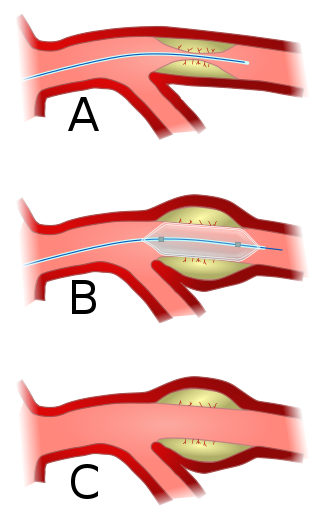
Angioplasty, also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA), is a minimally invasive endovascular procedure used to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat arterial atherosclerosis. A deflated balloon attached to a catheter is passed over a guide-wire into the narrowed vessel and then inflated to a fixed size. The balloon forces expansion of the blood vessel and the surrounding muscular wall, allowing an improved blood flow. A stent may be inserted at the time of ballooning to ensure the vessel remains open, and the balloon is then deflated and withdrawn. Angioplasty has come to include all manner of vascular interventions that are typically performed percutaneously.

Siemens AG is a German multinational technology conglomerate. Its operations encompass automation and digitalization in the process and manufacturing industries, intelligent infrastructure for buildings and distributed energy systems, rail transport solutions, as well as health technology and digital healthcare services. Siemens is the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe, and holds the position of global market leader in industrial automation and industrial software.
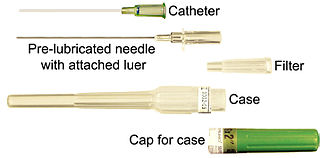
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Catheters are manufactured for specific applications, such as cardiovascular, urological, gastrointestinal, neurovascular and ophthalmic procedures. The process of inserting a catheter is catheterization.

In medicine, a stent is a metal or plastic tube inserted into the lumen of an anatomic vessel or duct to keep the passageway open, and stenting is the placement of a stent. A wide variety of stents are used for different purposes, from expandable coronary, vascular and biliary stents, to simple plastic stents that allow urine to flow between kidney and bladder. "Stent" is also used as a verb to describe the placement of such a device, particularly when a disease such as atherosclerosis has pathologically narrowed a structure such as an artery.
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures through very small incisions or body orifices. Diagnostic IR procedures are those intended to help make a diagnosis or guide further medical treatment, and include image-guided biopsy of a tumor or injection of an imaging contrast agent into a hollow structure, such as a blood vessel or a duct. By contrast, therapeutic IR procedures provide direct treatment—they include catheter-based medicine delivery, medical device placement, and angioplasty of narrowed structures.
Abbott Laboratories is an American multinational medical devices and health care company with headquarters in Abbott Park, Illinois, United States. The company was founded by Chicago physician Wallace Calvin Abbott in 1888 to formulate known drugs; today, it sells medical devices, diagnostics, branded generic medicines and nutritional products. It split off its research-based pharmaceuticals business into AbbVie in 2013.

Boston Scientific Corporation ("BSC"), incorporated in Delaware, is a biomedical/biotechnology engineering firm and multinational manufacturer of medical devices used in interventional medical specialties, including interventional radiology, interventional cardiology, peripheral interventions, neuromodulation, neurovascular intervention, electrophysiology, cardiac surgery, vascular surgery, endoscopy, oncology, urology and gynecology. Boston Scientific is widely known for the development of the Taxus Stent, a drug-eluting stent which is used to open clogged arteries. With the full acquisition of Cameron Health in June 2012, the company also became notable for offering a minimally invasive implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) which they call the EMBLEM subcutaneous implantable defibrillator (S-ICD).

Varian Medical Systems is an American radiation oncology treatments and software maker based in Palo Alto, California. Their medical devices include linear accelerators (LINACs) and software for treating cancer and other medical conditions with radiotherapy, radiosurgery, proton therapy, and brachytherapy. The company supplies software for managing cancer clinics, radiotherapy centers, and medical oncology practices. Varian Medical Systems employs more than 7,100 people at manufacturing sites in North America, Europe, and China and approximately 70 sites globally.
Guidant Corporation, part of Boston Scientific and Abbott Labs, designs and manufactures artificial cardiac pacemakers, implantable cardioverter-defibrillators, stents, and other cardiovascular medical products. Their company headquarters is located in Indianapolis, Indiana. Their main competitors are Medtronic, St. Jude Medical, and Johnson and Johnson.

Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a non-surgical procedure used to treat narrowing of the coronary arteries of the heart found in coronary artery disease. The process involves combining coronary angioplasty with stenting, which is the insertion of a permanent wire-meshed tube that is either drug eluting (DES) or composed of bare metal (BMS). The stent delivery balloon from the angioplasty catheter is inflated with media to force contact between the struts of the stent and the vessel wall, thus widening the blood vessel diameter. After accessing the blood stream through the femoral or radial artery, the procedure uses coronary catheterization to visualise the blood vessels on X-ray imaging. After this, an interventional cardiologist can perform a coronary angioplasty, using a balloon catheter in which a deflated balloon is advanced into the obstructed artery and inflated to relieve the narrowing; certain devices such as stents can be deployed to keep the blood vessel open. Various other procedures can also be performed.
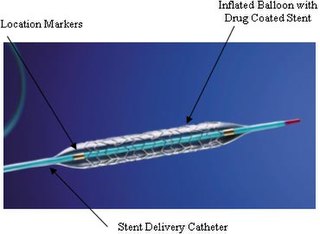
A drug-eluting stent (DES) is a peripheral or coronary stent placed into narrowed, diseased peripheral or coronary arteries that slowly release a drug to block cell proliferation. This prevents fibrosis that, together with clots (thrombi), could otherwise block the stented artery, a process called restenosis. The stent is usually placed within the peripheral or coronary artery by an interventional cardiologist or interventional radiologist during an angioplasty procedure.
Siemens Healthineers is a German company which provides healthcare solutions and services. It was spun off from its parent company Siemens in 2017, which retains a 75% stake. Siemens Healthineers is the parent company for several medical technology companies and is headquartered in Erlangen, Germany.
Julio Palmaz is a doctor of vascular radiology at University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. He studied at the National University of La Plata in Argentina, earning his medical degree in 1971. He then practiced vascular radiology at the San Martin University Hospital in La Plata before moving to the University of Texas Health and Science Center at San Antonio. He is known for inventing the balloon-expandable stent, for which he received a patent filed in 1985. It was recognized in Intellectual Property International Magazine as one of "Ten Patents that Changed the World" in the last century. His early stent research artifacts are now part of the medical collection of the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, DC. He continues to innovate on his initial designs, developing new endovascular devices.

Acclarent, Inc. began as a privately held, venture-backed company, and is now a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson. It is based in Irvine, Orange County, California. Acclarent develops technology for ENT related illnesses.

C. R. Bard, Inc., headquartered in Murray Hill, New Jersey, USA, was a developer, manufacturer, and marketer of medical technologies in the vascular medicine, urology, oncology, and surgical specialty fields. C. R. Bard marketed its products and services worldwide to hospitals, individual health care professionals, extended care facilities, and alternate site facilities. An S&P 500 company with approximately 14,000 employees in 2015, Bard is perhaps best known for having introduced the Foley catheter in 1934.
Biotronik is a limited partnership multi-national cardiovascular biomedical research and technology company, headquartered in Berlin, Germany.
OrbusNeich Medical Group Holdings Limited (OrbusNeich) ( or-bəs-NEESH) is a company that designs, develops, manufactures and markets medical devices for the treatment of vascular diseases.
DFINE, Inc. was an American medical device company with headquarters in San Jose, California. It was known for its development of minimally invasive therapeutic devices built upon a radiofrequency platform for the treatment of spinal diseases. The platform included two applications, the StabiliT Vertebral Augmentation System for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures and the STAR Tumor Ablation System for pain relief treatment of metastatic spinal tumors.

Tejas M. Patel is a cardiologist from Ahmedabad, India and chairman and chief interventional cardiologist at Apex Heart Institute, Ahmedabad. Patel, a recipient of the Dr. B. C. Roy Award, the highest Indian medical award, was honoured by the Government of India in 2015 with Padma Shri, the fourth highest Indian civilian award.

Kenneth Frank Binmoeller is a medical doctor and author of multiple scientific contributions and over 300 publications, as well as the inventor of the lumen-apposing metal stent (LAMS) and AXIOS System. These are medical devices used to relieve blockages while creating a direct connection between two bodily structures. He practices in the field of Gastroenterology with a specialty of Advanced Endoscopic Intervention. Binmoeller has been published for his innovations in medical devices and training in the field of Endoscopy.













