
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. The term column applies especially to a large round support with a capital and a base or pedestal, which is made of stone, or appearing to be so. A small wooden or metal support is typically called a post, and supports with a rectangular or other non-round section are usually called piers.
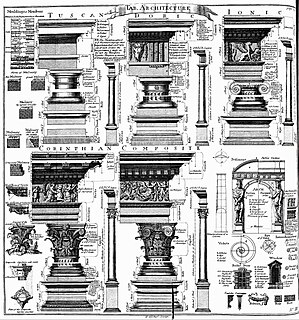
An order in architecture is a certain assemblage of parts subject to uniform established proportions, regulated by the office that each part has to perform. Coming down to the present from Ancient Greek and Ancient Roman civilization, the architectural orders are the styles of classical architecture, each distinguished by its proportions and characteristic profiles and details, and most readily recognizable by the type of column employed. The three orders of architecture—the Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian—originated in Greece. To these the Romans added, in practice if not in name, the Tuscan, which they made simpler than Doric, and the Composite, which was more ornamental than the Corinthian. The architectural order of a classical building is akin to the mode or key of classical music; the grammar or rhetoric of a written composition. It is established by certain modules like the intervals of music, and it raises certain expectations in an audience attuned to its language.

In architecture, the frieze is the wide central section part of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic or Doric order, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Paterae are also usually used to decorate friezes. Even when neither columns nor pilasters are expressed, on an astylar wall it lies upon the architrave and is capped by the moldings of the cornice. A frieze can be found on many Greek and Roman buildings, the Parthenon Frieze being the most famous, and perhaps the most elaborate. This style is typical for the Persians.
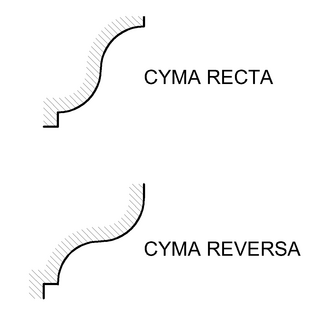
An ogee ( ) is the name given to objects, elements, and curves—often seen in architecture and building trades—that have been variously described as serpentine-, extended S-, or sigmoid-shaped. Ogees consist of a "double curve", the combination of two semicircular curves or arcs that, as a result of a point of inflection from concave to convex or vice versa, have ends of the overall curve that point in opposite directions.

In architecture the capital or chapiter forms the topmost member of a column. It mediates between the column and the load thrusting down upon it, broadening the area of the column's supporting surface. The capital, projecting on each side as it rises to support the abacus, joins the usually square abacus and the usually circular shaft of the column. The capital may be convex, as in the Doric order; concave, as in the inverted bell of the Corinthian order; or scrolling out, as in the Ionic order. These form the three principal types on which all capitals in the classical tradition are based. The Composite order established in the 16th century on a hint from the Arch of Titus, adds Ionic volutes to Corinthian acanthus leaves.

In architecture, an abacus is a flat slab forming the uppermost member or division of the capital of a column, above the bell. Its chief function is to provide a large supporting surface, tending to be wider than the capital, as an abutment to receive the weight of the arch or the architrave above. The diminutive of abacus, abaculus, is used to describe small mosaic tiles, also called abaciscus or tessera, used to create ornamental floors with detailed patterns of chequers or squares in a tessellated pavement.

An entablature is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and are commonly divided into the architrave, the frieze, and the cornice. The Greek and Roman temples are believed to be based on wooden structures, the design transition from wooden to stone structures being called petrification.

Moulding, also known as coving(United Kingdom, Australia), is a strip of material with various profiles used to cover transitions between surfaces or for decoration. It is traditionally made from solid milled wood or plaster, but may be of plastic or reformed wood. In classical architecture and sculpture, the molding is often carved in marble or other stones.

The palmette is a motif in decorative art which, in its most characteristic expression, resembles the fan-shaped leaves of a palm tree. It has a far-reaching history, originating in ancient Egypt with a subsequent development through the art of most of Eurasia, often in forms that bear relatively little resemblance to the original. In ancient Greek and Roman uses it is also known as the anthemion. It is found in most artistic media, but especially as an architectural ornament, whether carved or painted, and painted on ceramics. It is very often a component of the design of a frieze or border. The complex evolution of the palmette was first traced by Alois Riegl in his Stilfragen of 1893. The half-palmette, bisected vertically, is also a very common motif, found in many mutated and vestigial forms, and especially important in the development of plant-based scroll ornament.

The ovolo or echinus is a convex decorative molding profile used in architectural ornamentation. Its profile is a quarter to a half of a more or less flattened circle.
This page is a glossary of architecture.

A cavetto is a concave moulding with a regular curved profile that is part of a circle, widely used in architecture as well as furniture, picture frames, metalwork and other decorative arts. In describing vessels and similar shapes in pottery, metalwork and related fields, "cavetto" may be used of a variety of concave curves running round objects. The word comes from Italian, as a diminutive of cave, from the Latin for "hollow". A vernacular alternative is "cove", most often used where interior walls curve at the top to make a transition to the roof, or for "upside down" cavettos at the bases of elements.

The acanthus is one of the most common plant forms to make foliage ornament and decoration.

A taenia is a small "fillet" molding near the top of the architrave in a Doric column.

Egg-and-dart, also known as egg-and-tongue, egg and anchor, or egg and star, is an ornamental device adorning the fundamental quarter-round, convex ovolo profile of moulding, consisting of alternating details on the face of the ovolo—typically an egg-shaped object alternating with a V-shaped element. The device is carved or otherwise fashioned into ovolos composed of wood, stone, plaster, or other materials.
A fleuron is a flower-shaped ornament, and in architecture may have a number of meanings:
- It is a collective noun for the ornamental termination at the ridge of a roof, such as a crop, finial or épi.
- It is also a form of stylised Late Gothic decoration in the form of a four-leafed square, often seen on crockets and cavetto mouldings.
- It can be the ornament in the middle of each concave face of a Corinthian abacus.
- Finally, it can be a form of anthemion, the decorative Greek floral decoration.

The Lion Capital of Ashoka is a sculpture of four Asiatic lions standing back to back, on an elaborate base that includes other animals. A graphic representation of it was adopted as the official Emblem of India in 1950. It was originally placed on the top of the Ashoka pillar at the important Buddhist site of Sarnath by the Emperor Ashoka, in about 250 BCE during his rule over the Maurya Empire. The pillar, sometimes called the Aśoka Column, is still in its original location, but the Lion Capital is now in the Sarnath Museum, in the state of Uttar Pradesh, India. Standing 2.15 metres high including the base, it is more elaborate than the other very similar surviving capitals of the pillars of Ashoka bearing the Edicts of Ashoka that were placed throughout India several of which feature single animals at the top; one other damaged group of four lions survives, at Sanchi.

The Pataliputra capital is a monumental rectangular capital with volutes and Classical Greek designs, that was discovered in the palace ruins of the ancient Mauryan Empire capital city of Pataliputra. It is dated to the 3rd century BCE.

An anta capital is the crowning portion of an anta, the front edge of a supporting wall in Greek temple architecture. The anta is generally crowned by a stone block designed to spread the load from superstructure (entablature) it supports, called an "anta capitals" when it is structural, or sometimes "pilaster capital" if it is only decorative as often during the Roman period.
















