Related Research Articles

Kidney dialysis is the process of removing excess water, solutes, and toxins from the blood in people whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions naturally. This is referred to as renal replacement therapy. The first successful dialysis was performed in 1943.

Semipermeable membrane is a type of biological or synthetic, polymeric membrane that allows certain molecules or ions to pass through it by osmosis. The rate of passage depends on the pressure, concentration, and temperature of the molecules or solutes on either side, as well as the permeability of the membrane to each solute. Depending on the membrane and the solute, permeability may depend on solute size, solubility, properties, or chemistry. How the membrane is constructed to be selective in its permeability will determine the rate and the permeability. Many natural and synthetic materials which are rather thick are also semipermeable. One example of this is the thin film on the inside of an egg.

Hemodialysis, also spelled haemodialysis, or simply dialysis, is a process of purifying the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of dialysis achieves the extracorporeal removal of waste products such as creatinine and urea and free water from the blood when the kidneys are in a state of kidney failure. Hemodialysis is one of three renal replacement therapies. An alternative method for extracorporeal separation of blood components such as plasma or cells is apheresis.

Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications can relate to hormonal dysfunction of the kidneys and include high blood pressure, bone disease, and anemia. Additionally CKD patients have markedly increased cardiovascular complications with increased risks of death and hospitalization.
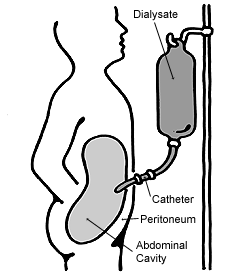
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a type of dialysis that uses the peritoneum in a person's abdomen as the membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with the blood. It is used to remove excess fluid, correct electrolyte problems, and remove toxins in those with kidney failure. Peritoneal dialysis has better outcomes than hemodialysis during the first couple of years. Other benefits include greater flexibility and better tolerability in those with significant heart disease.

Diabetic nephropathy, also known as diabetic kidney disease, is the chronic loss of kidney function occurring in those with diabetes mellitus. Diabetic nephropathy is the leading causes of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) globally. The triad of protein leaking into the urine, rising blood pressure with hypertension and then falling renal function is common to many forms of CKD. Protein loss in the urine due to damage of the glomeruli may become massive, and cause a low serum albumin with resulting generalized body swelling (edema) so called nephrotic syndrome. Likewise, the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) may progressively fall from a normal of over 90 ml/min/1.73m2 to less than 15, at which point the patient is said to have end-stage renal disease. It usually is slowly progressive over years.

Home hemodialysis (HHD) is the provision of hemodialysis to purify the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally, in their own home. One advantage to doing dialysis at home is that it can be done more frequently and slowly, which reduces the "washed out" feeling and other symptoms caused by rapid ultrafiltration, and it can often be done at night, while the person is sleeping.
Artificial kidney is often a synonym for hemodialysis, but may also refer to the other renal replacement therapies that are in use and/or in development. This article deals mainly with bioengineered kidneys/bioartificial kidneys that are grown from renal cell lines/renal tissue.

Hemofiltration, also haemofiltration, is a renal replacement therapy which is used in the intensive care setting. It is usually used to treat acute kidney injury (AKI), but may be of benefit in multiple organ dysfunction syndrome or sepsis. During hemofiltration, a patient's blood is passed through a set of tubing via a machine to a semipermeable membrane where waste products and water are removed by convection. Replacement fluid is added and the blood is returned to the patient.
Waldenström macroglobulinemia is a type of cancer affecting two types of B cells: lymphoplasmacytoid cells and plasma cells. Both cell types are white blood cells. It is characterized by having high levels of a circulating antibody, immunoglobulin M (IgM), which is made and secreted by the cells involved in the disease. Waldenström macroglobulinemia is an "indolent lymphoma" and a type of lymphoproliferative disease which shares clinical characteristics with the indolent non-Hodgkin lymphomas. It is commonly classified as a form of plasma cell dyscrasia, similar to other plasma cell dyscrasias that, for example, lead to multiple myeloma. Waldenström macroglobulinemia is commonly preceded by two clinically asymptomatic but progressively more pre-malignant phases, IgM monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and smoldering Waldenström macroglobulinemia. The Waldenström macroglobulinemia spectrum of dysplasias differs from other spectrums of plasma cell dyscrasias in that it involves not only aberrant plasma cells but also aberrant lymphoplasmacytoid cells and that it involves IgM while other plasma dyscrasias involve other antibody isoforms.

Temocillin is a β-lactamase-resistant penicillin introduced by Beecham, marketed by Eumedica Pharmaceuticals as Negaban. It is used primarily for the treatment of multiple drug-resistant, Gram-negative bacteria.
It is a 6-methoxy penicillin; it is also a carboxypenicillin.

β2 microglobulin (B2M) is a component of MHC class I molecules. MHC class I molecules have α1, α2, and α3 proteins which are present on all nucleated cells. In humans, the β2 microglobulin protein is encoded by the B2M gene.
An artificial cell, synthetic cell or minimal cell is an engineered particle that mimics one or many functions of a biological cell. Often, artificial cells are biological or polymeric membranes which enclose biologically active materials. As such, liposomes, polymersomes, nanoparticles, microcapsules and a number of other particles can qualify as artificial cells.

Cystatin C or cystatin 3, a protein encoded by the CST3 gene, is mainly used as a biomarker of kidney function. Recently, it has been studied for its role in predicting new-onset or deteriorating cardiovascular disease. It also seems to play a role in brain disorders involving amyloid, such as Alzheimer's disease. In humans, all cells with a nucleus produce cystatin C as a chain of 120 amino acids. It is found in virtually all tissues and body fluids. It is a potent inhibitor of lysosomal proteinases and probably one of the most important extracellular inhibitors of cysteine proteases. Cystatin C belongs to the type 2 cystatin gene family.

Dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DBH), also known as dopamine beta-monooxygenase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DBH gene. Dopamine beta-hydroxylase catalyzes the conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine.

Droxidopa is a synthetic amino acid precursor which acts as a prodrug to the neurotransmitter norepinephrine (noradrenaline). Unlike norepinephrine, droxidopa is capable of crossing the protective blood–brain barrier (BBB).
Amyloidosis is the accumulation on misfolded protein fibers in the body. This is very common condition associated with many of the chronic illness. Haemodialysis-associated amyloidosis is a form of systemic amyloidosis associated with chronic kidney failure. Even if this is common in CKD patients with chronic regular dialysis, it can be also seen in patient with CKD but have never dialysed too.
Placental alpha microglobulin-1 (PAMG-1) is a human protein that was first isolated in 1975 from amniotic fluid. PAMG-1 is an important biomarker for the detection of premature rupture of fetal membrane (PROM) The high concentration of PAMG-1 in amniotic fluid means it can be used to detect if this fluid is present in the cervico-vaginal discharge of pregnant women; the presence of PAMG-1 in the discharge suggests that amniotic fluid is present, and therefore suggests that PROM has occurred. PAMG-1 was originally referred to as specific alpha-1 globulin of placenta.
Peginesatide, developed by Affymax and Takeda, is an erythropoietic agent, a functional analog of erythropoietin.
A liver support system or diachysis is a type of therapeutic device to assist in performing the functions of the liver. Such systems focus either on removing the accumulating toxins, or providing additional replacement of the metabolic functions of the liver through the inclusion of hepatocytes to the device. This system is in trial to help people with acute liver failure (ALF) or acute-on-chronic liver failure.
References
- ↑ "Cuprophane". The Free Dictionary. Retrieved 15 August 2014.
- ↑ Sánchez-Villanueva, RJ; González, E; Quirce, S; Díaz, R; Alvarez, L; Menéndez, D; Rodríguez-Gayo, L; Bajo, MA; Selgas, R (July 14, 2014). "Hypersensitivity reactions to synthetic haemodialysis membranes". Nefrologia. 34 (4): 520–525. doi:10.3265/Nefrologia.pre2014.May.12552. PMID 25036066.
- ↑ Corlin, DB; Sen, JW; Ladefoged, S; Lund, GB; Nissen, MH; Heegaard, NH (July 2005). "Quantification of cleaved beta2-microglobulin in serum from patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis". Clinical Chemistry. 51 (7): 1177–84. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2005.049544. PMID 15890888.
- ↑ Traut, M; Haufe, CC; Eismann, U; Deppisch, RM; Stein, G; Wolf, G (2007). "Increased binding of beta-2-microglobulin to blood cells in dialysis patients treated with high-flux dialyzers compared with low-flux membranes contributed to reduced beta-2-microglobulin concentrations. Results of a cross-over study". Blood Purification. 25 (5–6): 432–40. doi:10.1159/000110069. PMID 17957097. S2CID 32302586.