Remembrance Day is a memorial day observed in Commonwealth member states since the end of the First World War to honour armed forces members who have died in the line of duty. The day is also marked by war remembrances in several other non-Commonwealth countries. In most countries, Remembrance Day is observed on 11 November to recall the end of First World War hostilities. Hostilities ended "at the 11th hour of the 11th day of the 11th month" of 1918, in accordance with the armistice signed by representatives of Germany and the Entente between 5:12 and 5:20 that morning. The First World War formally ended with the signing of the Treaty of Versailles on 28 June 1919.

Henri Philippe Bénoni Omer Joseph Pétain, better known as Philippe Pétain and Marshal Pétain, was a French general who commanded the French Army in World War I and later became the head of the collaborationist regime of Vichy France, from 1940 to 1944, during World War II.

Armistice Day, later known as Remembrance Day in the Commonwealth and Veterans Day in the United States, is commemorated every year on 11 November to mark the armistice signed between the Allies of World War I and Germany at Compiègne, France, at 5:45 am for the cessation of hostilities on the Western Front of World War I, which took effect at 11:00 am—the "eleventh hour of the eleventh day of the eleventh month" of 1918 although, according to Thomas R. Gowenlock, an intelligence officer with the U.S. First Division, shelling from both sides continued for the rest of the day, ending only at nightfall. The armistice initially expired after a period of 36 days and had to be extended several times. A formal peace agreement was reached only when the Treaty of Versailles was signed the following year.
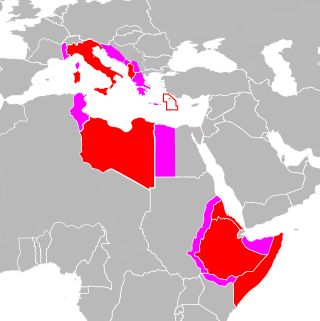
The participation of Italy in the Second World War was characterized by a complex framework of ideology, politics, and diplomacy, while its military actions were often heavily influenced by external factors. Italy joined the war as one of the Axis Powers in 1940 with a plan to concentrate Italian forces on a major offensive against the British Empire in Africa and the Middle East, known as the "parallel war", while expecting the collapse of British forces in the European theatre. The Italians bombed Mandatory Palestine, invaded Egypt and occupied British Somaliland with initial success. However, the British counterattacked, eventually necessitating German support to prevent an Italian collapse in North Africa. As the war carried on and German and Japanese actions in 1941 led to the entry of the Soviet Union and United States, respectively, into the war, the Italian plan of forcing Britain to agree to a negotiated peace settlement was foiled.

Compiègne is a commune in the Oise department of northern France. It is located on the river Oise, and its inhabitants are called Compiégnois.

Ferdinand Foch was a French general, Marshal of France and member of the Académie Française. He distinguished himself as Supreme Allied Commander on the Western Front during the First World War in 1918.

The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed at Le Francport near Compiègne that ended fighting on land, at sea, and in the air in World War I between the Entente and their last remaining opponent, Germany. Previous armistices had been agreed with Bulgaria, the Ottoman Empire and Austria-Hungary. It was concluded after the German government sent a message to American president Woodrow Wilson to negotiate terms on the basis of a recent speech of his and the earlier declared "Fourteen Points", which later became the basis of the German surrender at the Paris Peace Conference, which took place the following year.

The Armistice of 22 June 1940, sometimes referred to as the Second Armistice at Compiègne, was an agreement signed at 18:36 on 22 June 1940 near Compiègne, France by officials of Nazi Germany and the French Third Republic. It became effective at midnight on 25 June.

Case Anton was the military occupation of France carried out by Germany and Italy in November 1942. It marked the end of the Vichy regime as a nominally-independent state and the disbanding of its army, but it continued its existence as a puppet government in Occupied France. One of the last actions of the Vichy armed forces before their dissolution was the scuttling of the French fleet in Toulon to prevent it from falling into Axis hands.

The Armistice of Mudros ended hostilities in the Middle Eastern theatre between the Ottoman Empire and the Allies of World War I. It was signed on 30 October 1918 by the Ottoman Minister of Marine Affairs Rauf Bey and British Admiral Somerset Arthur Gough-Calthorpe, on board HMS Agamemnon in Moudros harbour on the Greek island of Lemnos, and it took effect at noon the next day.

The Forest of Compiègne is a large forest in the region of Picardy, France, near the city of Compiègne and approximately 80 kilometres (50 mi) north of Paris.

World War I or the First World War, also known as the Great War, was a global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in Europe and the Middle East, as well as in parts of Africa and the Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare and the use of artillery, machine guns, and chemical weapons (gas). World War I was one of the deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated 9 million military dead and 23 million wounded, plus up to 8 million civilian deaths from causes including genocide. The movement of large numbers of troops and civilians was a major factor in spreading the Spanish flu pandemic, which killed millions.

The Military Administration in France was an interim occupation authority established by Nazi Germany during World War II to administer the occupied zone in areas of northern and western France. This so-called zone occupée was established in June 1940, and renamed zone nord in November 1942, when the previously unoccupied zone in the south known as zone libre was also occupied and renamed zone sud.

The Armistice of Salonica was the armistice signed at 10:50 p.m. on 29 September 1918 between Bulgaria and the Allied Powers at the General Headquarters of the Allied Army of the Orient in Thessaloniki. The armistice came into force at noon on 30 September 1918. The armistice would remain in effect until the conclusion of the Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine, the final general peace treaty, in November 1919.

La Capelle is a commune in the Aisne department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. Its inhabitants are called Capellois.

Rethondes is a commune in the Oise department in northern France. It is associated with the signing of the armistice of 11 November 1918, which ended World War I, although the actual location of the signing was on the other side of the Aisne in the commune of Compiègne. The same spot was also where Nazi Germany had Vichy government sign the armistice of 22 June 1940, during World War II.
Events from the year 1940 in France.

Vichy France, officially the French State, was the French rump state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. It was named after its seat of government, the city of Vichy. Officially independent, but with half of its territory occupied under the harsh terms of the 1940 armistice with Nazi Germany, it adopted a policy of collaboration. Though Paris was nominally its capital, the government established itself in the resort town of Vichy in the unoccupied "free zone", where it remained responsible for the civil administration of France as well as its colonies. The occupation of France by Nazi Germany at first affected only the northern and western portions of the country, but in November 1942 the Germans and Italians occupied the remainder of Metropolitan France, ending any pretence of independence by the Vichy government.

The Glade of the Armistice is a French war memorial in the Forest of Compiègne in Picardy, France, near the city of Compiègne approximately 60 kilometres (37 mi) north of Paris. It was built at the location where the Germans signed the Armistice of 11 November 1918 that ended World War I. During World War II, Adolf Hitler chose the same spot for the French and Germans to sign the Armistice of 22 June 1940 after Germany won the Battle of France. The site was destroyed by the Germans but rebuilt after the war.

Aurore (Q192) was a French Navy submarine, the lead ship of the Aurore-class. She served in the naval forces of Vichy France during the early years of World War II and was scuttled in November 1942.