The History of Ecuador covers human habitation in the region reaching back 8,000 years.
Quito, officially San Francisco de Quito, is the capital of Ecuador, with an estimated population of 2.8 million in its metropolitan area. It is also the capital of the province of Pichincha. Quito is located in a valley on the eastern slopes of Pichincha, an active stratovolcano in the Andes, at an elevation of 2,850 m (9,350 ft), making it the second-highest capital city in the world.

In the history of art, prehistoric art is all art produced in preliterate, prehistorical cultures beginning somewhere in very late geological history, and generally continuing until that culture either develops writing or other methods of record-keeping, or makes significant contact with another culture that has, and that makes some record of major historical events. At this point ancient art begins, for the older literate cultures. The end-date for what is covered by the term thus varies greatly between different parts of the world.

Maya ceramics are ceramics produced in the Pre-Columbian Maya culture of Mesoamerica. The vessels used different colors, sizes, and had varied purposes. Vessels for the elite could be painted with very detailed scenes, while utilitarian vessels were undecorated or much simpler. Elite pottery, usually in the form of straight-sided beakers called "vases", used for drinking, was placed in burials, giving a number of survivals in good condition. Individual examples include the Princeton Vase and the Fenton Vase.

Santa Ana de los Cuatro Ríos de Cuenca, commonly referred to as Cuenca, is the capital and largest city of the Azuay Province of Ecuador. Cuenca is located in the highlands of Ecuador at about 2,560 metres above sea level, with an urban population of approximately 329,928 and 661,685 inhabitants in the larger metropolitan area.
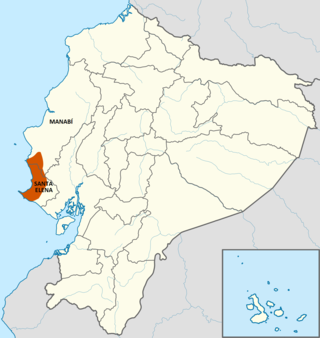
The Valdivia culture is one of the oldest settled cultures recorded in the Americas. It emerged from the earlier Las Vegas culture and thrived on the Santa Elena peninsula near the modern-day town of Valdivia, Ecuador between 3500 BCE and 1500 BCE.

Native American pottery is an art form with at least a 7500-year history in the Americas. Pottery is fired ceramics with clay as a component. Ceramics are used for utilitarian cooking vessels, serving and storage vessels, pipes, funerary urns, censers, musical instruments, ceremonial items, masks, toys, sculptures, and a myriad of other art forms.

Huaco or Guaco is the generic name given in Peru mostly to earthen vessels and other finely made pottery artworks by the indigenous peoples of the Americas found in pre-Columbian sites such as burial locations, sanctuaries, temples and other ancient ruins. Huacos are not mere earthenware but notable pottery specimens linked to ceremonial, religious, artistic or aesthetic uses in central Andean, pre-Columbian civilizations.

Pre-Columbian art refers to the visual arts of indigenous peoples of the Caribbean, North, Central, and South Americas from at least 13,000 BCE to the European conquests starting in the late 15th and early 16th centuries. The Pre-Columbian era continued for a time after these in many places, or had a transitional phase afterwards. Many types of perishable artifacts that were once very common, such as woven textiles, typically have not been preserved, but Precolumbian monumental sculpture, metalwork in gold, pottery, and painting on ceramics, walls, and rocks have survived more frequently.
Patayan is a group of prehistoric and contemporary Native American cultures residing in parts of modern-day Arizona, west to Lake Cahuilla in California, and in Baja California. This cultural grouping also included areas along the Gila River, Colorado River and Lower Colorado River Valley, the nearby uplands, and up north toward the vicinity of the Grand Canyon. Evidence shows that Patayan lifeways have persisted from AD 700 to the 1900’s.

The Quitu were Pre-Columbian indigenous peoples in Ecuador who founded Quito, which is the capital of present-day Ecuador. This people ruled the territory from 2000 BCE and persisted through the period known as the Regional Integration Period. They were overtaken by the invasion of the Inca. The Spanish invaded and conquered the center in 1534.

Indigenous peoples in Ecuador, or Native Ecuadorians, are the groups of people who were present in what became Ecuador before the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The term also includes their descendants from the time of the Spanish conquest to the present. Their history, which encompasses the last 11,000 years, reaches into the present; 25 percent of Ecuador's population is of indigenous heritage, while another 55-65 percent are Mestizos of mixed indigenous and European heritage. Genetic analysis indicates that Ecuadorian Mestizos are of predominantly indigenous ancestry.

Pre-Columbian Ecuador included numerous indigenous cultures, who thrived for thousands of years before the ascent of the Incan Empire. Las Vegas culture of coastal Ecuador, flourishing between 8000 and 4600 BC, is one of the oldest cultures in the Americas. The subsequent Valdivia culture in the Pacific coast region is another well-known early Ecuadorian culture. Ancient Valdivian artifacts from as early as 3500 BC have been found along the coast north of the Guayas Province in the modern city of Santa Elena.

The Chorrera culture or Chorrera tradition is a Late Formative indigenous culture that flourished between 1300 BCE and 300 BCE in Ecuador. Chorrera culture was one of the most widespread cultures in pre-Columbian Ecuador, spanning the Pacific lowlands to the Andean highlands, and even into southern Colombia.

Chupícuaro is an important prehispanic archeological site from the late preclassical or formative period. The culture that takes its name from the site dates to 400 BC to 200 AD, or alternatively 500 BC to 300 AD., although some academics suggest an origin as early as 800 BC.
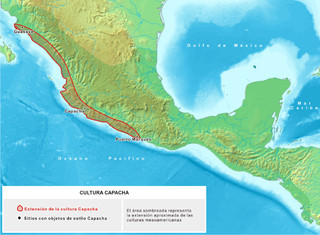
Capacha is an archaeological site located about 6 kilometers northeast of the Colima Municipality, in Colima State, Mexico. This site is the heart of the ancient Mesoamerican Capacha Culture.

Calima culture is a series of pre-Columbian cultures from the Valle del Cauca in Colombia.

Ceramic art is art made from ceramic materials, including clay. It may take varied forms, including artistic pottery, including tableware, tiles, figurines and other sculpture. As one of the plastic arts, ceramic art is a visual art. While some ceramics are considered fine art, such as pottery or sculpture, most are considered to be decorative, industrial or applied art objects. Ceramic art can be created by one person or by a group, in a pottery or a ceramic factory with a group designing and manufacturing the artware.
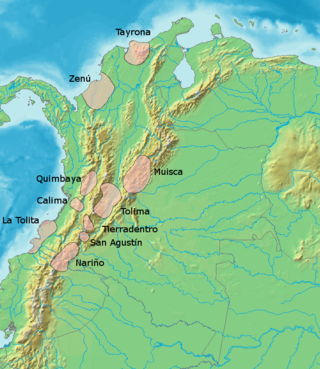
The pre-Columbian cultures of Colombia refers to the ancient cultures and civilizations that inhabited Colombia before the Spanish Conquest in the 16th century.

Pueblo pottery are ceramic objects made by the indigenous Pueblo people and their antecedents, the Ancestral Puebloans and Mogollon cultures in the Southwestern United States and Northern Mexico. For centuries, pottery has been central to pueblo life as a feature of ceremonial and utilitarian usage. The clay is locally sourced, most frequently handmade, and fired traditionally in an earthen pit. These items take the form of storage jars, canteens, serving bowls, seed jars, and ladles. Some utility wares were undecorated except from simple corrugations or marks made with a stick or fingernail, however many examples for centuries were painted with abstract or representational motifs. Some pueblos made effigy vessels, fetishes or figurines. During modern times, pueblo pottery was produced specifically as an art form to serve an economic function. This role is not dissimilar to prehistoric times when pottery was traded throughout the Southwest, and in historic times after contact with the Spanish colonialists.


















