Internet Small Computer Systems Interface or iSCSI is an Internet Protocol-based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities. iSCSI provides block-level access to storage devices by carrying SCSI commands over a TCP/IP network. iSCSI facilitates data transfers over intranets and to manage storage over long distances. It can be used to transmit data over local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), or the Internet and can enable location-independent data storage and retrieval.
Xserve RAID was a attachment mass-storage server that was offered by Apple Inc.
NetApp, Inc. is an American data storage and data management services company headquartered in San Jose, California. It has ranked in the Fortune 500 from 2012 to 2021. Founded in 1992 with an initial public offering in 1995, NetApp offers cloud data services for management of applications and data both online and physically.
Cisco PIX was a popular IP firewall and network address translation (NAT) appliance. It was one of the first products in this market segment.
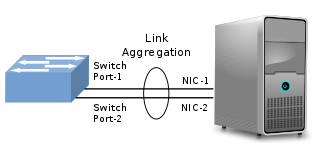
In computer networking, link aggregation is the combining of multiple network connections in parallel by any of several methods. Link aggregation increases total throughput beyond what a single connection could sustain, and provides redundancy where all but one of the physical links may fail without losing connectivity. A link aggregation group (LAG) is the combined collection of physical ports.
ATA over Ethernet (AoE) is a network protocol developed by the Brantley Coile Company, designed for simple, high-performance access of block storage devices over Ethernet networks. It is used to build storage area networks (SANs) with low-cost, standard technologies.
In audio and broadcast engineering, Audio over Ethernet is the use of an Ethernet-based network to distribute real-time digital audio. AoE replaces bulky snake cables or audio-specific installed low-voltage wiring with standard network structured cabling in a facility. AoE provides a reliable backbone for any audio application, such as for large-scale sound reinforcement in stadiums, airports and convention centers, multiple studios or stages.
Network Direct Attached Storage (NDAS) is a proprietary storage area network system, originally marketed by the company Ximeta, for connecting external digital storage devices such as hard-disks, flash memory and tape drives via the Ethernet family of computer networks. Unlike other more common forms of networked storage, NDAS does not use TCP/IP to communicate over the network. Instead a Lean Packet Exchange (LPX) protocol is used. NDAS also supports some limited RAID functions such as aggregation and mirroring.

The OpenFabrics Alliance is a non-profit organization that promotes remote direct memory access (RDMA) switched fabric technologies for server and storage connectivity. These high-speed data-transport technologies are used in high-performance computing facilities, in research and various industries.
Z-SAN is a proprietary type of storage area network licensed by Zetera corporation. Z-SAN hardware is bundled with a modified version of SAN-FS, which is a shared disk file system driver and management software product SAN File System (SFS) made by DataPlow. The shared disk file system allows multiple computers to access the same volume at block level. Zetera calls their version of the file system Z-SAN.

On Linux, network block device (NBD) is a network protocol that can be used to forward a block device from one machine to a second machine. As an example, a local machine can access a hard disk drive that is attached to another computer.

LayerWalker Technology, Inc. is a fabless integrated circuit design company that announced a network storage system on a chip (SoC). Their products targeted digital home, small business and consumer electronics markets.
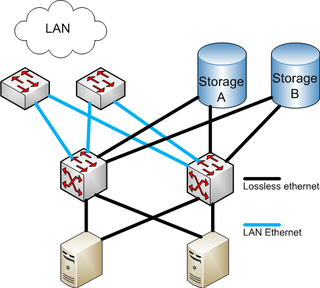
Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) is a computer network technology that encapsulates Fibre Channel frames over Ethernet networks. This allows Fibre Channel to use 10 Gigabit Ethernet networks while preserving the Fibre Channel protocol. The specification was part of the International Committee for Information Technology Standards T11 FC-BB-5 standard published in 2009.
Qumranet, Inc. was an enterprise software company offering a desktop virtualization platform based on hosted desktops in Kernel-based Virtual Machines (KVM) on servers, linked with their SPICE protocol. The company was also the creator, maintainer and global sponsor of the KVM open source hypervisor.

EtherDrive is a brand name for storage area network devices based upon the ATA over Ethernet (AoE) protocol. It was registered with the United States Patent and Trademark Office in 2004. The word was invented by Brantley Coile as a portmanteau of the words Ethernet and disk drive. EtherDrive was a trademark by Coraid from 2002 until 2015 when it was purchased by The Brantley Coile Company as part of the purchase of Coraid's software copyrights, trademarks and trade secrets in May 2015.

Fusion-io, Inc. was a computer hardware and software systems company based in Cottonwood Heights, Utah, that designed and manufactured products using flash memory technology. The Fusion ioMemory was marketed for applications such as databases, virtualization, cloud computing, big data. Their ioDrive product was considered around 2011 to be one of the fastest storage devices on the market.

In computing, Linux-IO (LIO) Target is an open-source implementation of the SCSI target that has become the standard one included in the Linux kernel. Internally, LIO does not initiate sessions, but instead provides one or more Logical Unit Numbers (LUNs), waits for SCSI commands from a SCSI initiator, and performs required input/output data transfers. LIO supports common storage fabrics, including FCoE, Fibre Channel, IEEE 1394, iSCSI, iSCSI Extensions for RDMA (iSER), SCSI RDMA Protocol (SRP) and USB. It is included in most Linux distributions; native support for LIO in QEMU/KVM, libvirt, and OpenStack makes LIO also a storage option for cloud deployments.
Brantley Coile is an inventor and founder of network technology companies, he worked for John Mayes as a programmer whose companies products include PIX Firewall, the first stateful-inspection firewall and Cisco Systems' first load-balancer, LocalDirector. Coile's patents include the fundamental patents on Network Address Translation (NAT).
Cumulus Networks was a computer software company headquartered in Mountain View, California, USA. The company designed and sold a Linux operating system for industry standard network switches, along with management software, for large datacenter, cloud computing, and enterprise environments.

Nexenta by DDN, Inc., is a subsidiary of DataDirect Networks that markets computer software for data storage and backup, headquartered in San Jose, California. Nexenta develops the products NexentaStor, NexentaCloud, NexentaFusion, and NexentaEdge. It was founded as Nexenta Systems, Inc., in 2005.









