
Coumarinolignoids are a class of phenolic compounds. They are a subset of lignans in which one of the two phenylpropanoids is found in the form of a coumarin.

Coumarinolignoids are a class of phenolic compounds. They are a subset of lignans in which one of the two phenylpropanoids is found in the form of a coumarin.

Vernicia fordii is a species of flowering plant in the spurge family native to southern China, Myanmar, and northern Vietnam. It is a small to medium-sized deciduous tree growing to 20 m tall, with a spreading crown. The bark is smooth and thin, and bleeds latex if cut. The leaves are alternate, simple, 4.5–25 cm long and 3.5–22 cm broad, heart-shaped or with three shallow, maple-like lobes, green above and below, red conspicuous glands at the base of the leaf, and with a 5.5–26 cm long petiole. The flowers are 2.5–3.5 cm diameter, with five pale pink to purple petals with streaks of darker red or purple in the throat; it is monoecious with individual flowers either male or female, but produced together in the inflorescences. The flowers appear before or with the leaves in loose, terminal clusters. The fruit is a hard, woody pear-shaped berry 4–6 cm long and 3–5 cm diameter, containing four or five large, oily seeds; it is green initially, becoming dull brown when ripe in autumn.
The lignans are a large group of low molecular weight polyphenols found in plants, particularly seeds, whole grains, and vegetables. The name derives from the Latin word for "wood". Lignans are precursors to phytoestrogens. They may play a role as antifeedants in the defense of seeds and plants against herbivores.

Gmelina arborea,, locally known as gamhar, is a fast-growing deciduous tree in the family Lamiaceae.

Umbelliferone, also known as 7-hydroxycoumarin, hydrangine, skimmetine, and beta-umbelliferone, is a natural product of the coumarin family.

Dirigent proteins are members of a class of proteins which dictate the stereochemistry of a compound synthesized by other enzymes. The first dirigent protein was discovered in Forsythia intermedia. This protein has been found to direct the stereoselective biosynthesis of (+)-pinoresinol from coniferyl alcohol monomers:

Malvin is a naturally occurring chemical of the anthocyanin family.

Petiveria is a genus of flowering plants in the pigeonberry family, Petiveriaceae. The sole species it contains, Petiveria alliacea, is native to Florida and the lower Rio Grande Valley of Texas in the United States, Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean, and tropical South America. Introduced populations occur in Benin and Nigeria. It is a deeply rooted herbaceous perennial shrub growing up to 1 m (3.3 ft) in height and has small greenish piccate flowers. The roots and leaves have a strong acrid, garlic-like odor which taints the milk and meat of animals that graze on it.
Neoflavonoids are a class of polyphenolic compounds. While flavonoids have the 2-phenylchromen-4-one backbone, neoflavonoids have the 4-phenylchromen backbone with no hydroxyl group substitution at position 2.
Phytoecdysteroids are plant-derived ecdysteroids. Phytoecdysteroids are a class of chemicals that plants synthesize for defense against phytophagous insects. These compounds are mimics of hormones used by arthropods in the molting process known as ecdysis. When insects eat the plants with these chemicals they may prematurely molt, lose weight, or suffer other metabolic damage and die.

Daidzin is a natural organic compound in the class of phytochemicals known as isoflavones. Daidzin can be found in Japanese plant kudzu and from soybean leaves.

Ononin is an isoflavone glycoside, the 7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside of formononetin, which in turn is the 4'-O-methoxy derivative of the parent isoflavone daidzein.

Ergosterol peroxide (5α,8α-epidioxy-22E-ergosta-6,22-dien-3β-ol) is a steroid derivative. It has been isolated from a variety of fungi, yeast, lichens and sponges, and has been reported to exhibit immunosuppressive, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, trypanocidal and antitumor activities in vitro.

Herbacetin is a flavonol, a type of flavonoid.

Rotenoids are naturally occurring substances containing a cis-fused tetrahydrochromeno[3,4-b]chromene nucleus. Many have insecticidal activity, such as the prototypical member of the family, rotenone. Rotenoids are related to the isoflavones.

Pinoresinol is a tetrahydrofuran lignan found in Styrax sp., Forsythia suspensa, and in Forsythia koreana. It is also found in the caterpillar of the cabbage butterfly, Pieris rapae where it serves as a defence against ants.

Pterocarpans are derivatives of isoflavonoids found in the family Fabaceae. It is a group of compounds which can be described as benzo-pyrano-furano-benzenes which can be formed by coupling of the B ring to the 4-one position.

Rhododendrin (betuloside) is an arylbutanoid glycoside and a phenylpropanoid, a type of natural phenol. It can be found in the leaves of Rhododendron aureum or in Cistus salviifolius.
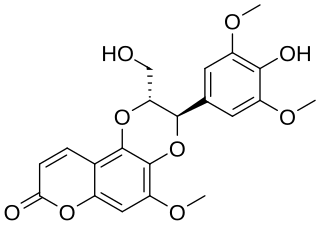
Aleuritin is a coumarinolignoid found in the tree Aleurites fordii.
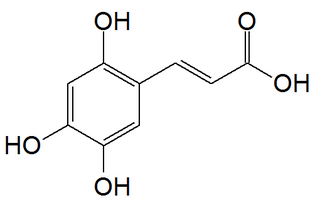
2,4,5-Trihydroxycinnamic acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid found in rooibos tea. cis-2,4,5-Trihydroxycinnamic acid can be isolated from seeds of Alisma orientale.
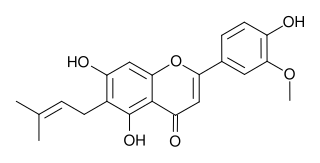
Cannflavins are a group of chemical compounds found in Cannabis sativa. Chemically, they are prenylflavonoids and are unrelated to THC and other cannabinoids. Cannflavins A and B were first identified in the 1980s and cannflavin C was identified in 2008.