
Digital television (DTV) is the transmission of television signals using digital encoding, in contrast to the earlier analog television technology which used analog signals. At the time of its development it was considered an innovative advancement and represented the first significant evolution in television technology since color television in the 1950s. Modern digital television is transmitted in high-definition television (HDTV) with greater resolution than analog TV. It typically uses a widescreen aspect ratio in contrast to the narrower format of analog TV. It makes more economical use of scarce radio spectrum space; it can transmit up to seven channels in the same bandwidth as a single analog channel, and provides many new features that analog television cannot. A transition from analog to digital broadcasting began around 2000. Different digital television broadcasting standards have been adopted in different parts of the world; below are the more widely used standards:

A set-top box (STB), also colloquially known as a cable box and historically television decoder, is an information appliance device that generally contains a TV-tuner input and displays output to a television set and an external source of signal, turning the source signal into content in a form that can then be displayed on the television screen or other display device. They are used in cable television, satellite television, and over-the-air television systems as well as other uses.

TiVo is a digital video recorder (DVR) developed and marketed by Xperi and introduced in 1999. TiVo provides an on-screen guide of scheduled broadcast programming television programs, whose features include "OnePass" schedules which record every new episode of a series, and "WishList" searches which allow the user to find and record shows that match their interests by title, actor, director, category, or keyword. TiVo also provides a range of features when the TiVo DVR is connected to a home network, including film and TV show downloads, advanced search, personal photo viewing, music offerings, and online scheduling.

DISH Network Corporation is an American television provider and the owner of the direct-broadcast satellite provider Dish, commonly known as Dish Network, and the over-the-top IPTV service, Sling TV. Additionally, Dish offers mobile wireless service, Dish Wireless. On July 1, 2020, Dish acquired prepaid service Boost Mobile and intends to add postpaid service as well in the future. Based out of unincorporated Douglas County, Colorado the company has approximately 16,000 employees.
A digital video recorder (DVR) is an electronic device that records video in a digital format to a disk drive, USB flash drive, SD memory card, SSD or other local or networked mass storage device. The term includes set-top boxes with direct to disk recording, portable media players and TV gateways with recording capability, and digital camcorders. Personal computers are often connected to video capture devices and used as DVRs; in such cases the application software used to record video is an integral part of the DVR. Many DVRs are classified as consumer electronic devices; such devices may alternatively be referred to as personal video recorders (PVRs), particularly in Canada. Similar small devices with built-in displays and SSD support may be used for professional film or video production, as these recorders often do not have the limitations that built-in recorders in cameras have, offering wider codec support, the removal of recording time limitations and higher bitrates.

The All-Channel Receiver Act of 1962 (ACRA), commonly known as the All-Channels Act, was passed by the United States Congress in 1961, to allow the Federal Communications Commission to require that all television set manufacturers must include UHF tuners, so that new UHF-band TV stations could be received by the public. This was a problem at the time since most affiliated stations of the Big Three television networks were well-established on VHF, while many local-only stations on UHF were struggling for survival.
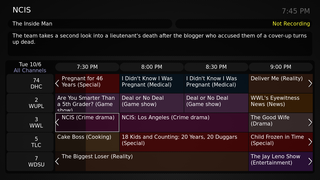
Electronic programming guides (EPGs) and interactive programming guides (IPGs) are menu-based systems that provide users of television, radio and other media applications with continuously updated menus that display scheduling information for current and upcoming broadcast programming. Some guides also feature backward scrolling to promote their catch up content. They are commonly known as guides or TV guides.
Smart antennas are antenna arrays with smart signal processing algorithms used to identify spatial signal signatures such as the direction of arrival (DOA) of the signal, and use them to calculate beamforming vectors which are used to track and locate the antenna beam on the mobile/target. Smart antennas should not be confused with reconfigurable antennas, which have similar capabilities but are single element antennas and not antenna arrays.
Zoran Corporation was a multinational digital technology company, founded in 1981 and headquartered in Silicon Valley, that was predominantly focused on designing and selling SoC integrated circuits for consumer electronics applications. The name Zoran is derived from the Hebrew word for silicon. Zoran was incorporated in the state of Delaware and had offices in Canada, China, England, Germany, India, Israel, Japan, Korea, Taiwan, and the US. Zoran had strong ties with Israel, with a strong R&D presence and being the beneficiary of incentives from organizations such as Israel's Ministry of Industry and Trade.
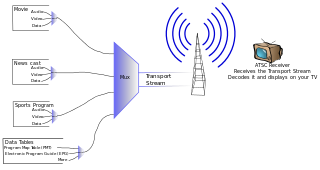
An ATSCtuner, often called an ATSC receiver or HDTV tuner, is a type of television tuner that allows reception of digital television (DTV) television channels that use ATSC standards, as transmitted by television stations in North America, parts of Central America, and South Korea. Such tuners are usually integrated into a television set, VCR, digital video recorder (DVR), or set-top box which provides audio/video output connectors of various types.

A digital television adapter (DTA), commonly known as a converter box or decoder box, is a television tuner that receives a digital television (DTV) transmission, and converts the digital signal into an analog signal that can be received and displayed on an analog television set. Some also have an HDMI output since some TVs with HDMI do not have a digital tuner. The input digital signal may be over-the-air terrestrial television signals received by a television antenna, or signals from a digital cable system. It normally does not refer to satellite TV, which has always required a set-top box either to operate the big satellite dish, or to be the integrated receiver/decoder (IRD) in the case of direct-broadcast satellites (DBS).

DIRECTV is an American multichannel video programming distributor based in El Segundo, California. Originally launched on June 17, 1994, its primary service is a digital satellite service serving the United States. It also provides traditional linear television service delivered by IP through its U-verse TV brand and a Virtual MVPD service through its DIRECTV STREAM brand. Its primary competitors are Dish Network, traditional cable television providers, IP-based television services, and other over-the-top video services.

A coupon-eligible converter box (CECB) was a digital television adapter that met eligibility specifications for subsidy "coupons" from the United States government. The subsidy program was enacted to provide terrestrial television viewers with an affordable way to continue receiving free digital terrestrial television services after the nation's television service transitioned to digital transmission and analog transmissions ceased. The specification was developed by the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA), with input from the broadcast and consumer electronics industries as well as public interest groups.
Digital television in the United States is available via digital terrestrial television (DTT), digital cable, satellite television, and IPTV providers.

A cable converter box or television converter box is an electronic tuning device that transposes/converts channels from a cable television service to an analog RF signal on a single channel, usually VHF channel 3 or 4, or to a different output for digital televisions such as HDMI.
When a descrambler is added to the Cable Converter Box in the same chassis, it is referred to as a Converter/Descrambler or sometimes a Combination Unit, and is a type of Set-top box, it allows : local broadcast channels, basic cable channels, authorized premium channels, "Pay-Per-View" (PPV), and “Video On Demand” (VOD) services to be viewed. A Combination Converter/Descrambler is generally called a Set-top box or STB it is a single (one-piece) system installed in a single cabinet and represents a single component that is capable of descrambling premium services, like HBO or Showtime, pay-per-view cable channels., Video on Demand, Games or other specialty pay services, and transposes the cable signal for RF output on channel 3 or 4. This unit contains a converter and a descrambler, enclosed in a common box and outputs the signal directly to a TV, VCR, DVR, PC, DVD or video projector.
Analog passthrough is a feature found on some digital-to-analog television converter boxes. Boxes without analog passthrough only allow digital TV to be viewed on older, analog-only TVs. Those with analog passthrough allow both digital and analog television to be viewed on older TVs.
The digital transition in the United States was the switchover from analog to exclusively digital broadcasting of terrestrial television programming. According to David Rehr, then president and CEO of the National Association of Broadcasters, this transition represented "the most significant advancement of television technology since color TV was introduced." For full-power TV stations, the transition went into effect on June 12, 2009, with stations ending regular programming on their analog signals no later than 11:59 p.m. local time that day.
The Community Broadcasters Association (CBA) was a trade organization representing low-power broadcasting interests, including LPTV and Class A television stations, in the United States of America. It ceased operations in 2009.

Hopper is a line of digital video recording (DVR) set-top boxes offered by the U.S. direct-broadcast satellite television provider Dish Network. First introduced at Consumer Electronics Show in January 2012, the Hopper was released in March 2012 as a component of the provider's whole-home DVR system, which networks the main Hopper unit with smaller "Joey" set-top boxes to form a client-server architecture.












