
In botany, a bud is an undeveloped or embryonic shoot and normally occurs in the axil of a leaf or at the tip of a stem. Once formed, a bud may remain for some time in a dormant condition, or it may form a shoot immediately. Buds may be specialized to develop flowers or short shoots or may have the potential for general shoot development. The term bud is also used in zoology, where it refers to an outgrowth from the body which can develop into a new individual.

A transect is a path along which one counts and records occurrences of the objects of study.
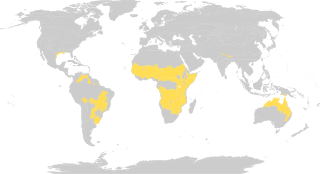
Tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands is a terrestrial biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. The biome is dominated by grass and/or shrubs located in semi-arid to semi-humid climate regions of subtropical and tropical latitudes. Tropical grasslands are mainly found between 5 degrees and 20 degrees in both North and south of the Equator.

A quadrat is a frame, traditionally square, used in ecology, geography, and biology to isolate a standard unit of area for study of the distribution of an item over a large area. Modern quadrats can for example be rectangular, circular, or irregular. The quadrat is suitable for sampling plants, slow-moving animals, and some aquatic organisms.

Lepidodendron is an extinct genus of primitive lycopodian vascular plants belonging the order Lepidodendrales. Like other Lepidodendrales, species of Lepidodendron grew as large-tree-like plants in wetland coal forest environments. They sometimes reached heights of 50 metres, and the trunks were often over 1 m (3.3 ft) in diameter. They are often known as "scale trees", due to their bark being covered in diamond shaped leaf-bases, from which leaves grew during earlier stages of growth. They thrived during the Carboniferous Period, and persisted until the end of the Permian around 252 million years ago. Sometimes erroneously called "giant club mosses", the genus was actually more closely related to modern quillworts than to modern club mosses. Within the form classification system used within paleobotany, Lepidodendron is both used for the whole plant as well as specifically the stems and leaves.

Organic horticulture is the science and art of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, or ornamental plants by following the essential principles of organic agriculture in soil building and conservation, pest management, and heirloom variety preservation.

Juniperus bermudiana is a species of juniper endemic to Bermuda. This species is most commonly known as Bermuda cedar, but is also referred to as Bermuda juniper. Historically, this tree formed woodland that covered much of Bermuda. Settlers cleared part of the forest and the tree was used for many purposes including building construction and was especially prized for shipbuilding. Scale insects introduced during the Second World War construction of United States airbases in Bermuda devastated the forests, killing over 99% of the species. Since then, the salt tolerant Casuarina equisetifolia has been planted as a replacement species, and a small number of Bermuda cedars have been found to be resistant to the scale insects. Populations of certain endemic birds which had co-evolved with the tree have plummeted as a result of its demise, while endemic cigalas and solitary bees were driven to extinction.
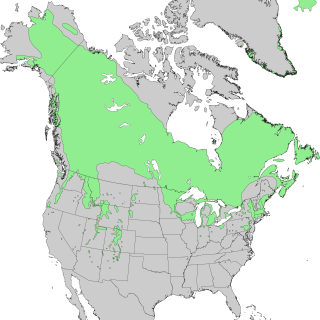
Species distribution, or speciesdispersion, is the manner in which a biological taxon is spatially arranged. The geographic limits of a particular taxon's distribution is its range, often represented as shaded areas on a map. Patterns of distribution change depending on the scale at which they are viewed, from the arrangement of individuals within a small family unit, to patterns within a population, or the distribution of the entire species as a whole (range). Species distribution is not to be confused with dispersal, which is the movement of individuals away from their region of origin or from a population center of high density.
An aeronautical chart is a map designed to assist in the navigation of aircraft, much as nautical charts do for watercraft, or a roadmap does for drivers. Using these charts and other tools, pilots are able to determine their position, safe altitude, best route to a destination, navigation aids along the way, alternative landing areas in case of an in-flight emergency, and other useful information such as radio frequencies and airspace boundaries. There are charts for all land masses on Earth, and long-distance charts for trans-oceanic travel.

A rank abundance curve or Whittaker plot is a chart used by ecologists to display relative species abundance, a component of biodiversity. It can also be used to visualize species richness and species evenness. It overcomes the shortcomings of biodiversity indices that cannot display the relative role different variables played in their calculation.
Trophic cascades are powerful indirect interactions that can control entire ecosystems, occurring when a trophic level in a food web is suppressed. For example, a top-down cascade will occur if predators are effective enough in predation to reduce the abundance, or alter the behavior of their prey, thereby releasing the next lower trophic level from predation.

In ecology, local abundance is the relative representation of a species in a particular ecosystem. It is usually measured as the number of individuals found per sample. The ratio of abundance of one species to one or multiple other species living in an ecosystem is referred to as relative species abundances. Both indicators are relevant for computing biodiversity.
In ecology, the occupancy–abundance (O–A) relationship is the relationship between the abundance of species and the size of their ranges within a region. This relationship is perhaps one of the most well-documented relationships in macroecology, and applies both intra- and interspecifically. In most cases, the O–A relationship is a positive relationship. Although an O–A relationship would be expected, given that a species colonizing a region must pass through the origin and could reach some theoretical maximum abundance and distribution, the relationship described here is somewhat more substantial, in that observed changes in range are associated with greater-than-proportional changes in abundance. Although this relationship appears to be pervasive, and has important implications for the conservation of endangered species, the mechanism(s) underlying it remain poorly understood

Conservation grazing or targeted grazing is the use of semi-feral or domesticated grazing livestock to maintain and increase the biodiversity of natural or semi-natural grasslands, heathlands, wood pasture, wetlands and many other habitats. Conservation grazing is generally less intensive than practices such as prescribed burning, but still needs to be managed to ensure that overgrazing does not occur. The practice has proven to be beneficial in moderation in restoring and maintaining grassland and heathland ecosystems. The optimal level of grazing will depend on the goal of conservation, and different levels of grazing, alongside other conservation practices, can be used to induce the desired results.
Abu Thaylah is a district in Qatar, located in the municipality of Umm Salal.
Tree-free paper, or tree-free newsprint, is described as an alternative to wood-pulp paper due to its raw material composition. It is claimed to be more eco-friendly when considering the product's entire life cycle.

The Entiminae are a large subfamily in the weevil family Curculionidae, containing most of the short-nosed weevils, including such genera as Entimus, Otiorhynchus, Phyllobius, Sitona, and Pachyrrhynchus. In comparison with their stunning diversity, only a few of these weevils are notorious pests of major economic importance. Entimines are commonly encountered in the field, including urban environments, and abundant in entomological collections.

Plant ecology is a subdiscipline of ecology that studies the distribution and abundance of plants, the effects of environmental factors upon the abundance of plants, and the interactions among plants and between plants and other organisms. Examples of these are the distribution of temperate deciduous forests in North America, the effects of drought or flooding upon plant survival, and competition among desert plants for water, or effects of herds of grazing animals upon the composition of grasslands.
In macroecology and community ecology, an occupancy frequency distribution (OFD) is the distribution of the numbers of species occupying different numbers of areas. It was first reported in 1918 by the Danish botanist Christen C. Raunkiær in his study on plant communities. The OFD is also known as the species-range size distribution in literature.

The abundances of plant species are often measured by plant cover, which is the relative area covered by different plant species in a small plot. Plant cover is not biased by the size and distributions of individuals, and is an important and often measured characteristic of the composition of plant communities.