Credo ut intelligam, alternatively spelled credo ut intellegam, is a Latin sentence of Anselm of Canterbury ( Proslogion , 1). The sentence is a reference to Isaiah 7:9. [1] The sentence translates as: "I believe so that I may understand".
In Anselm's writing, it is placed in juxtaposition to its converse, intellego ut credam ("I think so that I may believe"), when he says Neque enim quaero intelligere ut credam, sed credo ut intelligam [1] [2] ("I do not seek to understand in order that I may believe, but rather, I believe in order that I may understand"). [2]
The phrase credo ut intelligam is often associated with Anselm's other famous phrase fides quaerens intellectum [3] [2] ("faith seeking understanding"). [2]
The phrase is based on a sentence of Augustine of Hippo (crede ut intellegas, [4] lit. "believe so that you may understand") [5] [2] to relate faith and reason. Augustine understood the saying to mean that a person must believe in something in order to know anything about God. [6] This sentence by Augustine is also inspired from Isaiah 7:9. [7]
The Apostles' Creed, sometimes titled the Apostolic Creed or the Symbol of the Apostles, is a Christian creed or "symbol of faith".
Fideism is a term used to name a standpoint or an epistemological theory which maintains that faith is independent of reason, or that reason and faith are hostile to each other and faith is superior at arriving at particular truths. The word fideism comes from fides, the Latin word for faith, and literally means "faith-ism". Philosophers have identified a number of different forms of fideism. Strict fideists hold that reason has no place in discovering theological truths, while moderate fideists hold that though some truth can be known by reason, faith stands above reason.
Credo quia absurdum is a Latin phrase that means "I believe because it is absurd", originally misattributed to Tertullian in his De Carne Christi. It is believed to be a paraphrasing of Tertullian's "prorsus credibile est, quia ineptum est" which means "it is completely credible because it is unsuitable", or "certum est, quia impossibile" which means "it is certain because it is impossible". These are consistent with the anti-Marcionite context. Early modern, Protestant and Enlightenment rhetoric against Catholicism and religion more broadly resulted in this phrase being changed to "I believe because it is absurd", displaced from its original anti-Marcionite to a personally religious context.

The seven gifts of the Holy Spirit are an enumeration of seven spiritual gifts first found in the book of Isaiah, and much commented upon by patristic authors. They are: wisdom, understanding, counsel, fortitude, knowledge, piety, and fear of the Lord.

Tsang Lap Chuen is a Chinese philosopher in the analytic tradition. He is known for his theory of the sublime in which he presents the notion of limit-situations in life as being central to the human experience.

Matthew 5:8 is the eighth verse of the fifth chapter of the Gospel of Matthew in the New Testament. It is the sixth verse of the Sermon on the Mount, and also sixth of what are known as the Beatitudes.
Gaunilo or Gaunillon was a Benedictine monk of Marmoutier Abbey in Tours, France. He is best known for his contemporary criticism of the ontological argument for the existence of God which appeared in St Anselm's Proslogion. In his work In Behalf of the Fool, Gaunilo contends that St Anselm's ontological argument fails because logic of the same kind would force one to conclude many things exist which certainly do not. An empiricist, Gaunilo thought that the human intellect is only able to comprehend information provided by the senses.

The satisfaction theory of atonement is a theory in Catholic theology which holds that Jesus Christ redeemed humanity through making satisfaction for humankind's disobedience through his own supererogatory obedience. The theory draws primarily from the works of Anselm of Canterbury, specifically his Cur Deus Homo. Since one of God's characteristics is justice, affronts to that justice must be atoned for. It is thus connected with the legal concept of balancing out an injustice.

The Proslogion is a prayer written by the medieval cleric Saint Anselm of Canterbury between 1077 and 1078. In each chapter, Anselm juxtaposes contrasting attributes of God to resolve apparent contradictions in Christian theology. This meditation is considered the first-known philosophical formulation that sets out an ontological argument for the existence of God.
Fides et ratio is an encyclical promulgated by Pope John Paul II on 14 September 1998. It was one of 14 encyclicals issued by John Paul II. The encyclical primarily addresses the relationship between faith and reason.
Lex orandi, lex credendi, sometimes expanded as Lex orandi, lex credendi, lex vivendi, is a motto in Christian tradition, which means that prayer and belief are integral to each other and that liturgy is not distinct from theology. It refers to the relationship between worship and belief. Its simplistic applicability as a self-standing principle independent of hope and charity was bluntly denied by Pope Pius XII, who positioned liturgy as providing theological evidence not authority.

Eucharist is the name that Catholic Christians give to the sacrament by which, according to their belief, the body and blood of Christ are present in the bread and wine consecrated during the Catholic eucharistic liturgy, generally known as the Mass. The definition of the Eucharist in the 1983 Code of Canon Law as the sacrament where Christ himself “is contained, offered, and received” points to the three aspects of the Eucharist according to Catholic theology: the real presence of Christ in the Eucharist, Holy Communion, and the holy sacrifice of the Mass.
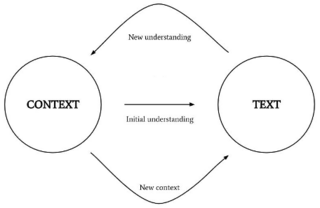
The hermeneutic circle describes the process of understanding a text hermeneutically. It refers to the idea that one's understanding of the text as a whole is established by reference to the individual parts and one's understanding of each individual part by reference to the whole. The circle is a metaphor for the procedure of transforming one's understanding of the part and the whole through iterative recontextualization.

Incurvatus in se is a theological phrase describing a life lived "inward" for oneself rather than "outward" for God and others.

Anselm of CanterburyOSB, also called Anselm of Aosta after his birthplace and Anselm of Bec after his monastery, was an Italian Benedictine monk, abbot, philosopher, and theologian of the Catholic Church, who held the office of Archbishop of Canterbury from 1093 to 1109. After his death, he was canonized as a saint; his feast day is 21 April. He was proclaimed a Doctor of the Church by a papal bull of Pope Clement XI in 1720.
St Augustine College of South Africa is a private tertiary academic institution in Johannesburg, South Africa.
In the philosophy of religion, an ontological argument is a deductive philosophical argument, made from an ontological basis, that is advanced in support of the existence of God. Such arguments tend to refer to the state of being or existing. More specifically, ontological arguments are commonly conceived a priori in regard to the organization of the universe, whereby, if such organizational structure is true, God must exist.
Articles related to philosophy of religion include:

Augustinianism is the philosophical and theological system of Augustine of Hippo and its subsequent development by other thinkers, notably Boethius, Anselm of Canterbury and Bonaventure. Among Augustine's most important works are The City of God, De doctrina Christiana, and Confessions.
Fides quaerens intellectum, means "faith seeking understanding" or "faith seeking intelligence", is a Latin sentence by Anselm of Canterbury.