In telecommunications, asynchronous communication is transmission of data, generally without the use of an external clock signal, where data can be transmitted intermittently rather than in a steady stream. Any timing required to recover data from the communication symbols is encoded within the symbols.
The Internet protocol suite is the conceptual model and set of communications protocols used in the Internet and similar computer networks. It is commonly known as TCP/IP because the foundational protocols in the suite are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP). It is occasionally known as the Department of Defense (DoD) model because the development of the networking method was funded by the United States Department of Defense through DARPA.
In computer networking, Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is a data link layer communications protocol used to establish a direct connection between two nodes. It connects two routers directly without any host or any other networking device in between. It can provide connection authentication, transmission encryption, and compression.
In telecommunication, a longitudinal redundancy check (LRC), or horizontal redundancy check, is a form of redundancy check that is applied independently to each of a parallel group of bit streams. The data must be divided into transmission blocks, to which the additional check data is added.
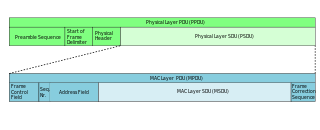
In telecommunications, a protocol data unit (PDU) is a single unit of information transmitted among peer entities of a computer network. A PDU is composed of protocol specific control information and user data. In the layered architectures of communication protocol stacks, each layer implements protocols tailored to the specific type or mode of data exchange.

The Infrared Data Association (IrDA) is an industry-driven interest group that was founded in 1993 by around 50 companies. IrDA provides specifications for a complete set of protocols for wireless infrared communications, and the name "IrDA" also refers to that set of protocols. The main reason for using IrDA had been wireless data transfer over the "last one meter" using point-and-shoot principles. Thus, it has been implemented in portable devices such as mobile telephones, laptops, cameras, printers, and medical devices. Main characteristics of this kind of wireless optical communication is physically secure data transfer, line-of-sight (LOS) and very low bit error rate (BER) that makes it very efficient.
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the presentation layer is layer 6 and serves as the data translator for the network. It is sometimes called the syntax layer.
In computer networking, the transport layer is a conceptual division of methods in the layered architecture of protocols in the network stack in the Internet protocol suite and the OSI model. The protocols of this layer provide host-to-host communication services for applications. It provides services such as connection-oriented communication, reliability, flow control, and multiplexing.
ISO/IEC 14443 Identification cards -- Contactless integrated circuit cards -- Proximity cards is an international standard that defines proximity cards used for identification, and the transmission protocols for communicating with it.
In electrical engineering and power system automation, the International Electrotechnical Commission 60870 standards define systems used for telecontrol. Such systems are used for controlling electric power transmission grids and other geographically widespread control systems. By use of standardized protocols, equipment from many different suppliers can be made to interoperate. IEC standard 60870 has six parts, defining general information related to the standard, operating conditions, electrical interfaces, performance requirements, and data transmission protocols. The 60870 standards are developed by IEC Technical Committee 57.
Manufacturing Message Specification (MMS) is an international standard dealing with messaging systems for transferring real time process data and supervisory control information between networked devices or computer applications. The standard is developed and maintained by the ISO Technical Committee 184 (TC184). MMS defines the following
IEC 62056 is a set of standards for Electricity metering data exchange by International Electrotechnical Commission. The IEC 62056 standards are the International Standard versions of the DLMS/COSEM specification.
DLMS or Device Language Message Specification, is the suite of standards developed and maintained by the DLMS User Association and has been adopted by the IEC TC13 WG14 into the IEC 62056 series of standards. The DLMS User Association maintains a D Type liaison with IEC TC13 WG14 responsible for international standards for meter data exchange and establishing the IEC 62056 series. In this role, the DLMS UA provides maintenance, registration and compliance certification services for IEC 62056 DLMS/COSEM.
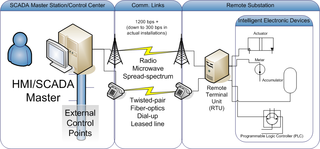
DNP3 is a set of communications protocols used between components in process automation systems. Its main use is in utilities such as electric and water companies. Usage in other industries is not common. It was developed for communications between various types of data acquisition and control equipment. It plays a crucial role in SCADA systems, where it is used by SCADA Master Stations, Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), and Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs). It is primarily used for communications between a master station and RTUs or IEDs. ICCP, the Inter-Control Center Communications Protocol, is used for inter-master station communications. Competing standards include the older Modbus protocol and the newer IEC 61850 protocol.
CANopen is a communication protocol and device profile specification for embedded systems used in automation. In terms of the OSI model, CANopen implements the layers above and including the network layer. The CANopen standard consists of an addressing scheme, several small communication protocols and an application layer defined by a device profile. The communication protocols have support for network management, device monitoring and communication between nodes, including a simple transport layer for message segmentation/desegmentation. The lower level protocol implementing the data link and physical layers is usually Controller Area Network (CAN), although devices using some other means of communication can also implement the CANopen device profile.
CEN ISO/IEEE 11073 Health informatics - Medical / health device communication standards enable communication between medical, health care and wellness devices and with external computer systems. They provide automatic and detailed electronic data capture of client-related and vital signs information, and of device operational data.
MIOS or Meter Inter Operability Solution is a specification for interoperability of electric meters for remote meter reading applications in India proposed by IEEMA in 2008. and is developed and maintained by Metering India which is a group of Meter Manufacturers.
IEC 60870 part 6 is one of the IEC 60870 set of standards which define systems used for telecontrol in electrical engineering and power system automation applications. The IEC Technical Committee 57 have developed part 6 to provide a communication profile for sending basic telecontrol messages between two systems which is compatible with ISO standards and ITU-T recommendations.
In telecommunication, a communication protocol is a system of rules that allow two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any kind of variation of a physical quantity. The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics and synchronization of communication and possible error recovery methods. Protocols may be implemented by hardware, software, or a combination of both.
IEC 60870 part 5 is one of the IEC 60870 set of standards which define systems used for telecontrol in electrical engineering and power system automation applications. Part 5 provides a communication profile for sending basic telecontrol messages between two systems, which uses permanent directly connected data circuits between the systems. The IEC Technical Committee 57 have developed a protocol standard for telecontrol, teleprotection, and associated telecommunications for electric power systems. The result of this work is IEC 60870-5. Five documents specify the base IEC 60870-5:





