Related Research Articles

Crystallography is the experimental science of determining the arrangement of atoms in crystalline solids. Crystallography is a fundamental subject in the fields of materials science and solid-state physics. The word crystallography is derived from the Ancient Greek word κρύσταλλος, with its meaning extending to all solids with some degree of transparency, and γράφειν. In July 2012, the United Nations recognised the importance of the science of crystallography by proclaiming that 2014 would be the International Year of Crystallography.

X-ray crystallography is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their crystallographic disorder, and various other information.
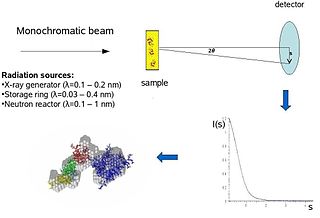
Biological small-angle scattering is a small-angle scattering method for structure analysis of biological materials. Small-angle scattering is used to study the structure of a variety of objects such as solutions of biological macromolecules, nanocomposites, alloys, and synthetic polymers. Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) are the two complementary techniques known jointly as small-angle scattering (SAS). SAS is an analogous method to X-ray and neutron diffraction, wide angle X-ray scattering, as well as to static light scattering. In contrast to other X-ray and neutron scattering methods, SAS yields information on the sizes and shapes of both crystalline and non-crystalline particles. When used to study biological materials, which are very often in aqueous solution, the scattering pattern is orientation averaged.
Electron crystallography is a method to determine the arrangement of atoms in solids using a transmission electron microscope (TEM). It can involve the use of high-resolution transmission electron microscopy images, electron diffraction patterns including convergent-beam electron diffraction or combinations of these. It has been successful in determining some bulk structures, and also surface structures. Two related methods are low-energy electron diffraction which has solved the structure of many surfaces, and reflection high-energy electron diffraction which is used to monitor surfaces often during growth.
The Henderson limit is the X-ray dose (energy per unit mass) a cryo-cooled crystal can absorb before the diffraction pattern decays to half of its original intensity. Its value is defined as 2 × 107 Gy (J/kg).

Transmission electron cryomicroscopy (CryoTEM), commonly known as cryo-EM, is a form of cryogenic electron microscopy, more specifically a type of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) where the sample is studied at cryogenic temperatures. Cryo-EM, specifically 3-dimensional electron microscopy (3DEM), is gaining popularity in structural biology.
Multi-wavelength anomalous diffraction is a technique used in X-ray crystallography that facilitates the determination of the three-dimensional structure of biological macromolecules via solution of the phase problem.
Diffraction topography is a imaging technique based on Bragg diffraction. Diffraction topographic images ("topographies") record the intensity profile of a beam of X-rays diffracted by a crystal. A topography thus represents a two-dimensional spatial intensity mapping of reflected X-rays, i.e. the spatial fine structure of a Laue reflection. This intensity mapping reflects the distribution of scattering power inside the crystal; topographs therefore reveal the irregularities in a non-ideal crystal lattice. X-ray diffraction topography is one variant of X-ray imaging, making use of diffraction contrast rather than absorption contrast which is usually used in radiography and computed tomography (CT). Topography is exploited to a lesser extends with neutrons, and has similarities to dark field imaging in the electron microscope community.
The International Union of Crystallography (IUCr) is an organisation devoted to the international promotion and coordination of the science of crystallography. The IUCr is a member of the International Council for Science (ICSU).
Acta Crystallographica is a series of peer-reviewed scientific journals, with articles centred on crystallography, published by the International Union of Crystallography (IUCr). Originally established in 1948 as a single journal called Acta Crystallographica, there are now six independent Acta Crystallographica titles:
Single-wavelength anomalous diffraction (SAD) is a technique used in X-ray crystallography that facilitates the determination of the structure of proteins or other biological macromolecules by allowing the solution of the phase problem. In contrast to multi-wavelength anomalous diffraction (MAD), SAD uses a single dataset at a single appropriate wavelength.
Cryofixation is a technique for fixation or stabilisation of biological materials as the first step in specimen preparation for electron microscopy and cryo-electron microscopy. Typical specimens for cryofixation include small samples of plant or animal tissue, cell suspensions of microorganisms or cultured cells, suspensions of viruses or virus capsids and samples of purified macromolecules, especially proteins.
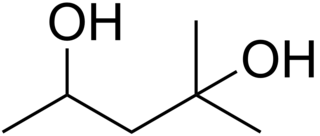
2-Methyl-2,4-pentanediol (MPD) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2C(OH)CH2CH(OH)CH3. This colourless liquid is a chiral diol. It is produced industrially from diacetone alcohol by hydrogenation. Total European and USA production was 15000 tonnes in 2000.

Protein crystallization is the process of formation of a regular array of individual protein molecules stabilized by crystal contacts. If the crystal is sufficiently ordered, it will diffract. Some proteins naturally form crystalline arrays, like aquaporin in the lens of the eye.
S. Samar Hasnain FInstP, FRSC, is the inaugural Max Perutz professor of Molecular Biophysics at the University of Liverpool. In 1991 he became a Fellow of the Institute of Physics and in 2002 he became a Fellow of the Royal Society of Chemistry. In 1997 he became a Fellow of the Third World Academy of Sciences. He became Foreign Fellows of Pakistan Academy of Sciences in 2017.

In the field of cryogenics, helium [He] is utilized for a variety of reasons. The combination of helium’s extremely low molecular weight and weak interatomic reactions yield interesting properties when helium is cooled below its critical temperature of 5.2 K to form a liquid. Even at absolute zero (0K), helium does not condense to form a solid under ambient pressure. In this state, the zero point vibrational energies of helium are comparable to very weak interatomic binding interactions, thus preventing lattice formation and giving helium its fluid characteristics. Within this liquid state, helium has two phases referred to as helium I and helium II. Helium I displays thermodynamic and hydrodynamic properties of classical fluids, along with quantum characteristics. However, below its lambda point of 2.17 K, helium transitions to He II and becomes a quantum superfluid with zero viscosity.

Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is a cryomicroscopy technique applied on samples cooled to cryogenic temperatures. For biological specimens, the structure is preserved by embedding in an environment of vitreous ice. An aqueous sample solution is applied to a grid-mesh and plunge-frozen in liquid ethane or a mixture of liquid ethane and propane. While development of the technique began in the 1970s, recent advances in detector technology and software algorithms have allowed for the determination of biomolecular structures at near-atomic resolution. This has attracted wide attention to the approach as an alternative to X-ray crystallography or NMR spectroscopy for macromolecular structure determination without the need for crystallization.
Microcrystal electron diffraction, or MicroED, is a CryoEM method that was developed by the Gonen laboratory in late 2013 at the Janelia Research Campus of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. MicroED is a form of electron crystallography where thin 3D crystals are used for structure determination by electron diffraction. Prior to this demonstration, macromolecular (protein) electron crystallography was only used on 2D crystals, for example.
This is a timeline of crystallography.
John R. Helliwell is a British crystallographer known for his pioneering work in the use of synchrotron radiation in macromolecular crystallography.
References
- ↑ Hope H (1988). "Cryocrystallography of biological macromolecules: a generally applicable method". Acta Crystallogr. B. 44 (1): 22–26. doi:10.1107/s0108768187008632. PMID 3271102.