Related Research Articles

In architecture, a hall is a relatively large space enclosed by a roof and walls. In the Iron Age and early Middle Ages in northern Europe, a mead hall was where a lord and his retainers ate and also slept. Later in the Middle Ages, the great hall was the largest room in castles and large houses, and where the servants usually slept. As more complex house plans developed, the hall remained a large room for dancing and large feasts, often still with servants sleeping there. It was usually immediately inside the main door. In modern British houses, an entrance hall next to the front door remains an indispensable feature, even if it is essentially merely a corridor.

Cyzicus was an ancient Greek town in Mysia in Anatolia in the current Balıkesir Province of Turkey. It was located on the shoreward side of the present Kapıdağ Peninsula, a tombolo which is said to have originally been an island in the Sea of Marmara only to be connected to the mainland in historic times either by artificial means or an earthquake.

Antiochus IX Eusebes Cyzicenus was a ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid kingdom. He was the son of Antiochus VII Sidetes and Cleopatra Thea. He left the kingdom in 129 BC and went to the city of Cyzicus, but he returned in 116 BC to challenge his half-brother Antiochus VIII for power.

A triforium is an interior gallery, opening onto the tall central space of a building at an upper level. In a church, it opens onto the nave from above the side aisles; it may occur at the level of the clerestory windows, or it may be located as a separate level below the clerestory. Masonry triforia are generally vaulted and separated from the central space by arcades. Early triforia were often wide and spacious, but later ones tend to be shallow, within the thickness of an inner wall, and may be blind arcades not wide enough to walk along. The outer wall of the triforium may itself have windows, or it may be solid stone. A narrow triforium may also be called a "blind-storey", and looks like a row of window frames.

In classical architecture, a colonnade is a long sequence of columns joined by their entablature, often free-standing, or part of a building. Paired or multiple pairs of columns are normally employed in a colonnade which can be straight or curved. The space enclosed may be covered or open. In St. Peter's Square in Rome, Bernini's great colonnade encloses a vast open elliptical space.

A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures.

A transept is a transverse part of any building, which lies across the main body of the building. In cruciform ("cross-shaped") churches, in particular within the Romanesque and Gothic Christian church architectural traditions, a transept is an area set crosswise to the nave. Each half of a transept is known as a semitransept.
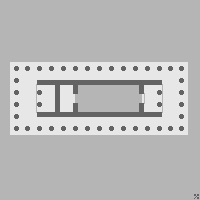
In Classical architecture, a cella or naos is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings, of a hermit's or monk's cell, and since the 17th century, of a biological cell in plants or animals.

In architecture, a hypostyle hall has a roof which is supported by columns.

An acrolith is a composite sculpture made of stone together with other materials such as wood or inferior stone such as limestone, as in the case of a figure whose clothed parts are made of wood, while the exposed flesh parts such as head, hands, and feet are made of marble. The wood was covered either by drapery or by gilding. This type of statuary was common and widespread in Classical antiquity.

Russell Sturgis was an American architect and art critic of the 19th and early 20th centuries. He was one of the founders of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in 1870.
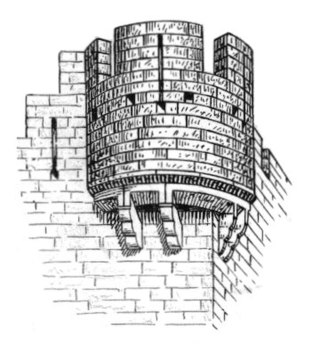
A bartizan, also called a guerite, garita, or échauguette, or spelled bartisan, is an overhanging turret projecting from the walls of late-medieval and early-modern fortifications from the early 14th century up to the 18th century. Most frequently found at corners, they protected a warder and enabled him to see his surroundings. Bartizans are generally furnished with oillets or arrow slits. The turret was usually supported by stepped masonry corbels and could be round, polygonal or square.

A festoon is a wreath or garland hanging from two points, and in architecture typically a carved ornament depicting conventional arrangement of flowers, foliage or fruit bound together and suspended by ribbons. The motif is sometimes known as a swag when depicting fabric or linen.
A bellcote, bell-cote or bell-cot is a small framework and shelter for one or more bells. Bellcotes are most common in church architecture but are also seen on institutions such as schools. The bellcote may be carried on brackets projecting from a wall or built on the roof of chapels or churches that have no towers. The bellcote often holds the Sanctus bell that is rung at the consecration of the Eucharist.
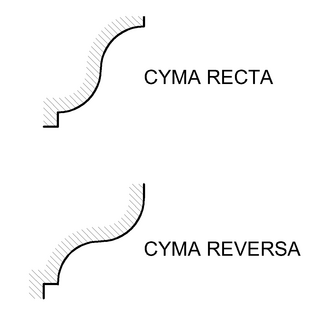
Ovolo is an Italian word that means "little egg".The ovolo or echinus is a convex decorative molding profile used in architectural ornamentation. Its profile is a quarter to a half of a more or less flattened circle.

Giorgio da Sebenico or Giorgio Orsini or Juraj Dalmatinac was a Venetian sculptor and architect from Dalmatia, who worked mainly in Sebenico, and in the city of Ancona, then a maritime republic.

A vestibule is a small room leading into a larger space such as a lobby, entrance hall, or passage, for the purpose of waiting, withholding the larger space from view, reducing heat loss, providing storage space for outdoor clothing, etc. The term applies to structures in both modern and classical architecture since ancient times.

Xystus was the Greek architectural term for the covered portico of the gymnasium, in which the exercises took place during the winter or in rainy weather. The Romans applied the term to the garden walk in front of the porticoes, which was divided into flower beds with borders of box, and to a promenade between rows of large trees.
Cyzicenus may refer to:
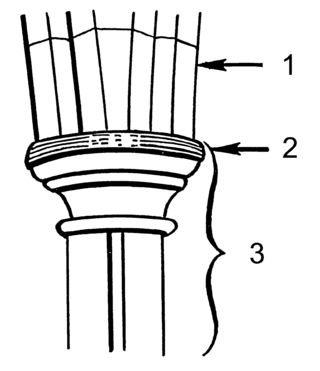
In architecture, an impost or impost block is a projecting block resting on top of a column or embedded in a wall, serving as the base for the springer or lowest voussoir of an arch.
References
- ↑ Chisholm 1911.
- ↑ Sturgis, Russell; Davis, Francis A. (2013). Sturgis' Illustrated Dictionary of Architecture and Building: An Unabridged Reprint of the 1901-2 Edition. Courier Corporation. p. 735. ISBN 978-0-486-14840-3.
- This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Cyzicenus". Encyclopædia Britannica . Vol. 7 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 720.
- Sturgis, Russel. " Cyzicene Hall" in A Dictionary of Architecture and Building, Biographical, Historical, . . . MacMillan Co., 1901, pp. 738–739.