
Usually found in gram-positive bacteria, the T box leader sequence is an RNA element that controls gene expression through the regulation of translation by binding directly to a specific tRNA and sensing its aminoacylation state. This interaction controls expression of downstream aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase genes, amino acid biosynthesis, and uptake-related genes in a negative feedback loop. The uncharged tRNA acts as the effector for transcription antitermination of genes in the T-box leader family. The anticodon of a specific tRNA base pairs to a specifier sequence within the T-box motif, and the NCCA acceptor tail of the tRNA base pairs to a conserved bulge in the T-box antiterminator hairpin.

Coronin-6 also known as coronin-like protein E (Clipin-E) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CORO6 gene.

The DUF1646 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. One of the two DUF1646 RNAs in Enterococcus faecalis was independently detected by term-seq. Data from both discoveries suggest that DUF1646 RNAs are cis-regulatory RNAss, and that at least some DUF1646 RNAs use Rho-independent transcription terminators as their mechanism to regulate gene expression.
DUF3800 RNA motifs refer to conserved RNA structures that were discovered by bioinformatics and are usually located nearby to genes that encode proteins containing the conserved domain called "DUF3800". However, the gene can be located 5′ or 3′ relative to the RNA, and could be on the same or on the opposite DNA strand. This arrangement is typical of RNA and proteins that function as an RNA-protein complex, but could have other explanations. The function of this protein domain is unknown, and no specific biological function has been proposed for the RNA. However, after the detection of the RNA motifs, DUF3800 domains were predicted to be involved with retrons.
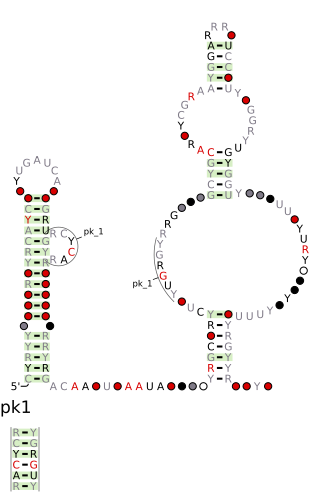
The DUF2800 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. DUF2800 motif RNAs are found in Bacillota. DUF2800 RNAs are also predicted in the phyla Actinomycetota and Synergistota, although these RNAs are likely the result of recent horizontal gene transfer or conceivably sequence contamination.

The DUF2815 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. As of 2018, the DUF2815 motif has not been identified in any classified organism, but is known through metagenomic sequences isolated from environmental sources.

The DUF3268 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. DUF3268 motifs are found in Bacillota and Clostridia.

The DUF805 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. The motif is subdivided into the DUF805 motif and the DUF805b motif, which have similar, but distinct secondary structures. Together, these motifs are found in Bacteroidota, Chlorobiota, and Pseudomonadota.
The freshwater-2 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Freshwater-2 motif RNAs are found in metagenomic sequences that are isolated from aquatic and especially freshwater environments. As of 2018, no freshwater-2 RNA has been identified in a classified organism.

The ftsZ-DE RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. ftsZ-DE motifs are found in bacteria belonging to the genus Fibrobacter.

The IMPDH RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. IMPDH motif RNAs are found in organisms classified within the genus Faecalibacterium.
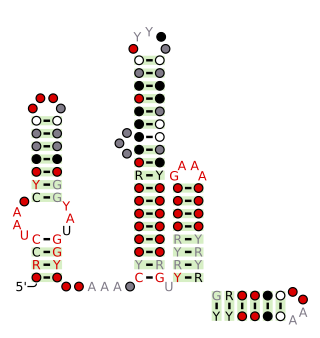
The Latescibacteria, OD1, OP11, TM7 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. LOOT motif RNAs are found in multiple bacterial phyla that have only recently been discovered, and are currently not well understood: Latescibacteria, OD1/Parcubacteria, OP11 AND TM7. In some cases, no specific organism has been isolated in the relevant phylum, but the existence of the bacterial phylum is known only through analysis of metagenomic sequences. Curiously, the LOOT motif is not known in any phylum that has been studied for a long time.
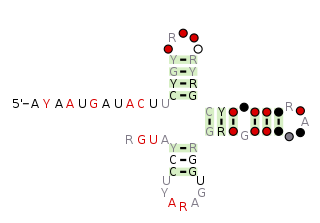
The pemK RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. pemK motif RNAs are found in organisms within the phylum Bacillota, and is very widespread in this phylum.

The PGK RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. PGK motif RNAs are found in metagenomic sequences isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of mammals. PGK RNAs have not yet been detected in a classified organism.
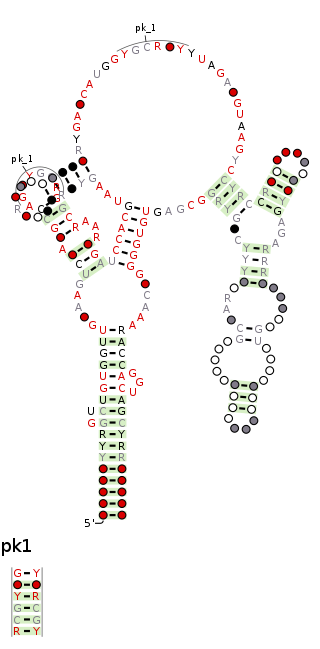
The raiA RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. raiA motif RNAs are found in Actinomycetota and Bacillota, and have many conserved features—including conserved nucleotide positions, conserved secondary structures and associated protein-coding genes—in both of these phyla. Some conserved features of the raiA RNA motif suggest that they function as cis-regulatory elements, but other aspects of the motif suggest otherwise.
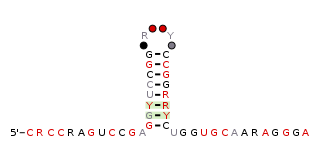
The raiA-hairpin RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. raiA-hairpin motif RNAs are found in organism classified within the genus Streptomyces.

The skipping-rope RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. skipping-rope motif RNAs are found in multiple phyla: Bacillota, Fusobacteriota, Pseudomonadota and Spirochaetota. A skipping-rope RNA was also found in a purified phage, specifically the phage Bacillus phage SPbeta, which infects Bacillus organisms that fit into the phylum Bacillota. Therefore, skipping-rope RNAs likely function, at least sometimes, to perform a function useful to phages.

The sul1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Energetically stable tetraloops often occur in this motif. sul1 motif RNAs are found in Alphaproteobacteria.

The terC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. terC motif RNAs are found in Pseudomonadota, within the sub-lineages Alphaproteobacteria and Pseudomonadales.

The uup RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. uup motif RNAs are found in Bacillota and Gammaproteobacteria.


















