Related Research Articles

Thomas Paine was an English-born American Founding Father, political activist, philosopher, political theorist, and revolutionary. He authored Common Sense (1776) and The American Crisis (1776–1783), two of the most influential pamphlets at the start of the American Revolution, and helped inspire the Patriots in 1776 to declare independence from Great Britain, theretofore an unpopular cause. His ideas reflected Enlightenment-era ideals of transnational human rights.

The United States Declaration of Independence, officially The unanimous Declaration of the thirteen united States of America, is the pronouncement and founding document adopted by the Second Continental Congress meeting at Pennsylvania State House, which was later renamed Independence Hall, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, on July 4, 1776. Enacted during the American Revolution, the Declaration explains why the Thirteen Colonies at war with the Kingdom of Great Britain regarded themselves as thirteen independent sovereign states and no longer subject to British colonial rule. With the Declaration, the 13 states took a collective first step in forming the United States and, de facto, formalized the American Revolutionary War, which had been ongoing since April 1775.
Between 1776 and 1789 thirteen British colonies emerged as a newly independent nation, the United States of America. Fighting in the American Revolutionary War started between colonial militias and the British Army in 1775. The Second Continental Congress issued the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The Articles of Confederation were ratified in 1781 to form the Congress of the Confederation. Under the leadership of General George Washington, the Continental Army and Navy defeated the British military, securing the independence of the thirteen colonies. The Confederation period continued until 1789, when the states replaced the Articles of Confederation with the Constitution of the United States, which remains the fundamental governing law of the United States.

Benjamin Rush was a Founding Father of the United States who signed the United States Declaration of Independence, and a civic leader in Philadelphia, where he was a physician, politician, social reformer, humanitarian, educator, and the founder of Dickinson College. Rush was a Pennsylvania delegate to the Continental Congress. His later self-description there was: "He aimed right." He served as surgeon general of the Continental Army and became a professor of chemistry, medical theory, and clinical practice at the University of Pennsylvania.

The Province of Pennsylvania, also known as the Pennsylvania Colony, was a British North American colony founded by William Penn, who received the land through a grant from Charles II of England in 1681. The name Pennsylvania was derived from "Penn's Woods", referring to William's father Admiral Sir William Penn.

The Founding Fathers of the United States, commonly referred to simply as the Founding Fathers or Founders, were a group of late-18th-century American revolutionary leaders who united the Thirteen Colonies, oversaw the War of Independence from Great Britain, established the United States, and crafted a framework of government for the new nation.

Joseph Galloway was an American attorney and a leading political figure in the events immediately preceding the founding of the United States in the late 1700s. As a staunch opponent of American independence, he would become one of the most prominent Loyalists in North America during the early part of the Revolutionary War.

Christ Church Burial Ground in Philadelphia is an important early-American cemetery. It is the final resting place of Benjamin Franklin and his wife, Deborah. Four other signers of the Declaration of Independence are buried here, Benjamin Rush, Francis Hopkinson, Joseph Hewes and George Ross. Two more signers are buried at Christ Church just a few blocks away.

The American Enlightenment was a period of intellectual ferment in the thirteen American colonies in the 18th to 19th century, which led to the American Revolution and the creation of the United States of America. The American Enlightenment was influenced by the 17th- and 18th-century Age of Enlightenment in Europe and native American philosophy. According to James MacGregor Burns, the spirit of the American Enlightenment was to give Enlightenment ideals a practical, useful form in the life of the nation and its people.
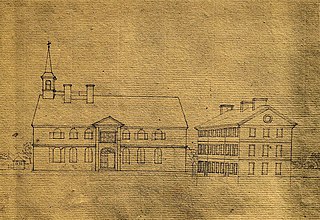
The Academy and College of Philadelphia (1749-1791) was a boys' school and men's college in Philadelphia, Colony of Pennsylvania.

Independence National Historical Park is a federally protected historic district in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania that preserves several sites associated with the American Revolution and the nation's founding history. Administered by the National Park Service, the 55-acre (22 ha) park comprises many of Philadelphia's most-visited historic sites within the Old City and Society Hill neighborhoods. The park has been nicknamed "America's most historic square mile" because of its abundance of historic landmarks.

The Library Company of Philadelphia (LCP) is a non-profit organization based on Locust Street in Center City Philadelphia. Founded in 1731 by Benjamin Franklin as a library, the Library Company of Philadelphia has accumulated one of the most significant collections of historically valuable manuscripts and printed material in the United States.

Pennsylvania was the site of many key events associated with the American Revolution and American Revolutionary War. The city of Philadelphia, then capital of the Thirteen Colonies and the largest city in the colonies, was a gathering place for the Founding Fathers who discussed, debated, developed, and ultimately implemented many of the acts, including signing the Declaration of Independence, that inspired and launched the revolution and the quest for independence from the British Empire.
Mary Maples Dunn was an American historian. She served as the eighth president of Smith College for ten years beginning in 1985. Dunn was also the director of the Schlesinger Library from 1995 to 2000. She was acting president of Radcliffe College when it merged with Harvard University, and she became the acting dean of the newly created Radcliffe Institute for Advanced Study after the merger.
Richard Roy Beeman was an American historian and biographer specializing in the American Revolution. Born in Seattle, he published multiple books, and was the John Walsh Centennial Professor of History at the University of Pennsylvania. Beeman was the 2003-4 Harold Vyvyan Harmsworth Professor of American History. He also served as the director of the Philadelphia Center for Early American Studies, on the board of trustees of the National Constitution Center, and as the editor of American Quarterly. He died in his home outside of Philadelphia from complications due to ALS.

The signing of the United States Declaration of Independence occurred primarily on August 2, 1776, at the Pennsylvania State House in Philadelphia, later to become known as Independence Hall. The 56 delegates to the Second Continental Congress represented the 13 colonies, 12 of which voted to approve the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The New York delegation abstained because they had not yet received instructions from Albany to vote for independence. The Declaration proclaimed the signatory colonies were now "free and independent States," no longer colonies of the Kingdom of Great Britain and, thus, no longer a part of the British Empire. The signers’ names are grouped by state, with the exception of John Hancock, as President of the Continental Congress; the states are arranged geographically from south to north, with Button Gwinnett from Georgia first, and Matthew Thornton from New Hampshire last.

Mary "Polly" Norris Dickinson was an early American land and estate owner and manager. She is known for her ownership of one of the largest libraries in the American colonies, her participation in political thought of the time, and her presence in or near events of the Constitutional Convention, including her marriage to Framer John Dickinson, one of the early drafters of the Constitution and one of its signers on behalf of the colony of Delaware. They bequeathed much of their combined library to the first college founded in the new United States. The college was originally named "John and Mary's College", by Benjamin Rush, for Norris Dickinson and her husband and is now called Dickinson College.
The following bibliography includes notable books concerning the American Revolutionary War. These books are listed in the bibliographies of books by prominent historians as shown in the footnotes.

The Honourable William Leslie was a British nobleman and soldier. He was the second son of the Earl of Leven and Melville from Scotland and a captain in the 17th Foot of the British Army during the American War of Independence. He was mortally wounded during the Battle of Princeton and buried with military honours by American General George Washington at Pluckemin, New Jersey.

The Death of General Mercer at the Battle of Princeton, January 3, 1777 is the title of an oil painting by the American artist John Trumbull depicting the death of the American General Hugh Mercer at the Battle of Princeton on Friday, January 3, 1777, during the American Revolutionary War. The painting was Trumbull’s first depiction of an American victory. It is one of a series of historical paintings on the war, which also includes the Declaration of Independence and The Capture of the Hessians at Trenton, December 26, 1776.
References
- ↑ "David F. Hawke, 75, American Historian". The New York Times. June 25, 1999 – via NYTimes.com.
- ↑ "David F. Hawke, 75, American Historian". The New York Times . 25 June 1999. Retrieved 28 January 2017.