, without the need for culturing cells. The aim of this technique is to quickly and efficiently compare two genomic DNA samples arising from two sources, which are most often closely related, because it is suspected that they contain differences in terms of either gains or losses of either whole chromosomes or subchromosomal regions (a portion of a whole chromosome). This technique was originally developed for the evaluation of the differences between the chromosomal complements of solid tumor and normal tissue, and has an improved resolution of 5–10 megabases compared to the more traditional cytogenetic analysis techniques of giemsa banding and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) which are limited by the resolution of the microscope utilized.

Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is a molecular cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to only particular parts of a nucleic acid sequence with a high degree of sequence complementarity. It was developed by biomedical researchers in the early 1980s to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. Fluorescence microscopy can be used to find out where the fluorescent probe is bound to the chromosomes. FISH is often used for finding specific features in DNA for use in genetic counseling, medicine, and species identification. FISH can also be used to detect and localize specific RNA targets in cells, circulating tumor cells, and tissue samples. In this context, it can help define the spatial-temporal patterns of gene expression within cells and tissues.

Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) is a type of genetic abnormality in diploid organisms in which one copy of an entire gene and its surrounding chromosomal region are lost. Since diploid cells have two copies of their genes, one from each parent, a single copy of the lost gene still remains when this happens, but any heterozygosity is no longer present.

Copy number variation (CNV) is a phenomenon in which sections of the genome are repeated and the number of repeats in the genome varies between individuals. Copy number variation is a type of structural variation: specifically, it is a type of duplication or deletion event that affects a considerable number of base pairs. Approximately two-thirds of the entire human genome may be composed of repeats and 4.8–9.5% of the human genome can be classified as copy number variations. In mammals, copy number variations play an important role in generating necessary variation in the population as well as disease phenotype.
In molecular biology, SNP array is a type of DNA microarray which is used to detect polymorphisms within a population. A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), a variation at a single site in DNA, is the most frequent type of variation in the genome. Around 335 million SNPs have been identified in the human genome, 15 million of which are present at frequencies of 1% or higher across different populations worldwide.

Microarray analysis techniques are used in interpreting the data generated from experiments on DNA, RNA, and protein microarrays, which allow researchers to investigate the expression state of a large number of genes - in many cases, an organism's entire genome - in a single experiment. Such experiments can generate very large amounts of data, allowing researchers to assess the overall state of a cell or organism. Data in such large quantities is difficult - if not impossible - to analyze without the help of computer programs.

Molecular cytogenetics combines two disciplines, molecular biology and cytogenetics, and involves the analysis of chromosome structure to help distinguish normal and cancer-causing cells. Human cytogenetics began in 1956 when it was discovered that normal human cells contain 46 chromosomes. However, the first microscopic observations of chromosomes were reported by Arnold, Flemming, and Hansemann in the late 1800s. Their work was ignored for decades until the actual chromosome number in humans was discovered as 46. In 1879, Arnold examined sarcoma and carcinoma cells having very large nuclei. Today, the study of molecular cytogenetics can be useful in diagnosing and treating various malignancies such as hematological malignancies, brain tumors, and other precursors of cancer. The field is overall focused on studying the evolution of chromosomes, more specifically the number, structure, function, and origin of chromosome abnormalities. It includes a series of techniques referred to as fluorescence in situ hybridization, or FISH, in which DNA probes are labeled with different colored fluorescent tags to visualize one or more specific regions of the genome. Introduced in the 1980s, FISH uses probes with complementary base sequences to locate the presence or absence of the specific DNA regions. FISH can either be performed as a direct approach to metaphase chromosomes or interphase nuclei. Alternatively, an indirect approach can be taken in which the entire genome can be assessed for copy number changes using virtual karyotyping. Virtual karyotypes are generated from arrays made of thousands to millions of probes, and computational tools are used to recreate the genome in silico.
SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles. SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase of interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.
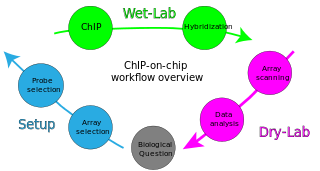
ChIP-on-chip is a technology that combines chromatin immunoprecipitation ('ChIP') with DNA microarray ("chip"). Like regular ChIP, ChIP-on-chip is used to investigate interactions between proteins and DNA in vivo. Specifically, it allows the identification of the cistrome, the sum of binding sites, for DNA-binding proteins on a genome-wide basis. Whole-genome analysis can be performed to determine the locations of binding sites for almost any protein of interest. As the name of the technique suggests, such proteins are generally those operating in the context of chromatin. The most prominent representatives of this class are transcription factors, replication-related proteins, like origin recognition complex protein (ORC), histones, their variants, and histone modifications.

Tiling arrays are a subtype of microarray chips. Like traditional microarrays, they function by hybridizing labeled DNA or RNA target molecules to probes fixed onto a solid surface.
The Illumina Methylation Assay using the Infinium I platform uses 'BeadChip' technology to generate a comprehensive genome-wide profiling of human DNA methylation. Similar to bisulfite sequencing and pyrosequencing, this method quantifies methylation levels at various loci within the genome. This assay is used for methylation probes on the Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation27 BeadChip. Probes on the 27k array target regions of the human genome to measure methylation levels at 27,578 CpG dinucleotides in 14,495 genes. The Infinium HumanMethylation450 BeadChip array targets > 450,000 methylation sites. In 2016, the Infinium MethylationEPIC BeadChip was released, which interrogates over 850,000 methylation sites across the human genome.
Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation is a large-scale purification technique in molecular biology that is used to enrich for methylated DNA sequences. It consists of isolating methylated DNA fragments via an antibody raised against 5-methylcytosine (5mC). This technique was first described by Weber M. et al. in 2005 and has helped pave the way for viable methylome-level assessment efforts, as the purified fraction of methylated DNA can be input to high-throughput DNA detection methods such as high-resolution DNA microarrays (MeDIP-chip) or next-generation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). Nonetheless, understanding of the methylome remains rudimentary; its study is complicated by the fact that, like other epigenetic properties, patterns vary from cell-type to cell-type.
Virtual karyotype is the digital information reflecting a karyotype, resulting from the analysis of short sequences of DNA from specific loci all over the genome, which are isolated and enumerated. It detects genomic copy number variations at a higher resolution for level than conventional karyotyping or chromosome-based comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). The main methods used for creating virtual karyotypes are array-comparative genomic hybridization and SNP arrays.
Diversity Arrays Technology (DArT) is a high-throughput genetic marker technique that can detect allelic variations to provides comprehensive genome coverage without any DNA sequence information for genotyping and other genetic analysis. The general steps involve reducing the complexity of the genomic DNA with specific restriction enzymes, choosing diverse fragments to serve as representations for the parent genomes, amplify via polymerase chain reaction (PCR), insert fragments into a vector to be placed as probes within a microarray, then fluorescent targets from a reference sequence will be allowed to hybridize with probes and put through an imaging system. The objective is to identify and quantify various forms of DNA polymorphism within genomic DNA of sampled species.
Molecular Inversion Probe (MIP) belongs to the class of Capture by Circularization molecular techniques for performing genomic partitioning, a process through which one captures and enriches specific regions of the genome. Probes used in this technique are single stranded DNA molecules and, similar to other genomic partitioning techniques, contain sequences that are complementary to the target in the genome; these probes hybridize to and capture the genomic target. MIP stands unique from other genomic partitioning strategies in that MIP probes share the common design of two genomic target complementary segments separated by a linker region. With this design, when the probe hybridizes to the target, it undergoes an inversion in configuration and circularizes. Specifically, the two target complementary regions at the 5’ and 3’ ends of the probe become adjacent to one another while the internal linker region forms a free hanging loop. The technology has been used extensively in the HapMap project for large-scale SNP genotyping as well as for studying gene copy alterations and characteristics of specific genomic loci to identify biomarkers for different diseases such as cancer. Key strengths of the MIP technology include its high specificity to the target and its scalability for high-throughput, multiplexed analyses where tens of thousands of genomic loci are assayed simultaneously.

Exome sequencing, also known as whole exome sequencing (WES), is a genomic technique for sequencing all of the protein-coding regions of genes in a genome. It consists of two steps: the first step is to select only the subset of DNA that encodes proteins. These regions are known as exons—humans have about 180,000 exons, constituting about 1% of the human genome, or approximately 30 million base pairs. The second step is to sequence the exonic DNA using any high-throughput DNA sequencing technology.
DECIPHER is a web-based resource and database of genomic variation data from analysis of patient DNA. It documents submicroscopic chromosome abnormalities and pathogenic sequence variants, from over 25000 patients and maps them to the human genome using Ensembl or UCSC Genome Browser. In addition it catalogues the clinical characteristics from each patient and maintains a database of microdeletion/duplication syndromes, together with links to relevant scientific reports and support groups.
FlexGen was a biotechnology company based in Leiden, Netherlands. FlexGen was a spin-off from Leiden University Medical Centre and Dutch Space and had proprietary technologies for laser based in-situ synthesis of oligonucleotides and other biomolecules. On 21 December 2015, Flexgen Bv in Leiden was declared bankrupt by the court in Gelderland Source.
The Cancer Genome Anatomy Project (CGAP), created by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) in 1997 and introduced by Al Gore, is an online database on normal, pre-cancerous and cancerous genomes. It also provides tools for viewing and analysis of the data, allowing for identification of genes involved in various aspects of tumor progression. The goal of CGAP is to characterize cancer at a molecular level by providing a platform with readily accessible updated data and a set of tools such that researchers can easily relate their findings to existing knowledge. There is also a focus on development of software tools that improve the usage of large and complex datasets. The project is directed by Daniela S. Gerhard, and includes sub-projects or initiatives, with notable ones including the Cancer Chromosome Aberration Project (CCAP) and the Genetic Annotation Initiative (GAI). CGAP contributes to many databases and organisations such as the NCBI contribute to CGAP's databases.









