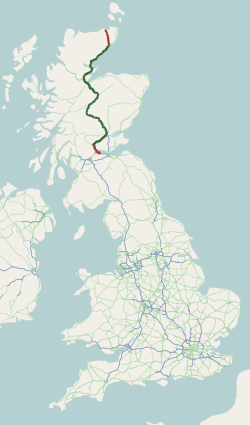
The A9 is a major road in Scotland running from the Falkirk council area in central Scotland to Scrabster Harbour, Thurso in the far north, via Stirling, Bridge of Allan, Perth and Inverness. At 273 mi (439 km), it is the longest road in Scotland and the fifth-longest A-road in the United Kingdom. Historically it was the main road between Edinburgh and John o' Groats, and has been called the spine of Scotland. It is one of the three major north–south trunk routes linking the Central Belt to the Highlands - the others being the A82 and the A90.

Newmarket railway station is located on the Craigieburn line in Victoria, Australia. It serves the northern Melbourne suburb of Flemington, and it opened on 1 November 1860.

The Severn Railway Bridge was a bridge carrying the railway across the River Severn between Sharpness and Lydney in Gloucestershire, England. It was built in the 1870s by the Severn Bridge Railway Company, primarily to carry coal from the Forest of Dean to the docks at Sharpness; it was the furthest-downstream bridge over the Severn until the opening of the Severn road bridge in 1966. When the company got into financial difficulties in 1893, it was taken over jointly by the Great Western Railway and the Midland Railway companies. The bridge continued to be used for freight and passenger services until 1960, and saw temporary extra traffic on the occasions that the Severn Tunnel was closed for engineering work.

The Ouse Bridge is a reinforced concrete plate girder bridge that spans River Ouse between Goole and Howden in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. It carries the M62 and is situated between junctions 36 and 37. It was built between 1973 and 1976 by Costain and was designed by Scott Wilson Kirkpatrick & Partners. The bridge was officially opened to traffic on 24 May 1976 by nine-year-old Martin Brigham.

The Kyle of Lochalsh line is a primarily single-track railway line in the Scottish Highlands, from Dingwall to Kyle of Lochalsh. Many of the passengers are tourists, but there are also locals visiting Inverness for shopping, and commuters. All services are provided by ScotRail and run beyond Dingwall to Inverness. In the past there were some through services to and from Glasgow, Edinburgh or Aberdeen. None of the line is electrified, and all trains on the line are diesel-powered, as are all other trains in the Scottish Highlands.

The Far North Line is a rural railway line entirely within the Highland area of Scotland, extending from Inverness to Thurso and Wick. As the name suggests, it is the northernmost railway in the United Kingdom. The line is entirely single-track, with only passing loops at some intermediate stations allowing trains to pass each other. In common with other railway lines in the Highlands and northern Lowlands, it is not electrified and all trains are diesel-powered.

The Redheugh Bridge is a road bridge spanning the River Tyne west of Newcastle upon Tyne city centre on the north bank and Gateshead town centre on the south bank, in North East England. It currently carries the A189 road.
The City of Glasgow Union Railway - City Union Line, also known as the Tron Line, was a railway company founded in Glasgow, Scotland, in 1864 to build a line connecting the railway systems north and south of the River Clyde, and to build a central passenger terminus and a general goods depot for the city. The through line, running from south-west to north-east across the city, opened in 1870–1, and the passenger terminal was St Enoch railway station, opened in 1876. The railway bridge across the Clyde was the first in the city.

The Victoria Bridge (Penrith), also known as the Victoria Bridge over the Nepean River, is a heritage-listed former railway bridge and now wrought iron box plate girder road bridge across the Nepean River on the Great Western Highway in the western Sydney suburb of Penrith in the City of Penrith local government area of New South Wales, Australia. The bridge was designed by John Whitton, the Engineer–in–Chief of New South Wales Government Railways, and built from 1862 to 1867 by William Piper, Peto Brassey and Betts (superstructure), William Watkins (piers). It is also known as Victoria Bridge, The Nepean Bridge and RTA Bridge No. 333. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 27 May 2016.

The Lochaber Narrow Gauge Railway was a 3 ft narrow-gauge industrial railway. It was a relatively long line, built for the construction and subsequent maintenance of a 15-mile-long (24-kilometre) tunnel from Loch Treig to a factory near Fort William in Scotland. The tunnel was excavated to carry water for the Lochaber hydroelectric scheme in connection with aluminium production by British Aluminium. The railway came to be known colloquially as the 'Old Puggy Line'.

The River Conon is a river in the Highlands of Scotland. It begins at Loch Luichart, and flows in a south-easterly direction to be joined by the River Meig at Scatwell before passing through Loch Achonachie. It is joined by the Black Water at Moy Bridge, and the River Orrin at Urray, before flowing past Conon Bridge and into the Cromarty Firth.

The Dingwall Canal was a short tidal canal running from the town of Dingwall to the Cromarty Firth in the county of Ross and Cromarty, Scotland. It was completed by 1819, to provide better access to the town, but was not a commercial success, and was abandoned in the 1880s after the arrival of the railways.

Nigg Bay is a large, relatively shallow sandy bay, consisting of mudflats, saltmarsh and wet grassland, located on the north east coast of the Cromarty Firth, 5 miles (8 km) east of Invergordon, in the district of Ross and Cromarty and in the Scottish council area of Highland. At low tide, the Sands of Nigg are exposed. Nigg Bay can be said to start at Balintraid pier – probably the oldest pier on the Cromarty Firth – built by Thomas Telford in 1821. There is a wartime mining base alongside the pier and a series of coastal gun emplacements on the road to North Sutor.

New Semington Aqueduct carries the Kennet and Avon Canal over the carriageway of the A350 road Trowbridge Bypass, at Semington in west Wiltshire, England. Although the construction of new canals is no longer common practice in England, new aqueducts such as this are sometimes built in relation to new roads or road widening schemes.
The Cromarty and Dingwall Light Railway was a never-completed light railway linking Cromarty in the Black Isle, Ross and Cromarty, Scotland to the Highland Railway system at Conon.

The Dornoch Firth Bridge is a road bridge over the Dornoch Firth, carrying traffic between Tain and Dornoch.
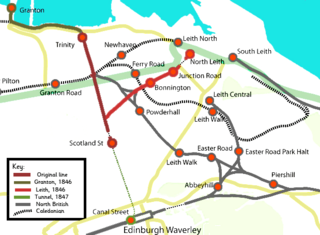
The Edinburgh, Leith and Newhaven Railway was a railway company formed in 1836 to connect the city of Edinburgh with the harbours on the Firth of Forth. When the line connected to Granton, the company name was changed to the Edinburgh, Leith and Granton Railway. It opened part of its route in 1846, but reaching the centre of Edinburgh involved the difficult construction of a long tunnel; this was opened in 1847. It was on a steep incline and was worked by rope haulage.

The North British, Arbroath and Montrose Railway was a company established by Act of Parliament in 1871 to construct and operate a railway line from north of Arbroath via Montrose to Kinnaber Junction, 38 miles (61 km) south of Aberdeen. The company was originally a subsidiary of the North British Railway but was absorbed into its parent in 1880.

Burdekin River Rail Bridge is a heritage-listed former railway bridge on the Great Northern railway over the Burdekin River at Dotswood, Charters Towers Region, Queensland, Australia. It was designed by Henry Charles Stanley and built from c. 1896 to 1899 by Swanson Brothers. It is also known as Macrossan Bridge. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 21 October 1992.



















