
Chlamydomonas is a genus of green algae consisting of about 325 species all unicellular flagellates, found in stagnant water and on damp soil, in freshwater, seawater, and even in snow as "snow algae". Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics. One of the many striking features of Chlamydomonas is that it contains ion channels (channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light. Some regulatory systems of Chlamydomonas are more complex than their homologs in Gymnosperms, with evolutionarily related regulatory proteins being larger and containing additional domains.

Habu (波布) is a Ryukyuan and Japanese name referring to certain venomous snakes:
In biology, a homonym is a name for a taxon that is identical in spelling to another such name, that belongs to a different taxon.
The Ryūkyū scops-owl or elegant scops-owl is a small rufous-brown owl with a brown face disk and a cinnamon facial ruff. The bill is olive-grey and it has yellow eyes.

The Jamaican slider also known as the Cat Island slider is a species of fresh water turtle in the family Emydidae. It is found in the Bahamas and Jamaica. As it is not currently found on any of the other surrounding islands in the region it is assumed that the Jamaican slider was introduced from one of these countries to the other. Even though the popular theory was that these turtles originated from Jamaica, current geological evidence may suggest that they were in the Bahamas long before the native Indians first went to the Bahama islands. There is also evidence from archeological sites on San Salvador that the native Indians ate these turtles and transplanted them around the West Indies.

Calcinus elegans, also known as the blue line hermit crab, is a small, tropical hermit crab.

Peyssonnelia is a genus of thalloid red alga comprising approximately 63 species. It includes the algae commonly known as rumoi-iwanokawa, mayoi-iwanokawa and akase-iwanokawa. Specimens can reach around 20 cm in size. Peyssonnelia produces tetraspores.

Protobothrops elegans is a venomous pitviper species endemic to Japan in the southern Ryukyu Islands. No subspecies are currently recognized. Common names include: elegant pitviper, Sakishima habu (サキシマハブ), and elegant tree viper.
Okinawa habu may refer to:
Cruoriopsis is a genus of red algae. It has sometimes been considered a synonym of Cruoriella Crouan & Crouan or part of the large genus Peyssonnelia. A 2007 dissertation by Krayesky recognizes this genus, as does ITIS.

Haminoea is a genus of medium-sized sea snails or bubble snails, marine opisthobranch gastropod molluscs in the family Haminoeidae, the haminoea bubble snails, part of the clade Cephalaspidea, the headshield slugs and bubble snails.

Gibbonsia elegans, the spotted kelpfish, is a species of clinid native to subtropical waters of the Pacific Ocean from central California, U.S. to southern Baja California, Mexico. It prefers subtidal rocky habitats with seaweed down to a depth of about 56 metres (184 ft). This species can reach a maximum length of 16 centimetres (6.3 in) TL. This species feeds on benthic crustaceans, gastropods, and polychaete worms. Gibbonsia is named after Dr. William P. Gibbsons who was a naturalist in the California Academy of Science. It is found in three different colors depending on their habitat. Males and females do not show sexual dimorphism.

Pagurus samuelis, the blueband hermit crab, is a species of hermit crab from the west coast of North America, and the most common hermit crab in California. It is a small species, with distinctive blue bands on its legs. It prefers to live in the shell of the black turban snail, and is a nocturnal scavenger of algae and carrion.

Draconichthys elegans is a selenosteid arthrodire placoderm from the Late Frasnian Kellwasserkalk facies of the Anti-Atlas Mountains of what is now Morocco. During the Late Devonian, the region would have been a shallow, algae-dimmed sea.

The wildlife of Antarctica are extremophiles, having to adapt to the dryness, low temperatures, and high exposure common in Antarctica. The extreme weather of the interior contrasts to the relatively mild conditions on the Antarctic Peninsula and the subantarctic islands, which have warmer temperatures and more liquid water. Much of the ocean around the mainland is covered by sea ice. The oceans themselves are a more stable environment for life, both in the water column and on the seabed.
C. elegans most commonly refers to the model round worm Caenorhabditis elegans. It may also refer to any of the species below. They are listed, first in taxonomic order and, second, alphabetically.
Cruoriella is a genus of red algae in the family Peyssonneliaceae.

Kyphosus elegans, the Cortez sea chub or Cortez chub, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a sea chub from the family Kyphosidae. It is found in the eastern Pacific Ocean where it is of minor importance to commercial fisheries.
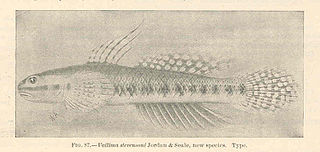
Stiphodon elegans is a species of freshwater goby. It is found in Polynesia, from Wallis and Futuna, Samoa, Cook Islands and French Polynesia. It occurs in clear, fast flowing streams in rainforest near the coast and it feeds on algae.
Griffithsia elegans is a species of red algae in the family Wrangeliaceae. It is found in Australia and New Zealand. The type locality is Robe, South Australia.











