
The Niger River is the main river of West Africa, extending about 4,180 kilometres. Its drainage basin is 2,117,700 km2 (817,600 sq mi) in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, Niger, on the border with Benin and then through Nigeria, discharging through a massive delta, known as the Niger Delta, into the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean. The Niger is the third-longest river in Africa, exceeded by the Nile and the Congo River. Its main tributary is the Benue River.

The Kura is an east-flowing river south of the Greater Caucasus Mountains which drains the southern slopes of the Greater Caucasus east into the Caspian Sea. It also drains the north side of the Lesser Caucasus, while its main tributary, the Aras, drains the south side of those mountains. Starting in northeastern Turkey, the Kura flows through Turkey to Georgia, then to Azerbaijan, where it receives the Aras as a right tributary, and enters the Caspian Sea at Neftçala. The total length of the river is 1,515 kilometres (941 mi).

N'guigmi is a city and Commune of fifteen thousand in the easternmost part of Niger, very near to Lake Chad – lying on its shore until the lake retreated. It is a crossroads for the traditional camel caravans of the Toureg and for traders plying North and South across the Sahara.
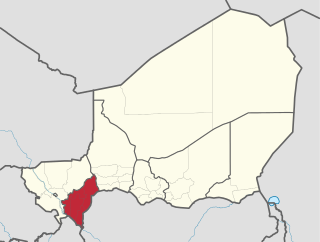
Dosso is one of the eight Regions of Niger. The region has an area of 31,002 square kilometres (11,970 sq mi), with a population of 2,754,500 as of 2020.

Periyar, IPA:[peɾijɐːr], is the longest river and the river with the largest discharge potential in the Indian state of Kerala. It is one of the few perennial rivers in the region and provides drinking water for several major towns. The Periyar is of utmost significance to the economy of Kerala. It generates a significant proportion of Kerala's electrical power via the Idukki Dam and flows along a region of industrial and commercial activity. The river also provides water for irrigation and domestic use throughout its course besides supporting a rich fishery. Due to these reasons, the river has been named the "Lifeline of Kerala". Kochi city, in the vicinity of the river mouth, draws its water supply from Aluva, an upstream site sufficiently free of seawater intrusion. Twenty five percent of Kerala's industries are along the banks of the Periyar. These are mostly crowded within a stretch of 5 kilometres (3 mi) in the Eloor-Edayar region (Udhyogamandal), about 10 kilometres (6 mi) north of Kochi harbor.

Abalak is a town located in the Tahoua Region, Abalak Department of northern Niger. It is both a town and Commune: a local administrative division. It is the seat (Chef-lieu) of Abalak Department, one of eight subdivisions of Tahoua Region. The town had a population of less than 74,719 at the 2012 census.

Dongondoutchi is a commune in Niger. It is located about 300 km east of the capital Niamey and 40 km from the Nigerian border. It lies on national route 1 which links the capital to the towns of Maradi and Zinder to the east and the RN25 heading to north to Tahoua, Agadez and Arlit.

The North Saskatchewan River is a glacier-fed river that flows from the Canadian Rockies continental divide east to central Saskatchewan, where it joins with the South Saskatchewan River to make up the Saskatchewan River. Its water flows eventually into the Hudson Bay.
In-Gall is a department, commune and town in the Agadez Region of northeast Niger, with a year-round population of less than 500. Known for its oasis and salt flats, In-Gall is the gathering point for the Cure Salee festival of Tuareg and Wodaabe pastoralists to celebrate the end of the rainy season each September. During the festival, In-Gall's population grows to several thousand nomads, officials, and tourists. As of 2011, the commune had a total population of 47,170 people.

The Zarma people are an ethnic group predominantly found in westernmost Niger. They are also found in significant numbers in the adjacent areas of Nigeria and Benin, along with smaller numbers in Burkina Faso, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Togo, and Sudan. In Niger, the Zarma are often considered by outsiders to be of the same ethnicity as the neighboring Songhaiborai, although the two groups claim differences, having different histories and speaking different dialects. They are sometimes lumped together as the Zarma-Songhay or Songhay-Zarma.

The Azawagh is a dry basin covering what is today the northwestern Niger, as well as parts of northeastern Mali and southern Algeria. The Azawagh is mainly made up of Sahelian and Saharan flatlands and has a population that is predominantly Tuareg, with some Arabic-speaking and Wodaabe minorities and a recent influx of Hausa and Zarma.

Filingué is a town in southwestern Niger and is the capital city of Filingué Department. It is situated on the eastern bank of the Dallol Bosso valley, some 180 km northeast of Niger's capital city Niamey.
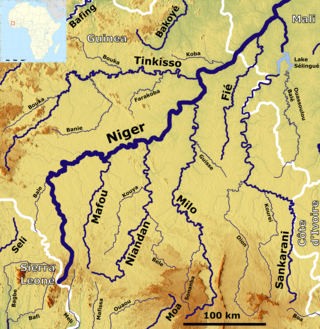
The Sankarani River is a tributary of the Niger River. Flowing northward from the Guinea Highlands of the Fouta Djallon in Guinea, it crosses into southern Mali, where it joins the Niger approximately 40 kilometres (25 mi) upstream of Bamako, the capital of Mali. It forms part of the Ivory Coast-Guinea and Guinea–Mali borders.
The Dosso Kingdom is a precolonial state in what is now southwest Niger which has survived in a ceremonial role to the modern day.
The Dosso Partial Faunal Reserve is a nature reserve in the southwest Dosso Region of Niger. It is a Partial Faunal Reserve IUCN type IV, established 1 January 1962. The reserve covers 3,065 square kilometres in the mouth of Dallol Bosso valley, a seasonal wash and ancient riverbed running from the Azawagh region, near where it reaches the Niger River valley. It is situated near the W du Niger National Park.

Harikanassou is a large village and rural commune in the Boboye Department of the Dosso Region of southwest Niger, 90.7 kilometres (56.4 mi) by road southeast of the capital of Niamey. At the time of the 2012 census, the rural community had 23,567 residents living in 3,340 households. Onion cultivation is a chief source of income for many, along with the cultivation of lettuce, beans, squashes, and tomatoes.
Tondikandia is a rural commune in Filingué Department, Tillabéri Region, Niger. Its chief place and administrative center is the town of Damana.
Kouré is a rural community located 60 kilometres (37 mi) east of Niamey, the capital of Niger. The town lies on both sides of the road from Niamey to Dallol Bosso. As of 2012, it had a population of 46,249.
The Maouri people are an ethnic group in western Africa. They are one of the major ethnic groups of Niger, and are concentrated around the Dallol Maouri of the Niger River, extending from Matankari, near Niamey, to Gaya. They are a subgroup of the Hausa people, and speak both the Hausa language and the Djerma language. When using the Zarma language, they are known as the Arawa people.

The Benin–Niger border is 277 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Burkina Faso in the west to the tripoint with Nigeria in the east.















