A coupling is a device used to connect two shafts together at their ends for the purpose of transmitting power.The primary purpose of couplings is to join two pieces of rotating equipment while permitting some degree of misalignment or end movement or both. In a more general context, a coupling can also be a mechanical device that serves to connect the ends of adjacent parts or objects. Couplings do not normally allow disconnection of shafts during operation, however there are torque limiting couplings which can slip or disconnect when some torque limit is exceeded. Selection, installation and maintenance of couplings can lead to reduced maintenance time and maintenance cost.

An axle is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearings or bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle is supported. In the latter case, a bearing or bushing sits inside a central hole in the wheel to allow the wheel or gear to rotate around the axle. Sometimes, especially on bicycles, the latter type axle is referred to as a spindle.
Strength of materials, also called mechanics of materials, is a subject which deals with the behavior of solid objects subject to stresses and strains. The complete theory began with the consideration of the behavior of one and two dimensional members of structures, whose states of stress can be approximated as two dimensional, and was then generalized to three dimensions to develop a more complete theory of the elastic and plastic behavior of materials. An important founding pioneer in mechanics of materials was Stephen Timoshenko.
In science, buckling is a mathematical instability that leads to a failure mode.

A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, tailshaft, propeller shaft, or Cardan shaft is a mechanical component for transmitting torque and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drive train that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement between them.
Torsional vibration is angular vibration of an object—commonly a shaft along its axis of rotation. Torsional vibration is often a concern in power transmission systems using rotating shafts or couplings where it can cause failures if not controlled. A second effect of torsional vibrations applies to passenger cars. Torsional vibrations can lead to seat vibrations or noise at certain speeds. Both reduce the comfort.
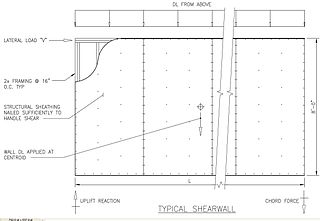
In structural engineering, a shear wall is a vertical element of a seismic force resisting system that is designed to resist in-plane lateral forces, typically wind and seismic loads. In many jurisdictions, the International Building Code and International Residential Code govern the design of shear walls.
Alan Arnold Griffith was the son of Victorian science fiction author George Griffith and an English engineer. Among many other contributions he is best known for his work on stress and fracture in metals that is now known as metal fatigue, as well as being one of the first to develop a strong theoretical basis for the jet engine. Griffith's advanced axial-flow turbojet engine designs, were integral in the creation of Britain's first operational axial-flow turbojet engine, the Metropolitan-Vickers F.2 which first ran successfully in 1941. Griffith however had little direct involvement in actually producing the engine, after he moved in 1939 from leading the engine department at the Royal Aircraft Establishment to start work at Rolls Royce

The reverse bungee is a modern type of fairground ride that was invented by Troy Griffin in c. 1978.
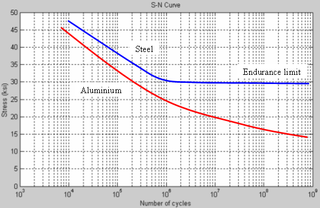
Fatigue limit, endurance limit, and fatigue strength are all expressions used to describe a property of materials: the amplitude of cyclic stress that can be applied to the material without causing fatigue failure. Ferrous alloys and titanium alloys have a distinct limit, called the endurance limit, which is the amplitude of completely reversed bending stress below which there appears to be no number of cycles that will cause failure. Other structural metals such as aluminium and copper do not have a distinct limit and will eventually fail even from small stress amplitudes. In these cases, the term endurance strength is used. Endurance strength is defined as the maximum value of completely reversed bending stress that a material can withstand for a finite number of cycles without a fatigue failure.

Plastic bending is a nonlinear behavior particular to members made of ductile materials that frequently achieve

A swashplate, invented by Anthony George Maldon Michell in 1917, is a device used in mechanical engineering to translate the motion of a rotating shaft into reciprocating motion, or vice versa. The working principles is similar to crankshaft, Scotch yoke, or wobble/nutator/Z-crank drives, in engine designs. It was originally invented to replace a crankshaft, and is one of the most popular concepts used in crankless engines.
A string potentiometer is a transducer used to detect and measure linear position and velocity using a flexible cable and spring-loaded spool. Other common names include "string pot", "cable-extension transducer", "draw wire sensor", and "yo-yo sensor".

A rowing cycle is a wheeled vehicle propelled by a rowing motion of the body. Steering, braking, and shifting are usually done by the handlebars. Feet are on symmetrical foot rests, as opposed to rotating pedals. Unlike many rowing boats, the rider faces forward. Rowing cycles exist in numerous designs, particularly with respect to frames and drive mechanisms. Commercial production numbers for rowing cycles are small compared to that of standard bicycles.
The balancing of rotating bodies is important to avoid vibration. In heavy industrial machines such as gas turbines and electric generators, vibration can cause catastrophic failure, as well as noise and discomfort. In the case of a narrow wheel, balancing simply involves moving the center of gravity to the centre of rotation. For a system to be in complete balance both force and couple polygons should be closed.in order to prevent the effect of centrifugal force..
Polymer fracture is the study of the fracture surface of an already failed material to determine the method of crack formation and extension in polymers both fiber reinforced and otherwise. Failure in polymer components can occur at relatively low stress levels, far below the tensile strength because of four major reasons: long term stress or creep rupture, cyclic stresses or fatigue, the presence of structural flaws and stress-cracking agents. Formations of submicroscopic cracks in polymers under load have been studied by x ray scattering techniques and the main regularities of crack formation under different loading conditions have been analyzed. The low strength of polymers compared to theoretically predicted values are mainly due to the many microscopic imperfections found in the material. These defects namely dislocations, crystalline boundaries, amorphous interlayers and block structure can all lead to the non-uniform distribution of mechanical stress.
A nickel titanium (NiTi) rotary file is an engine-driven tapered and pointed endodontic instrument made of nickel titanium alloy with cutting edges used to mechanically shape and prepare the root canals during endodontic therapy or to remove the root canal obturating material while performing retreatment. The first NiTi file was introduced to the market in 1991. Superelasticity and shape memory are the properties that make Niti files very flexible. The high flexibility of Niti files makes them superior to stainless steel files for the purpose of rotary root canal preparation. The use of NiTi rotary files in dentistry is a common practice.