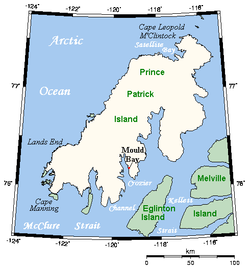
The Crozier Channel ( 76°0′N119°0′W / 76.000°N 119.000°W ) is a natural waterway through the central Canadian Arctic Archipelago in the Northwest Territories of Canada. It separates Prince Patrick Island (to the north-west) and Eglinton Island (to the south-east). [1] It opens into the McClure Strait at its southern end. It is named for the explorer, Francis Crozier; one of several such memorials in the Canadian Arctic.