Mount Everest is Earth's highest mountain above sea level, located in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas. The China–Nepal border runs across its summit point. Its elevation of 8,848.86 m was most recently established in 2020 by the Chinese and Nepali authorities.

MacGillycuddy's Reeks is a sandstone and siltstone mountain range in the Iveragh Peninsula in County Kerry, Ireland. Stretching 19 kilometres, from the Gap of Dunloe in the east, to Glencar in the west, the Reeks is Ireland's highest mountain range, and includes most of the highest peaks and sharpest ridges in Ireland, and the only peaks on the island over 1,000 metres in height.

Manaslu is the eighth-highest mountain in the world at 8,163 metres (26,781 ft) above sea level. It is in the Mansiri Himal, part of the Nepalese Himalayas, in west-central Nepal. Manaslu means "mountain of the spirit" and the word is derived from the Sanskrit word manasa, meaning "intellect" or "soul". Manaslu was first climbed on May 9, 1956, by Toshio Imanishi and Gyalzen Norbu, members of a Japanese expedition. It is said that, given the many unsuccessful attempts by the British to climb Everest before Nepali Tenzing Norgay and New Zealander Edmund Hillary, "just as the British consider Everest their mountain, Manaslu has always been a Japanese mountain".

Chimborazo is an inactive stratovolcano situated in the Cordillera Occidental range of the Andes. Its last known eruption is believed to have occurred around 550 A.D. Although not the tallest mountain in the Andes or on Earth relative to sea level, its summit is the farthest point on Earth's surface from the Earth's center, due to its location along the planet's equatorial bulge. Chimborazo's height is 6,263 m (20,548 ft), well below that of Mount Everest.
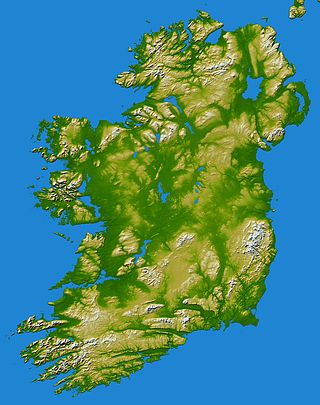
In these lists of mountains in Ireland, those within Northern Ireland, or on the Republic of Ireland – United Kingdom border, are marked with an asterisk, while the rest are within the Republic of Ireland. Where mountains are ranked by height, the definition of the topographical prominence used to classify the mountain, is noted. In British definitions, a height of 600 metres (1,969 ft) is required for a mountain, whereas in Ireland, a lower threshold of 500 metres (1,640 ft) is sometimes advocated.
A pilot report or PIREP is a report of actual flight or ground conditions encountered by an aircraft. Reports commonly include information about atmospheric conditions or airport conditions. This information is usually relayed by radio to the nearest ground station, but other options also exist in some regions. The message would then be encoded and relayed to other weather offices and air traffic service units.

Telescope Peak is the highest point within Death Valley National Park, in the U.S. state of California. It is also the highest point of the Panamint Range, and lies in Inyo County. From atop this desert mountain one can see for over one hundred miles in many directions, including west to Mount Whitney, and east to Charleston Peak. The mountain was named for the great distance visible from the summit.

Goode Mountain is one of the major peaks of the North Cascades in the U.S. state of Washington. Named for topographer Richard Urquhart Goode of the United States Geological Survey, it is the highest peak located in North Cascades National Park, between the Skagit River and Lake Chelan. It is the fourth-highest non-volcanic peak in Washington, and the twelfth-highest summit overall.

The mountains and hills of the British Isles are categorised into various lists based on different combinations of elevation, prominence, and other criteria such as isolation. These lists are used for peak bagging, whereby hillwalkers attempt to reach all the summits on a given list, the oldest being the 282 Munros in Scotland, created in 1891.

The Whitney Classic is an 136-mile-long (219 km) endurance mountain bike race that is held in late September or October every year. The ride runs from the Badwater Basin in Death Valley to Whitney Portal. Badwater, at 279 feet (85 m) below sea level, is the lowest place in the North America and Whitney Portal at 8,360 feet (2,550 m) is the trailhead that leads to Mount Whitney, the highest peak in the contiguous United States with an elevation of 14,505 feet (4,421 m).

Iron Mountain is a mountain in the San Gabriel Mountains of Los Angeles County, California. It is within the San Gabriel Mountains National Monument, in the section managed by the Angeles National Forest.

Rusk Mountain is a peak located in the towns of Jewett and Lexington in Greene County, New York, United States. At 3,680 feet (1,120 m) in elevation, it is the 20th-highest peak in the Catskill Mountains and considered a member of the Catskill High Peaks. While there is no maintained trail, a bushwhack to the summit is considered relatively easy, and required for membership in the Catskill Mountain 3500 Club.

On 8 February 1989, Independent Air Flight 1851, a Boeing 707 on an American charter flight from Bergamo, Italy, to Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, struck Pico Alto while on approach to Santa Maria Airport in the Azores for a scheduled stopover. The aircraft was destroyed, with the loss of all 144 people on board, resulting in the deadliest plane crash in Portugal's history. All of the passengers on board were Italian and all of the crew were Americans. The crash is also known as "The disaster of the Azores".

Mount Hood climbing accidents are incidents related to mountain climbing or hiking on Oregon's Mount Hood. As of 2007, about 10,000 people attempt to climb the mountain each year. As of May 2002, more than 130 people are known to have died climbing Mount Hood since records have been kept. One of the worst climbing accidents occurred in 1986, when seven high school students and two teachers froze to death while attempting to retreat from a storm.

Snowy Mountain is a mountain located in Hamilton County, New York. Initially known as 'Squaw Bonnet', its summit is the highest point in the county. While most maps show the elevation as 3899 feet, some suggest that more recent surveys have it as 3904 feet or even 3908 feet.

Balsam Lake Mountain is one of the Catskill Mountains, located in the Town of Hardenburgh, New York, United States. It is the westernmost of the range's 35 High Peaks. Its exact height has not been determined, but the highest contour line on topographic maps, 3,720 feet (1,130 m), is usually given as its elevation.

In climbing and mountaineering, a traverse is a section of a climbing route where the climber moves laterally, as opposed to in an upward direction. The term has broad application, and its use can range from describing a brief section of lateral movement on a pitch of a climbing route, to large multi-pitch climbing routes that almost entirely consist of lateral movement such as girdle traverses that span the entire rock face of a crag, to mountain traverses that span entire ridges connecting chains of mountain peaks.

Sierra de San Carlos, also known as the Sierra Chiquita, is an isolated mountain range in the state of Tamaulipas, Mexico. The climate is semi-arid. The highest point is Cerro El Hongo with an elevation of 1,786 metres (5,860 ft) at a location of 24° 34′ 20″ North Latitude and 99° 04′ 24″ West Longitude. Most of the San Carlos range is much lower, averaging 600 metres (2,000 ft) to 800 metres (2,600 ft) in elevation.