
Korean cuisine has evolved through centuries of social and political change. Originating from ancient agricultural and nomadic traditions in Korea and southern Manchuria, Korean cuisine reflects a complex interaction of the natural environment and different cultural trends.

The police are a constituted body of persons empowered by a state, with the aim to enforce the law, to ensure the safety, health, and possessions of citizens, and to prevent crime and civil disorder. Their lawful powers include arrest and the use of force legitimized by the state via the monopoly on violence. The term is most commonly associated with the police forces of a sovereign state that are authorized to exercise the police power of that state within a defined legal or territorial area of responsibility. Police forces are often defined as being separate from the military and other organizations involved in the defense of the state against foreign aggressors; however, gendarmerie are military units charged with civil policing. Police forces are usually public sector services, funded through taxes.

Yi Sun-sin was a Korean admiral and military general famed for his victories against the Japanese navy during the Imjin war in the Joseon Dynasty.

The national flag of the Republic of Korea, also known as the Taegeukgi, has three parts: a white rectangular background, a red and blue Taegeuk in its center, accompanied by four black trigrams, one in each corner. Flags similar to the current Taegeukgi were used as the national flag of Korea by the Joseon dynasty, the Korean Empire, as well as the Korean government-in-exile during Japanese rule. South Korea adopted the Taegeukgi as its national flag when it gained independence from Japan on 15 August 1945.

Joseon, officially Great Joseon, was the last dynastic kingdom of Korea, lasting just over 500 years. It was founded by Yi Seong-gye in July 1392 and replaced by the Korean Empire in October 1897. The kingdom was founded following the aftermath of the overthrow of Goryeo in what is today the city of Kaesong. Early on, Korea was retitled and the capital was relocated to modern-day Seoul. The kingdom's northernmost borders were expanded to the natural boundaries at the rivers of Amrok and Tuman through the subjugation of the Jurchens.
Racism in Japan comprises negative attitudes and views on race or ethnicity which are related to each other, are held by various people and groups in Japan, and have been reflected in discriminatory laws, practices and actions at various times in the history of Japan against racial or ethnic groups.
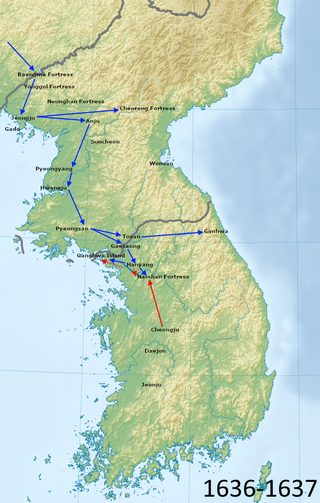
The Qing invasion of Joseon occurred in the winter of 1636 when the newly established Qing dynasty invaded the Joseon dynasty, establishing the former's status as the hegemon in the Imperial Chinese Tributary System and formally severing Joseon's relationship with the Ming dynasty. The invasion was preceded by the Later Jin invasion of Joseon in 1627.

Gyeongbokgung, also known as Gyeongbokgung Palace, was the main royal palace of the Joseon dynasty. Built in 1395, it is located in northern Seoul, South Korea. The largest of the Five Grand Palaces built by the Joseon dynasty, Gyeongbokgung served as the home of the royal family and the seat of government.

The National Intelligence Service is the chief intelligence agency of South Korea. The agency was officially established in 1961 as the Korean Central Intelligence Agency, during the rule of President Park Chung-hee's military Supreme Council for National Reconstruction, which displaced the Second Republic of Korea. The original duties of the KCIA were to supervise and coordinate both international and domestic intelligence activities and criminal investigations by all government intelligence agencies, including that of the military. The agency's broad powers allowed it to actively intervene in politics. Agents undergo years of training and checks before they are officially inducted and receive their first assignments.

The Korean tea ceremony is a traditional form of tea ceremony practiced in Korea. Darye literally refers to "etiquette for tea" or "tea rite" and has been kept among Korean people for over a thousand years. The chief element of the Korean tea ceremony is the ease and naturalness of enjoying tea within an easy formal setting.

Korean ceramic history begins with the oldest earthenware from around 8000 BC. Throughout the history, the Korean peninsula has been home to lively, innovative, and sophisticated art making. Long periods of stability have allowed for the establishment of spiritual traditions, and artisan technologies specific to the region. Korean ceramics in Neolithic period have a unique geometric patterns of sunshine, or it is decorated with twists. In Southern part of Korea, Mumun pottery were popular. Mumun togi used specific minerals to make colors of red and black. Korean pottery developed a distinct style of its own, with its own shapes, such as the moon jar or Buncheong sagi which is a new form between earthenware and porcelain, white clay inlay celadon of Goryeo, and later styles like minimalism that represents Korean Joseon philosophers' idea. Many talented Korean potters were captured and brought to Japan during the invasions of Korea, where they heavily contributed to advancing Japanese pottery. Arita ware, founded by Yi Sam-pyeong opened a new era of porcelain in Japan. Another Japanese representative porcelain, Satsuma ware was also founded by Dang-gil Shim and Pyeong-ui Park. 14th generation of Su-kwan Shim have been using the same name to his grandfather and father to honor they are originally Korean, 14th Su-kwan Shim is honorable citizen of Namwon, Korea.

Korean royal court cuisine was the style of cookery within Korean cuisine traditionally consumed at the court of the Joseon Dynasty, which ruled Korea from 1392 to 1910. There has been a revival of this cookery style in the 21st century. It is said that twelve dishes should be served along with rice and soup, with most dishes served in bangjja (bronzeware).

Bingsu, sometimes written as bingsoo, is a milk-based Korean shaved ice dessert with sweet toppings that may include chopped fruit, condensed milk, fruit syrup, and red beans.

Damo is a 2003 South Korean fusion historical drama, starring Ha Ji-won, Lee Seo-jin, and Kim Min-jun. Set in the Joseon Dynasty, it tells the story of Chae-ok, a damo relegated to the low-status job of a female police detective who investigates crimes involving women of the upper class. It aired on MBC from July 28 to September 9, 2003 on Mondays and Tuesdays at 21:55 for 14 episodes.

Banchan are small side dishes served along with cooked rice in Korean cuisine. Banchan are set in the middle of the table to be shared. At the center of the table is the secondary main course, such as galbi or bulgogi, and a shared pot of jjigae. Bowls of cooked rice and guk (soup) are set individually. Banchan are served in small portions, meant to be finished at each meal and replenished during the meal if not enough. Usually, the more formal the meals are, the more banchan there will be. Jeolla province is particularly famous for serving many different varieties of banchan in a single meal.

Yakgwa, also called gwajul (과줄), is a type of yumil-gwa, which is deep-fried, wheat-based hangwa made with honey, cheongju, sesame oil, and ginger juice. Traditionally, the sweet was offered in a jesa and enjoyed on festive days such as chuseok, marriages, or hwangap (sixtieth-birthday) celebrations. In modern South Korea, it is also served as a dessert and can be bought at traditional markets or supermarkets.
Sexuality in South Korea has been influenced by culture, religion, and westernization. Viewpoints in contemporary society can be viewed as a conflict between the traditional, conservative older generation and the more liberal and 'modern' generation. Due to this conflict, several issues in Korea, including sexual education, homosexuality, and sexual behavior are highly contested.

Sageuk in Korean denotes historical dramas, including traditional drama plays, films or television series. In English language literature sageuk usually refers to historical films and television series. In North Korea, South Korean historical dramas are generally called 고전 영화 or classic film.
The North Korean Embassy in Madrid incident is an event that occurred on 22 February 2019 at the North Korean embassy in Madrid, Spain. The political group Free Joseon, which is opposed to the incumbent Kim Jong Un regime of North Korea, is alleged to have attacked and raided the embassy, while the group maintains that they were invited in to facilitate a high-level defection. A group of individuals stole mobile telephones, two pen drives and a hard drive from the embassy and handed them to the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) in the United States. The event took place after the Singapore summit between North Korea (DPRK) and the United States and prior to the approach of the Hanoi summit. As of early April 2019, one person had been arrested in connection with the incident and two international arrest warrants had been issued by the Spanish Audiencia Nacional. The suspected perpetrators are citizens of Mexico, the US and South Korea, although the latter two governments denied any connection with the incident.
















