
Smart growth is an urban planning and transportation theory that concentrates growth in compact walkable urban centers to avoid sprawl. It also advocates compact, transit-oriented, walkable, bicycle-friendly land use, including neighborhood schools, complete streets, and mixed-use development with a range of housing choices. The term "smart growth" is particularly used in North America. In Europe and particularly the UK, the terms "compact city", "urban densification" or "urban intensification" have often been used to describe similar concepts, which have influenced government planning policies in the UK, the Netherlands and several other European countries.

Reclaim the Streets also known as RTS, are a collective with a shared ideal of community ownership of public spaces. Participants characterise the collective as a resistance movement opposed to the dominance of corporate forces in globalisation, and to the car as the dominant mode of transport.

Traffic calming uses physical design and other measures to improve safety for motorists, pedestrians and cyclists. It has become a tool to combat speeding and other unsafe behaviours of drivers in the neighbourhoods. It aims to encourage safer, more responsible driving and potentially reduce traffic flow. Urban planners and traffic engineers have many strategies for traffic calming, including narrowed roads and speed humps. Such measures are common in Australia and Europe, but less so in North America. Traffic calming is a calque of the German word Verkehrsberuhigung – the term's first published use in English was in 1985 by Carmen Hass-Klau.

Bicycle-friendly policies and practices help some people feel more comfortable about traveling by bicycle with other traffic. The level of bicycle-friendliness of an environment can be influenced by many factors including town planning and cycling infrastructure decisions. A stigma towards people who ride bicycles and fear of cycling is a social construct that needs to be fully understood when promoting a bicycle friendly culture.

Parking is the act of stopping and disengaging a vehicle and leaving it unoccupied. Parking on one or both sides of a road is often permitted, though sometimes with restrictions. Some buildings have parking facilities for use of the buildings' users. Countries and local governments have rules for design and use of parking spaces.
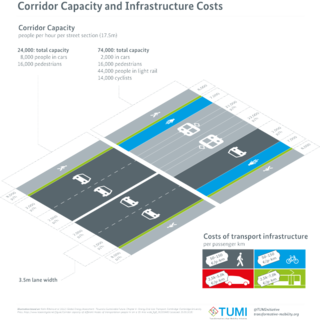
Street reclaiming is the process of converting, or otherwise returning streets to a stronger focus on non-car use — such as walking, cycling and active street life. It is advocated by many urban planners and urban economists, of widely varying political points of view. Its primary benefits are thought to be:

Pedestrian zones are areas of a city or town restricted to use by people on foot or human-powered transport such as bicycles, with non-emergency motor traffic not allowed. Converting a street or an area to pedestrian-only use is called pedestrianisation.

Speed bumps are a class of traffic calming devices that use vertical deflection to slow motor-vehicle traffic in order to improve safety conditions. Variations include the speed hump, speed cushion, and speed table.

A living street is a street designed with the interests of pedestrians and cyclists in mind by providing enriching and experiential spaces. Living streets also act as social spaces, allowing children to play and encouraging social interactions on a human scale, safely and legally. Living streets consider all pedestrians granting equal access to elders and those who are disabled. These roads are still available for use by motor vehicles; however, their design aims to reduce both the speed and dominance of motorized transport. The reduction of motor vehicle dominance creates more opportunities for public transportation. Living Streets achieve these strategies by implementing the shared space approach. Reducing demarcations between vehicle traffic and pedestrians create a cohesive space without segregating different modes of transportation. Vehicle parking may also be restricted to designated bays. These street design principles first became popularized in the Netherlands during the 1970s, and the Dutch word woonerf is often used as a synonym for living street.

Shared space is an urban design approach that minimises the segregation between modes of road user. This is done by removing features such as kerbs, road surface markings, traffic signs, and traffic lights. Hans Monderman and others have suggested that, by creating a greater sense of uncertainty and making it unclear who has priority, drivers will reduce their speed, in turn reducing the dominance of vehicles, reducing road casualty rates, and improving safety for other road users.

A carfree city is an urban area absent of motor vehicles. Carfree cities rely on public transport, walking, and cycling for travel as opposed to motor vehicles. Districts where motor vehicles are prohibited are referred to as carfree zones. Carfree city models have gained traction in the second half of the 20th century due to issues with congestion and infrastructure, and proposed environmental and quality of life benefits. Many cities in Asia, Europe, and Africa have carfree areas due to the cities being created before the invention of motor vehicles, while many developing cities in Asia are using the carfree model to modernize their infrastructure.

Livability or liveability is the degree to which a place is good for living. Livability refers to the concerns that are related to the long-term wellbeing of individuals and communities. It encompasses factors like neighborhood amenities, including parks, open space, walkways, grocery shops and restaurants as well as environmental quality, safety and health. It also incorporates things like cost and friendliness. These features contribute to the pleasantness and accessibility of communities. Additionally, livability considers the availability and quality of public transport, educational institutions and healthcare facilities. It also considers the overall cultural and social atmosphere of a place, including the presence of diverse recreational activities and community engagement opportunities. All these factors combined create an environment that enhances the overall quality of life for residents.

A sustainable city, eco-city, or green city is a city designed with consideration for social, economic, environmental impact, and resilient habitat for existing populations, without compromising the ability of future generations to experience the same. The UN Sustainable Development Goal 11 defines sustainable cities as those that are dedicated to achieving green sustainability, social sustainability and economic sustainability. They are committed to doing so by enabling opportunities for all through a design focused on inclusivity as well as maintaining a sustainable economic growth. The focus will also includes minimizing required inputs of energy, water, and food, and drastically reducing waste, output of heat, air pollution – CO2, methane, and water pollution. Richard Register, a visual artist, first coined the term ecocity in his 1987 book Ecocity Berkeley: Building Cities for a Healthy Future, where he offers innovative city planning solutions that would work anywhere. Other leading figures who envisioned sustainable cities are architect Paul F Downton, who later founded the company Ecopolis Pty Ltd, as well as authors Timothy Beatley and Steffen Lehmann, who have written extensively on the subject. The field of industrial ecology is sometimes used in planning these cities.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines aging in place as "the ability to live in one's own home and community safely, independently, and comfortably, regardless of age, income, or ability level".
The EcoDensity Initiative was officially launched in 2006 in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, in conjunction with the World Urban Forum. The initiative was a response to deconcentration of urban land use due to urban sprawl. The initiative used density, design and land use as catalysts towards livability, affordability and environmental sustainability. Some of the program's objectives were to reduce car reliance, deliver more efficient urban land use, improve green energy systems and build a resilient and adaptable community. In high-density urban areas, utilizing the existing infrastructure and transit and community amenities tends to lead towards a more sustainable and livable state. Accordingly, EcoDensity was designed to strategically enhance densification with the primary aim of efficiently structured neighbourhoods, denser urban-patterns and increased affordable housing.

Healthy community design is planning and designing communities that make it easier for people to live healthy lives. Healthy community design offers important benefits:
Open Plans is a non-profit that advocates for making the streets of New York City livable for all residents. Open Plans uses tactical urbanism, grassroots advocacy, policy and targeted journalism to promote structural reforms within city government that support livable streets, neighborhoods and the city-at-large. The organization was founded in 1999 by Mark Gorton, the creator of LimeWire.

Donald Sidney Appleyard was an English-American urban designer and theorist, teaching at the University of California, Berkeley.
Pace Car Programs are initiatives that aim to reduce traffic speeds and encourage safe driving in neighborhoods and cities in the United States and Canada. Willing drivers register an intention to abide by a safe driving code.

Urban vitality is the quality of spaces in cities that attract diverse groups of people for varied activities over frequent, varied times. These spaces may be perceived as alive, lively or vibrant, in contrast with low-vitality areas, which may repel people and be perceived as unsafe.
















